Research Summary Report
Research Summary Report of A04
Category: Research Summary Report
Integrated Additive Manufacturing Processes for Reinforced Shotcrete 3D Printing (SC3DP) Elements with Precise Surface Quality [20.01.2023] David, Martin; Doctoral Researcher, m.david@tu-braunschweig.de, TU Braunschweig, Institute for Machine Tools and Production Technology (IWF) Summary Project A04 aims to investigate cooperative Additive Manufacturing (AM) processes based on Shotcrete 3D Printing (SC3DP) for the production of material-efficient, force-optimised, reinforced, load-bearing concrete components with precise surface quality and geometrical precision. The goal is to produce large-scale concrete elements using significantly lower amounts of reinforcement and concrete as compared to standard concrete construction principles. Hereby, different robot guided end effectors are subject for research in a flexible and automated process chain. Current state of research Currently, there are two focal points in the research …
Research Summary Report of A05
Category: Research Summary Report
Integration of Individualized Prefabricated Fibre Reinforcement in Additive Manufacturing with Concrete [03.02.2023] Rothe, Tom; Doctoral researcher, t.rothe@tu-braunschweig.de, Hühne, Christian; Project Leader, Christian.Huehne@tu-braunschweig.de, TU Braunschweig, Institute for Mechanics and Adaptronics (IMA) The individual integration of fibre reinforcement into large concrete components produced by Additive Manufacturing allows new design freedoms and reduces concrete consumption due to reduced concrete cover. The project A05 develops strategies to integrate freely formable reinforcement strands for the different AM processes. For doing so, a Dynamic Winding Machine is developed and constantly updated. This machine is used to consolidate and impregnate a primary fibre strand and wind a secondary yarn around it as a surface structuring. Thus, these reinforcement strands can be adapted for different purposes and …
Research Summary Report of A06
Category: Research Summary Report
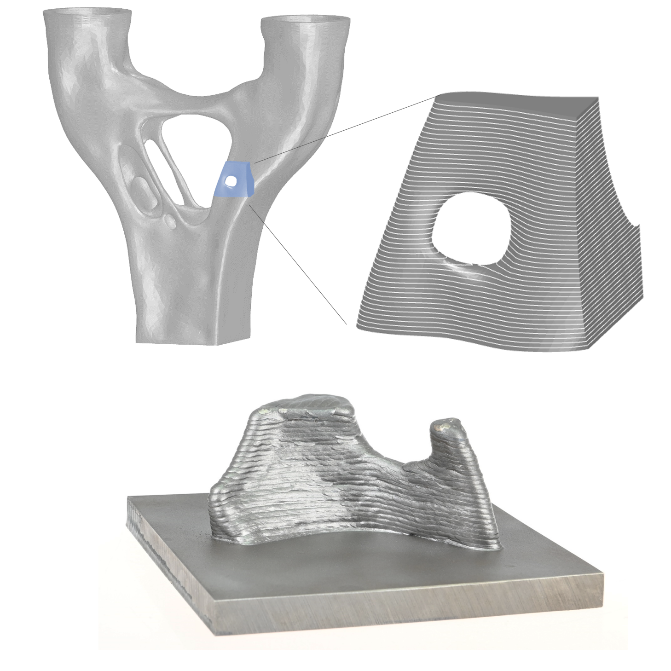
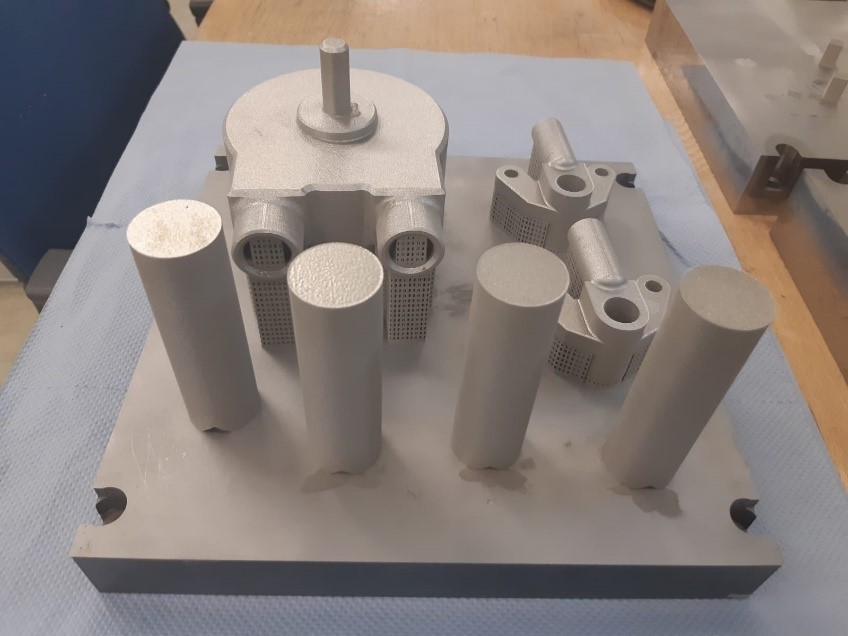
Laser Powder-Bed Fusion (LPBF) of Steel Elements for Construction – Basics of Design and Mechanical Resilience [27.01.2023] Wenzler, David; doctoral researcher; david.wenzler@tum.de Technical University of Munich, Institute for Machine Tools and Industrial Management Diller, Johannes; doctoral researcher; johannes.diller@tum.de Siebert, Dorina; doctoral researcher; dorina.siebert@tum.de Technical University of Munich, Chair of Metal Structures Summary The project A06 aims to explore and evaluate the factors influencing the manufacturing of safe and durable structural steel elements by laser powder-bed fusion (LPBF). Thereby, the LPBF process, the post-treatment, and the influence of the part geometry on the microstructure and the mechanical properties will be investigated. From the results, correlations between these aspects will be determined. In the 1st funding period, the project …
Research Summary Report of A07
Category: Research Summary Report
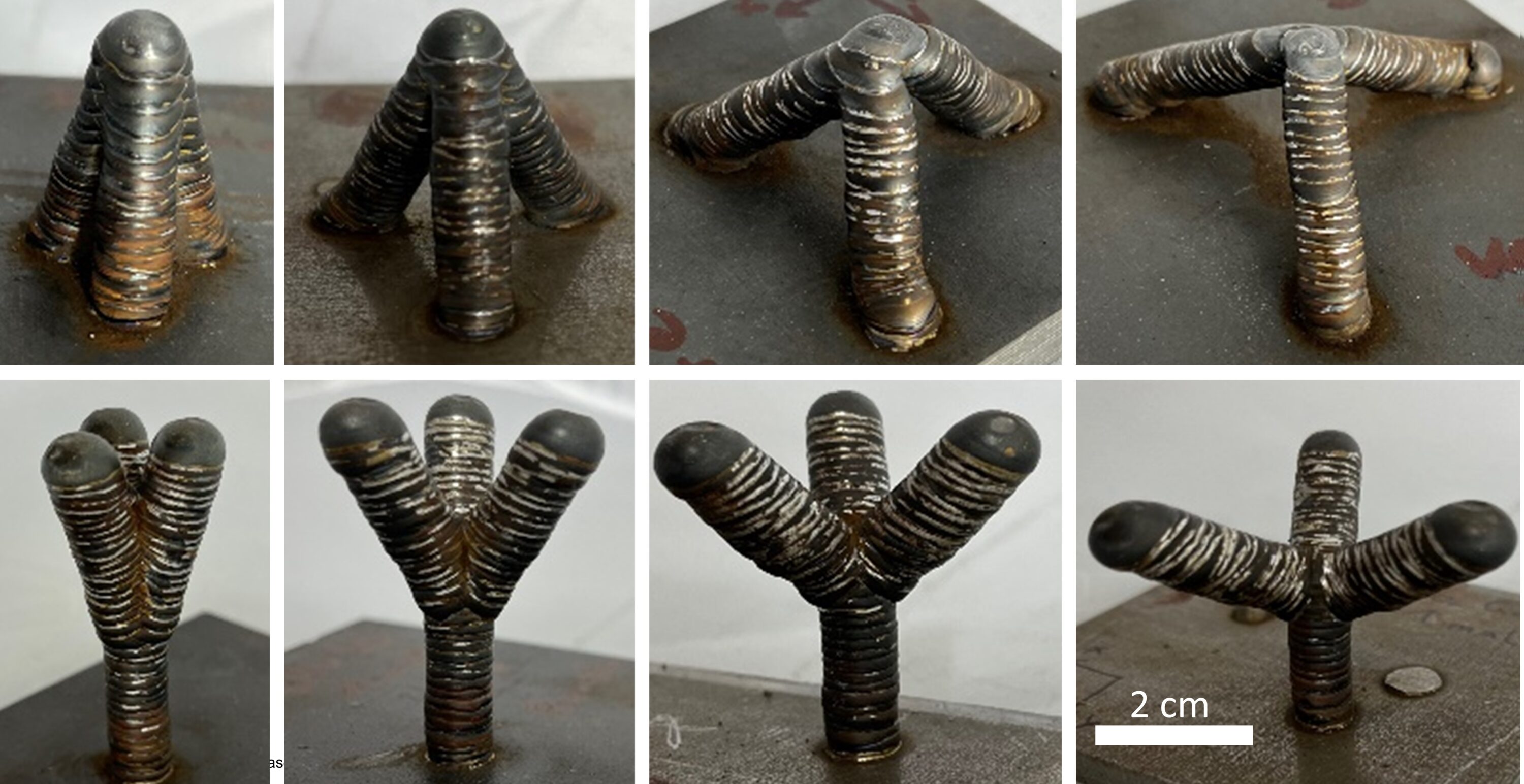
Wire and Arc Additive Manufacturing (WAAM) of Complex Individualized Steel Components [13.01.2023] Jahns, Hendrik; Doctoral researcher; h.jahns@stahlbau.tu-braunschweig.de Unglaub, Julian; Principle Investigator; j.unglaub@stahlbau.tu-braunschweig.de Thiele, Klaus; Principle Investigator; k.thiele@stahlbau.tu-braunschweig.de Institute of Steel Structures Technische Universität Braunschweig In project A07 the design, manufacturing and mechanical properties of complex individualized WAAM steel nodes for use in construction is investigated. A new method is developed to design force flow optimized steel nodes as connectors between semi-finished parts and anchorage structures considering the manufacturing possibilities of the WAAM-process and the resulting material behaviour. The manufacturing possibilities will be identified by case study demonstrators, which represent occurring features of the designed node. The produced parts are characterized regarding their mechanical properties. For that an advanced material …
Research Summary Report of A08
Category: Research Summary Report
Structural Timber by Individual Layer Fabrication (ILF) [06.01.2023] Asshoff, Carsten; Doctoral researcher; carsten.asshoff@wki.fraunhofer.de Fraunhofer Institute for Wood Research Wilhelm-Klauditz-Institut WKI The main goal of the project ’A08 – Structural Timber by Individual Layer Fabrication (ILF)’ is to develop a process to additively manufacture large-scale, wood composite objects with a maximum content of wood material and strength values suited for applications in construction. In the course of the project multiple process variants and material combinations are explored. For this, the necessary machinery is developed in iterative steps and the mechanical properties of the resulting objects as well as the geometric capacity of the processes are investigated. Finally, multiple demonstrators are fabricated for showcase purposes. Summary Working group Bunzel is …
Research Summary Report of B04
Category: Research Summary Report
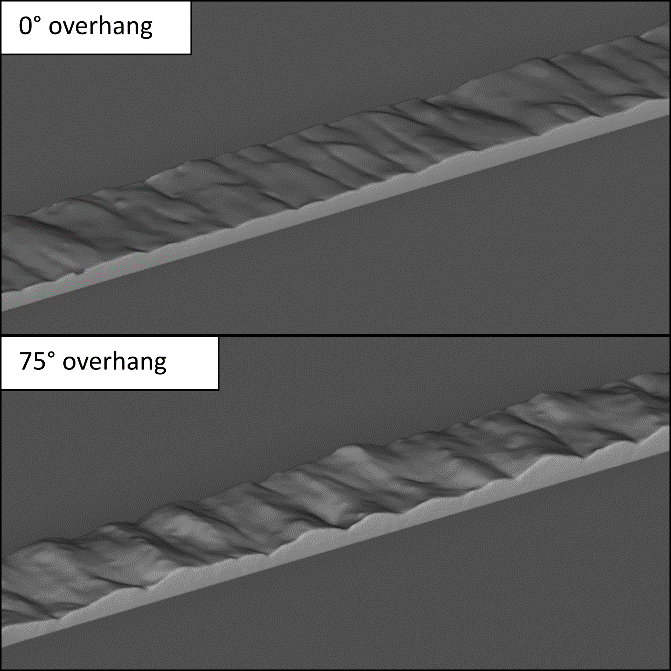
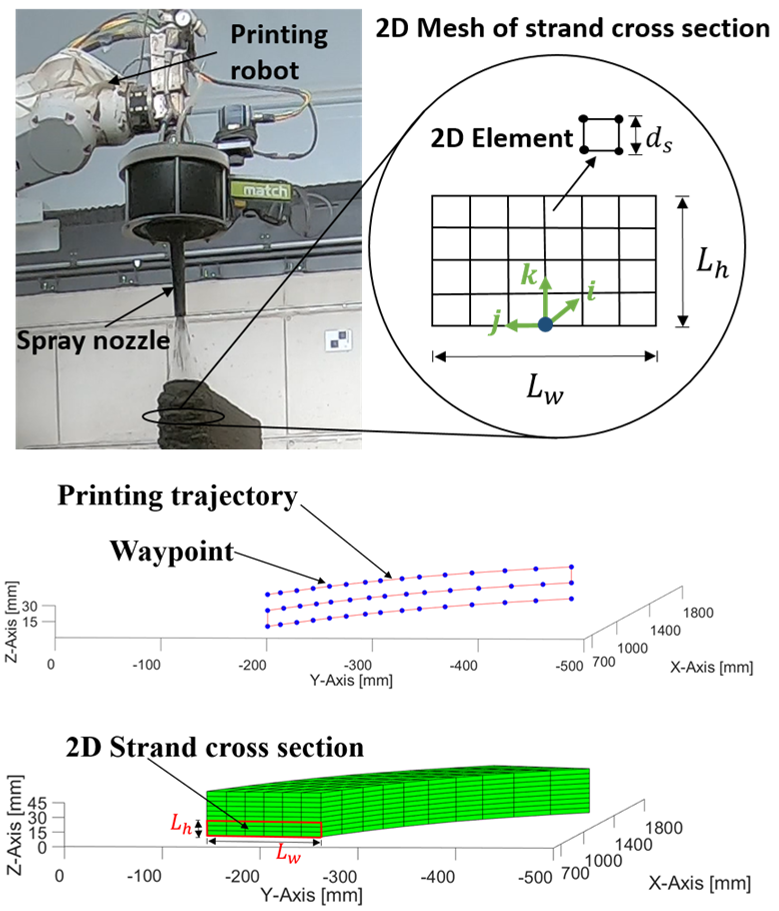
Process Control and Adaptive Path Planning for Additive Manufacturing Processes Based on Industrial Robots with an Extended Degree of Freedom [11.01.2023] Ekanayaka, Virama; Doctoral researcher, v.ekanayaka@tu-braunschweig.de, Hürkamp, André; Project Leader, a.huerkamp@tu-braunschweig.de, TU Braunschweig, Institute of Machine Tools and Production Technology (IWF) The integration of robot-guided additive manufacturing in the construction industry increases the degree of automation and can thus lead to an increased productivity and increased component quality. In shotcrete 3D printing (SC3DP), reproducible manufacturing results and ensuring component quality are major challenges, as the properties of shotcrete depend on many different parameters (e.g. temperature, pressure, water-cement ratio, hardening accelerator). The goal of this research project is to develop a reproducible, robot-guided shotcrete process based on multi-model adaptive path …
Research Summary Report of C06
Category: Research Summary Report
Integration of Additive Manufacturing in the Construction Process [23.12.2022] Mawas, Karam; Doctoral researcher, k.mawas@tu-braunschweig.de, Gerke, Markus; Project leader, m.gerke@tu-braunschweig.de, Maboudi, Mehdi; Associated scientist, m.maboudi@tu-braunschweig.de, TU Braunschweig, Institute of Geodesy and Photogrammetry (IGP) Main goal In order to ensure that a robust process is followed and the printed object adheres faithfully to the designed model, continuous and automatic data capturing and inspection of the process is required. Quality control also ensures that the combination of components into objects can be realized. Summary As a result of variations in manufacturing processes, specimens may differ from their as-designed models. Therefore, all manufacturing steps should be equipped with a proper quality control process. Although quality control of a printed specimen is mainly about …
Research Summary Report of A03
Category: Research Summary Report
Extrusion of Near-Nozzle Mixed Concrete –Individually Graded in Density and in Rate of 3D Fibre Reinforcement [09.12.2022] M.Sc. Dahlenburg, Maximilian; TP editor, maximilian.dahleburg@tum.de, Prof. Dr.-Ing. Fottner, Johannes; Project leader, j.fottner@tum.de, TUM, Chair of Materials Handling, Material Flow, Logistics The main goal of A03 is to establish a novel concrete extrusion process using a near nozzle mixing (NNM) process to enable the change and non-discrete gradation of material and its properties during printing. With this approach multi-functional and multi-material parts can be printed, with an overall higher building rate due to a lower workability demand of the process and higher structuration rates of the used materials. Printed parts can thus simultaneously fulfill load-bearing and thermal insulation functions by locally changing the material properties. Thus, the …
Research Summary Report of A01
Category: Research Summary Report
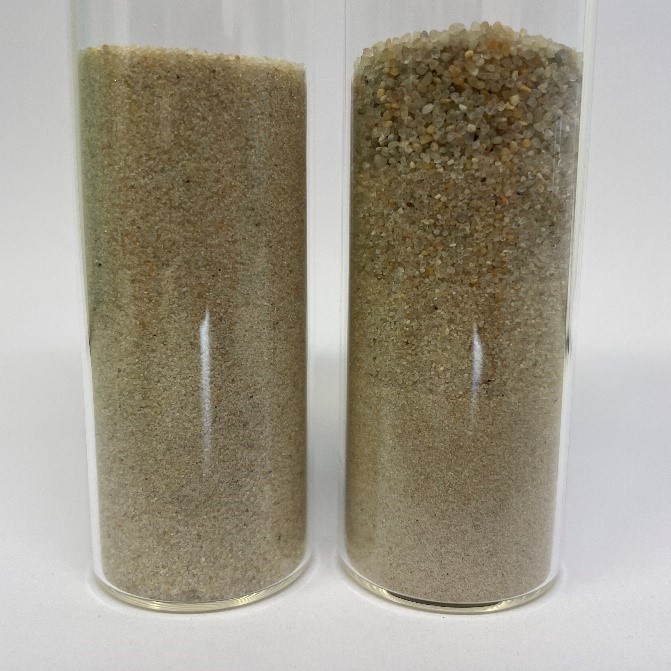
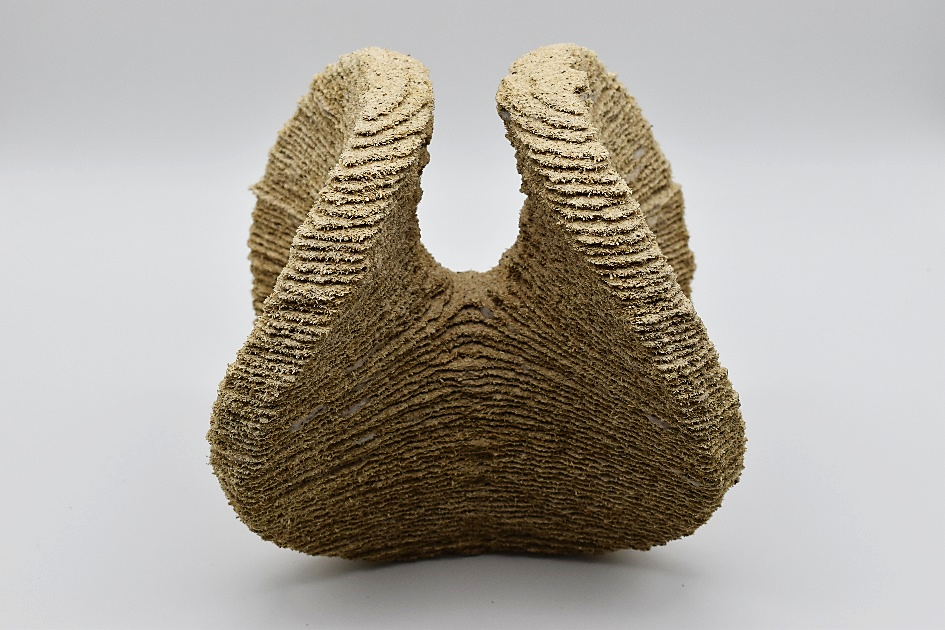
Particle-Bed 3D Printing by Selective Cement Activation (SCA) – Particle Surface Functionalisation, Particle-Bed Compaction and Reinforcement Implementation [25.11.2022] Meier, Niklas; Researcher, niklas.meier@tu-braunschweig.de Zetzener, Harald; Leading researcher, h.zetzener@tu-braunschweig.de Kwade, Arno; Project Leader, a.kwade@tu-braunschweig.de all: TU Braunschweig, Institute for particle technology The main goal of our research in project A01 is to improve the mechanical strength and shape accuracy of the printed concrete parts as well as the printing speed. While our work at the iPAT is improving the powder properties the project partner iBMB focuses on the material-process interaction. Summary Previous research has shown, that higher component densities often lead to higher compressive strength in selective cement activation. As shown in the previous research summary report, the former work aimed …
Research Summary Report of C03
Category: Research Summary Report
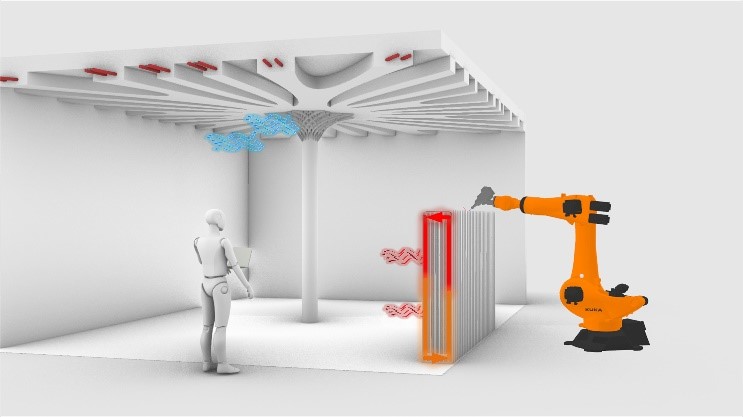
Integration of Passive and Active Functions in Additively Manufactured Construction Elements [18.11.2022] Auer, Thomas; PL, thomas.auer@tum.de Briels, David; doctoral researcher, david.briels@tum.de Nouman, Ahmad; doctoral researcher, ahmad.nouman@tum.de all: Technical University of Munich, TUM School of Engineering and Design, Chair of Building Technology and Climate Responsive Design This research explores the potential of AM for building components with (a) directly incorporated active performative features (e.g. ventilation, thermal activation, or building services distribution), as well as (b) passive design strategies (e.g. thermal insulation, sound insulation, acoustics, or controlled solar gains) via material and geometric differentiation. The objectives are a more robust building operation, reducing embodied and operational carbon emissions, and improving user comfort, achieved by a more holistic, climate-aware, and fabrication-aware design, …
Research Summary Report of B05
Category: Research Summary Report
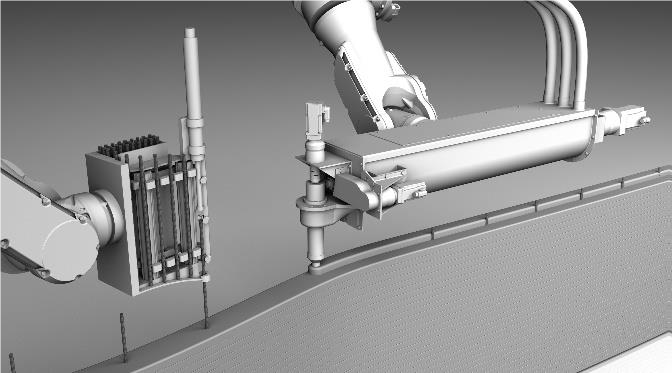
Principles of Mobile Robotics for Additive Manufacturing in Construction [21.10.2022] Dielemans, Gido; Doctoral researcher, gido.dielemans@tum.de, Technical University of Munich, Department of Architecture, TT Professorship Digital Fabrication This research examines the architectural implications of mobile robotics for AM in construction and develops methods for their implementation. The material deposition method of clay and concrete extrusion 3D printing is used to investigate mobile part-based AM strategies, that is, to produce large objects whose size exceeds the static workspace of the robot. By implementing advanced sensor and control solutions, autonomous localization and precise manipulation techniques for mobile AM are explored. In addition, this research aims to provide scalability to AM processes by examining the use of multiple robots to collaborate on single …
Research Summary Report of A08
Category: Research Summary Report
Structural Timber by Individual Layer Fabrication (ILF) [14.10.2022] Buschmann, Birger; Doctoral researcher, birger.buschmann@tum.de, Talke, Daniel; Doctoral researcher, talke@tum.de Henke, Klaudius; Project leader, henke@tum.de Technical University of Munich, Chair of Timber Structures and Building Construction The main goal of the project ‘A08 -Structural Timber by Individual Layer Fabrication (ILF)’ is to develop a process to additively manufacture large-scale, wood composite objects with a maximum content of wood material and strength values suited for applications in construction. In the course of the project multiple process variants and material combinations are explored. For this, the necessary machinery is developed in iterative steps and the mechanical properties of the resulting objects as well as the geometric capacity of the processes are investigated. Finally, …
Research Summary Report of A04
Category: Research Summary Report
Integrated Additive Manufacturing Processes for Reinforced Shotcrete 3D Printing (SC3DP) Elements with Precise Surface Quality [11.11.2022] Freund, Niklas; doctoral researcher, n.freund@ibmb.tu-bs.de Lowke, Dirk; project leader, d.lowke@ibmb.tu-bs.de all: TU Braunschweig, Institute of Building Materials and Concrete Construction and Fire Safety (iBMB) Project A04 investigates cooperative Additive Manufacturing (AM) processes based on Shotcrete 3D Printing (SC3DP) for the production of material-efficient, force-optimized, reinforced, load-bearing concrete components with precise surface quality and high geometric precision. The goal is to produce large-scale concrete elements using significantly lower amounts of reinforcement and concrete as compared to standard concrete construction principles. Summary In SC3DP applications, the precise control of rheological material properties represents a necessity. Here, data based rheological material models are required that allow the …
Research Summary Report of A05
Category: Research Summary Report
Integration of Individualized Prefabricated Fibre Reinforcement in Additive Manufacturing with Concrete [02.11.2022] Gantner, Stefan; Scientific Researcher, stefan.gantner@tu-bs.de, TU Braunschweig, Institute of Structural Design (ITE) Summary Cement-based additive manufacturing techniques need to be enhanced by the ability of integrating reinforcement, in order to fulfil requirements of construction. This project focuses on non-metallic continuous fibre reinforcement, which is not only corrosion resistant but also flexible in handling. Instead of bending and welding, glass or carbon fibre rovings can be processed by winding onto a support structure. Based on three fundamental AM-principles, namely material jetting and extrusion, as well as particle bed printing, a set of winding concepts for integrating reinforcement has been developed. Within a holistic framework all relevant aspects from …
Research Summary Report of A02
Category: Research Summary Report
Particle-Bed 3D Printing by Selective Cement Paste Intrusion (SPI) – Particle Surface Functionalisation, Particle Synthesis and Integration of WAAM Reinforcement [28.10.2022] Riegger, Felix; Doctoral researcher; Felix.Riegger@iwb.tum.de Wimmer, Andreas; Head of the research group; Andreas.Wimmer@iwb.tum.de All: Technical University of Munich, Institute for Machine Tools and Industrial Management The main goal of project A02 is the implementation of reinforcement with Wire and Arc Additive Manufacturing (WAAM) in concrete elements produced by Selective Paste Intrusion (SPI) by means of a simultaneously additive manufacturing process. The combination of SPI and WAAM is accompanied by obstacles that must be overcome to ensure the collaborated functionality. One major challenge occurs from the high energy input of WAAM (temperatures up to 1600 °C), which negatively affects …
Research Summary Report of C06
Category: Research Summary Report
Integration of Additive Manufacturing in the Construction Process [06.10.2022] Placzek, Gerrit; Doctoral researcher, g.placzek@tu-braunschweig.de TU Braunschweig, IBB The integration of additive manufacturing into construction requires an interdisciplinary approach. The different competences of the team – digital fabrication in architecture (Hack), geodesy and photogrammetry (Gerke) and construction management (Schwerdtner) – lead to research from diverse perspectives on the various scalar levels of construction to be viewed holistically: component, building and industry scale. Within Subproject C06, our goal is to create a continuous digital and lean-based process chain from design (using BIM method) to fabrication (using AM method). Based on process models, we investigate construction processes and how to change them into a construction industry 4.0. Summary The most well-known approach …
Research Summary Report A07
Category: Research Summary Report
Wire and Arc Additive Manufacturing (WAAM) of complex individualized steel components [30.09.2022] Müller, Johanna; doctoral researcher johanna.mueller@tu-braunschweig.de TU Braunschweig, Institute of Joining and Welding Main goal The aim of TP A07 is the design, the manufacturing and the testing of complex individualized steel components by means of WAAM. That contains the fundamental investigation of design and the design process for WAAM components. For the manufacturing of steel components by WAAM, stable and reliable processes for basic geometries are qualified and based on that, case study demonstrators for the identification of manufacturing restraints are fabricated. Furthermore, a novel approach for material and component testing is developed to identify local material and component properties. Summary The aim of WG Hensel …
Research Summary Report C05
Category: Research Summary Report
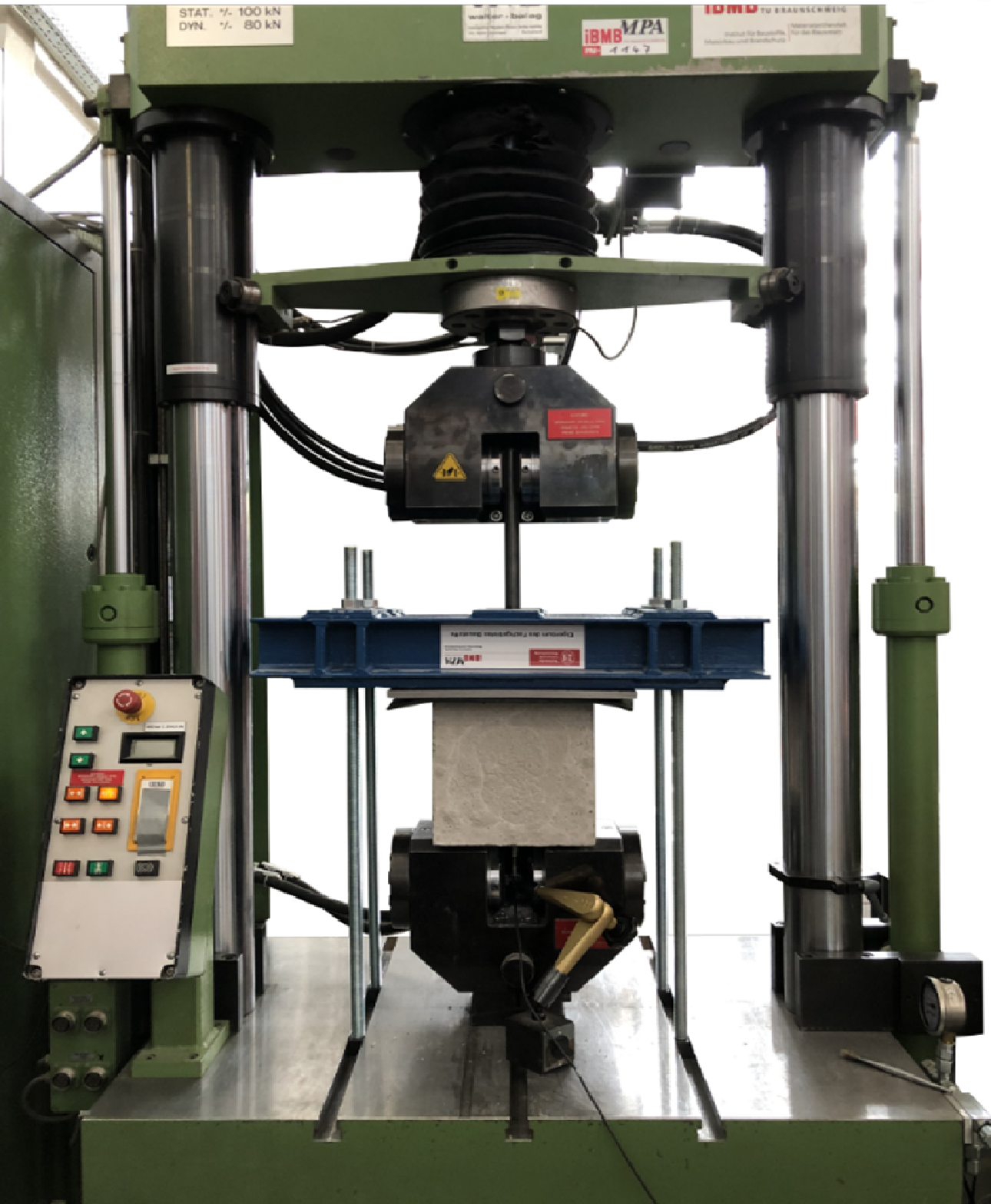
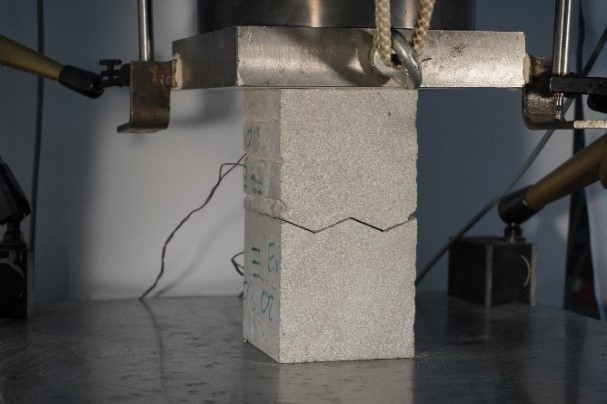
Jointing Principles for Combination of Concrete Elements Produced by Different Additive Manufacturing Processes [23.09.2022] Empelmann, Martin; Project Leader, m.empelmann@ibmb.tu-bs.de Weigel, Hendrik; Doctoral Researcher, h.weigel@ibmb.tu-bs.de TU Braunschweig, Institute of Building Materials, Concrete Construction and Fire Safety (iBMB), Division of Concrete Construction Main goal The main goal of the C05 project is gaining fundamental knowledge for the design of dry joints in AM components. Therefore, the correlation between the execution and manufacturing on the load-bearing behaviour of dry joints will be investigated. Many different joint geometries are gathered, compared and evaluated by experimental testing and numerical methods. Summary The selected joint profiles from the so-called joint catalogue (see last RSR) are tested in terms of their compressive load-bearing behaviour. The …
Research Summary Report A06
Category: Research Summary Report
Laser Powder-Bed Fusion (LPBF) of Steel Elements for Construction – Basics of Design and Mechanical Resilience [16.09.2022] Wenzler, David; Doctoral researcher; david.wenzler@tum.de Technical University of Munich, Institute for Machine Tools and Industrial Management Diller, Johannes; Doctoral researcher; johannes.diller@tum.de, Siebert, Dorina; Doctoral researcher; dorina.siebert@tum.de Technical University of Munich, Chair of Metal Structures The project A06 aims to explore and evaluate the factors influencing the manufacturing of safe and durable structural steel elements by Powder Bed Fusion of Metals using a Laser Beam (PBF-LB/M). Thereby, the PBF-LB/M process, the post-treatment, and the geometrical aspects in terms of microstructure and mechanical properties are investigated and correlations are determined. In the first funding period, the project is focused on analyzing small-scale specimens as well …
Research Summary Report C02
Category: Research Summary Report
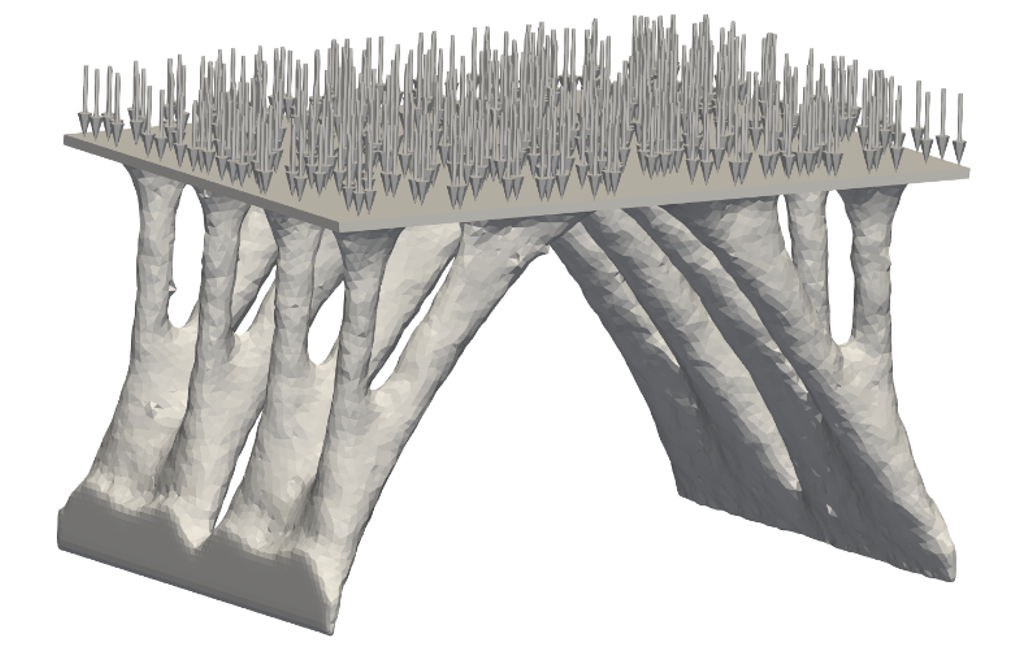
3D Structural Puzzle – Numerical Multi Scale Shape and Topology Optimisation Methods to Additively Manufacture Optimal Structures from Optimised Pieces [01.09.2022] Dr.-Ing. Reza Najian Asl (reza.najian-asl@tum.de); Prof. Dr.-Ing Kai-Uwe Bletzinger; TUM, Chair of Structural Analysis Current state of research Additive manufacturing in construction is a real enabler for the creation of optimal structures. It breaks the limitations of classical construction and provides the possibility of design and optimization for every feature and property of the structure, especially material and shape. To that end, a simulation-based optimization tool has been developed at the Chair of Structural Analysis, TU Munich. The tool is implemented in the Kratos-Multiphysics open-source frame work and has the following state of the art features: (a) efficient and …