News
Research Summary Report of C06
Category: Research Summary Report
Integration of Additive Manufacturing into a Cyber-Physical Construction System [16.04.2024] Placzek, Gerrit; Doctoral researcher, g.placzek@tu-braunschweig.de, Schwerdtner, Patrick; Project Leader, patrick.schwerdtner@tu-braunschweig.de both: TU Braunschweig, IBB Main Goal The integration of additive manufacturing into construction requires an interdisciplinary approach. The different competences of the team – digital fabrication in architecture (Hack), geodesy and photogrammetry (Gerke) and construction management (Schwerdtner) – lead to research from diverse perspectives on the various scalar levels of construction to be viewed holistically: component, building and industry scale. Within Subproject C06, the goal of the first phase was to create a continuous digital and lean-based process chain from design (using BIM method) to fabrication (using AM method). Based on process models und strategic decisions, we investigated …
Research Associate (Doctoral Candidate) (m/f/d) in the field of digital and additive manufacturing (3D-printing)
Category: Jobs
We are looking for candidates who have demonstrated excellent achievements in research and teaching in an internationally recognized scientific environment, relative to the relevant career level (please see www.tum.de/en/faculty-recruiting-faq/ for further information). A university degree and an outstanding doctoral degree or equivalent scientific qualification, as well as pedagogical aptitude, are prerequisites. Substantial research experience abroad is expected.
Research Summary Report of A07
Category: Research Summary Report
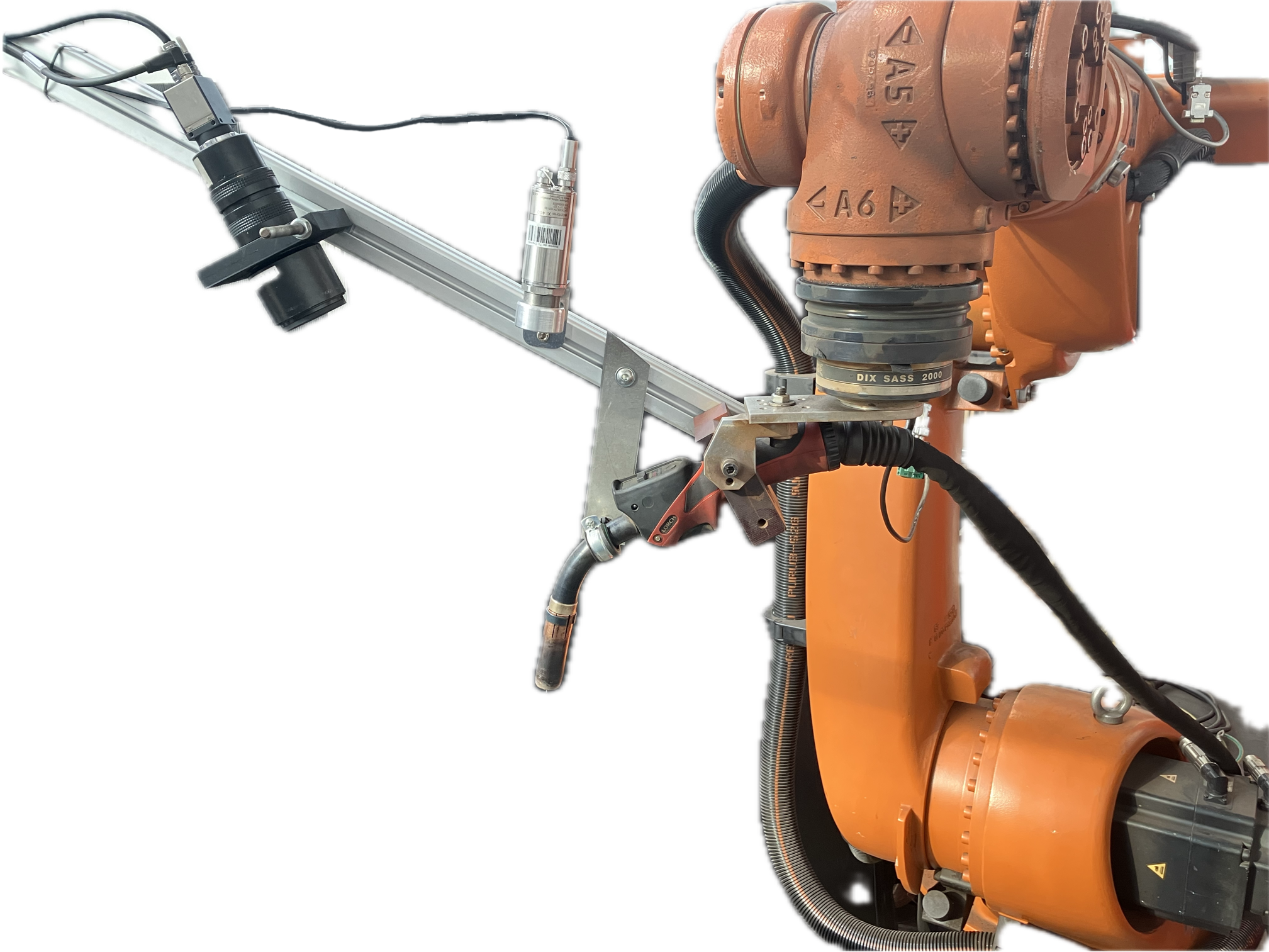
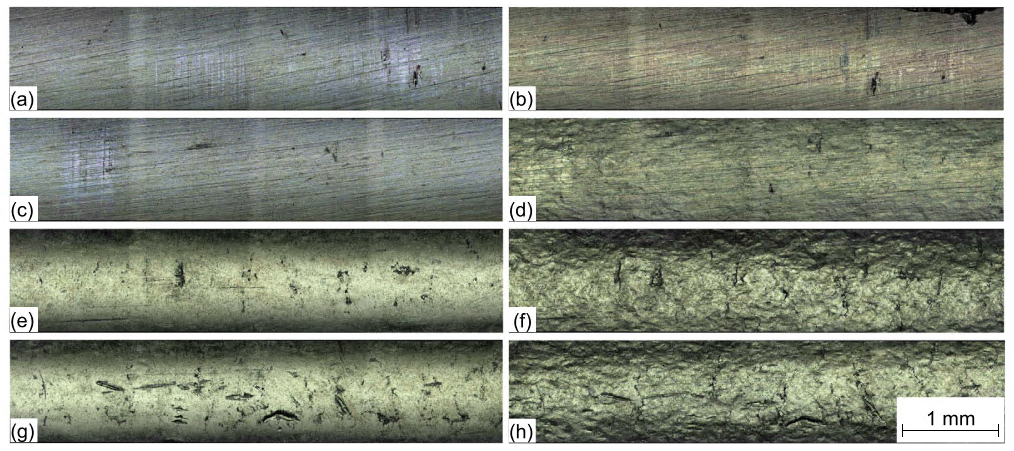
Wire Arc Additive Manufacturing (WAAM) of High Strength and Individualized Steel Components [05.04.2024] Jurke, Florian; Research Assistant, florian.jurke@mb.tu-chemnitz.de Kevin Hoefer, Research Assistant, kevin.hoefer@mb.tu-chemnitz.de Hensel, Jonas; Project Leader, jonas.hensel@mb.tu-chemnitz.de Main Goal A07 focuses on understanding the interaction between DED-arc components and existing structures, developing load-specific strengthening solutions and designing welding strategies. A design framework will incorporate manufacturing constraints and optimization tools for efficient structural components. Additionally, online-process control will be implemented to compensate deviations in component geometry and temperature within the process, using a “Learning-by-Printing” approach. Overall, the project seeks to advance DED-arc application in construction by improving efficiency, reducing material usage and enhancing structural performance. Summary Before Johanna Müller left from the TRR after four years, she constructed …
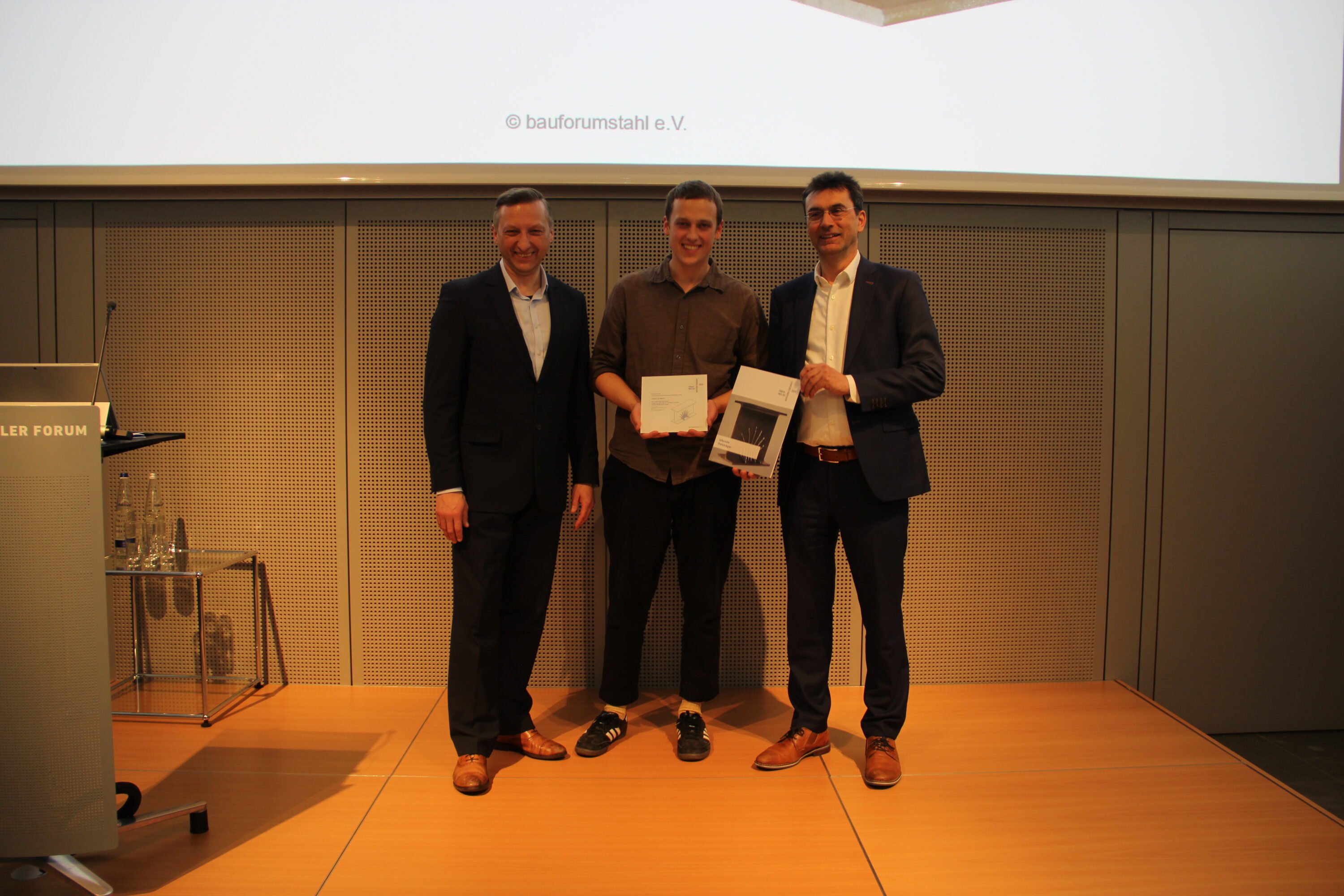
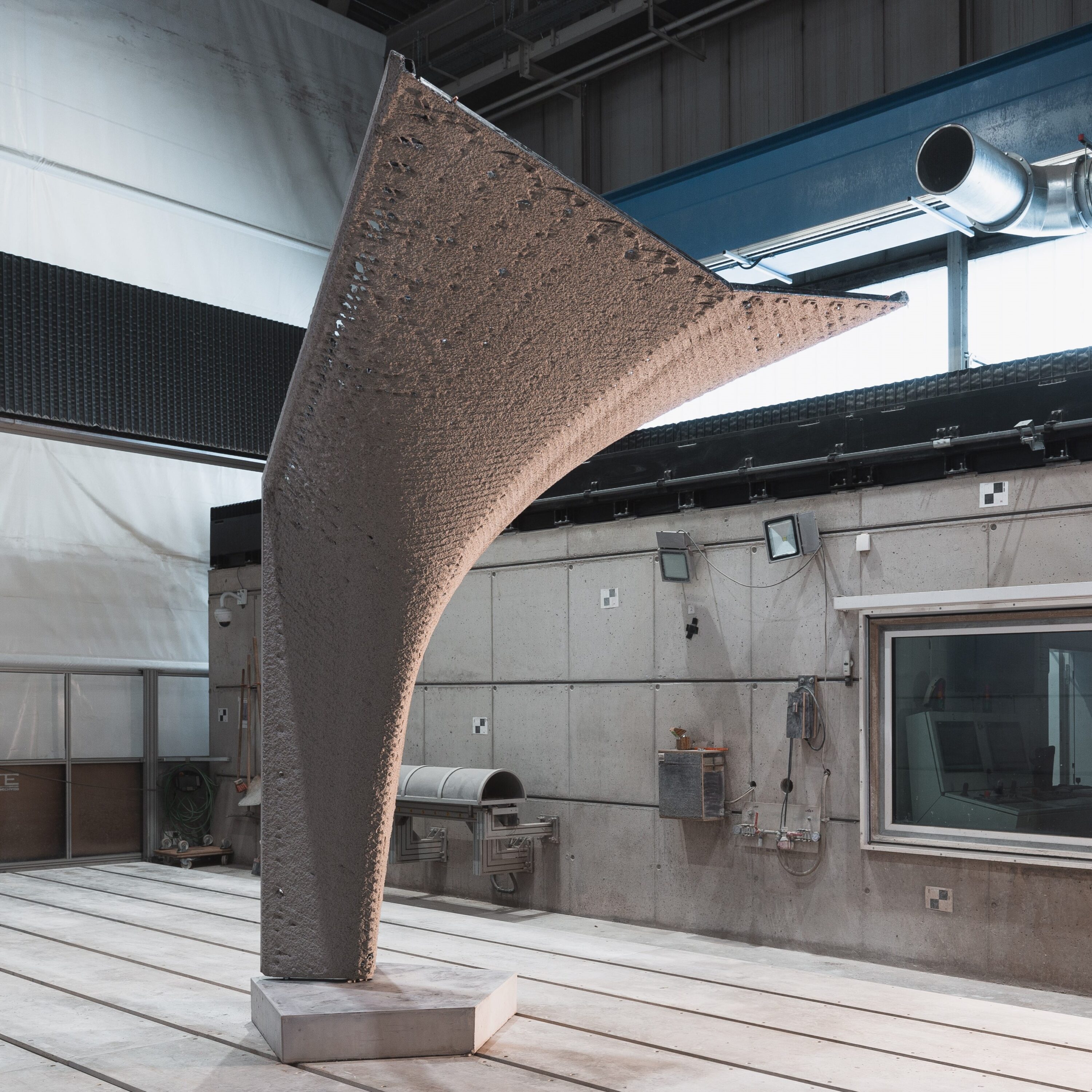
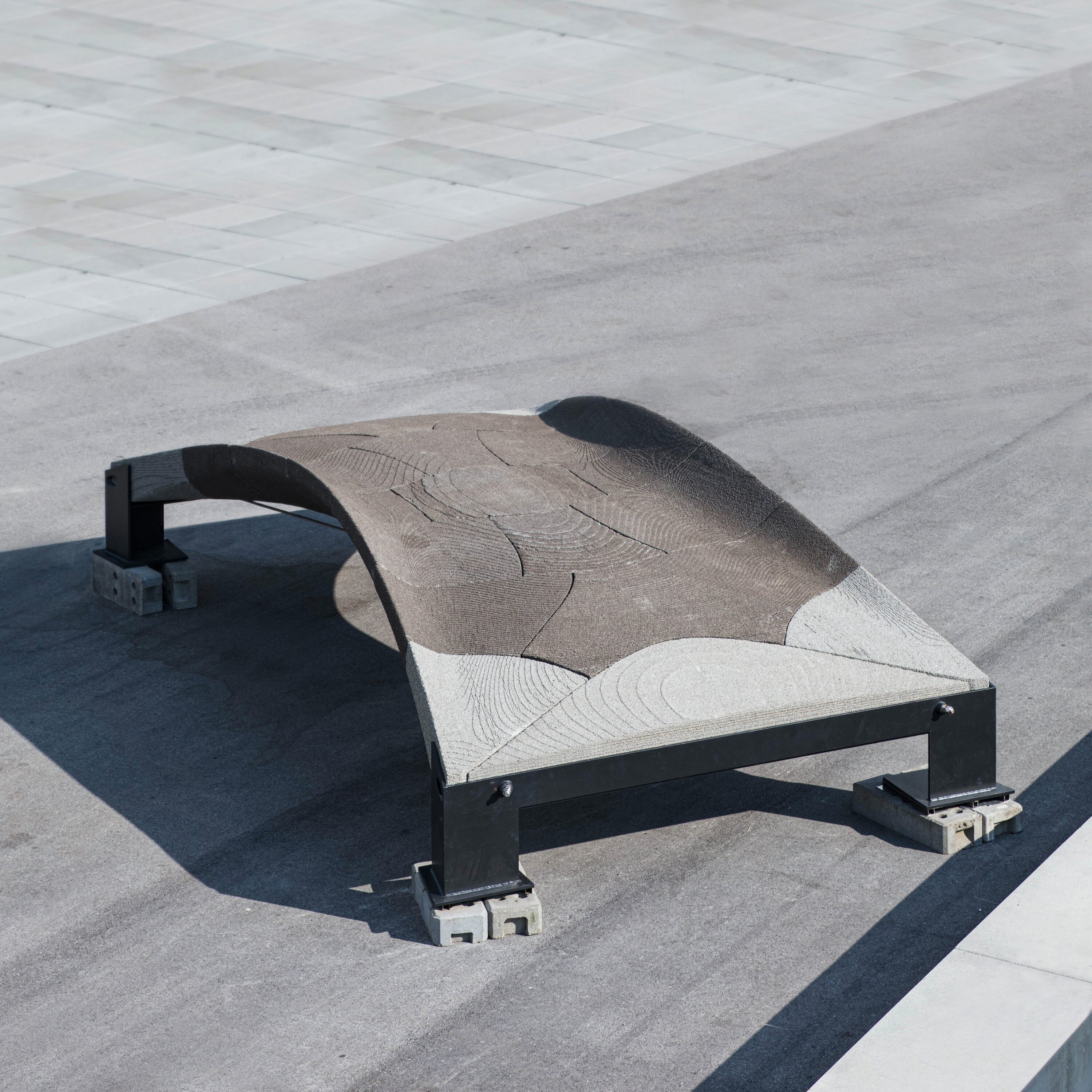
German Steel Construction Award for Linus Schmitz
and the winner is… Linus Paul Schmitz, winner of the German Steel Construction Award 2024 for his term paper on the topic: SERIAL becomes INDIVIDUAL, local reinforcement of standard I-profiles using WAAM technology. Steel beams can be exposed to individual load situations, creating a need for additional reinforcement. His solution: Using WAAM, i.e. the free additive application of material at the points where the load case is increased, can be individually reinforced without having to use a generally reinforced steel girder. This saves material. We congratulate Linus on this great success and of course all those involved, such as the ITE, TU Braunschweig, the AMC, TU Braunschweig and TU Munich as well as Harald Kloft as supervisor. If you want …
Research Summary Report of A06
Category: Research Summary Report
Laser Powder-Bed Fusion (LPBF) of Steel Elements for Construction – Basics of Design and Mechanical Resilience [19.03.2024] Blankenhagen, Jakob; doctoral researcher; Jakob.blankenhagen@tum.de Technical University of Munich, Chair of Metal Structures Wenzler, David; doctoral researcher; david.wenzler@tum.de Technical University of Munich, Institute for Machine Tools and Industrial Management Summary The project A06 aims to develop a methodology for producing safe and functional structural steel elements for construction using LPBF. This involves integrating complex LPBF parts into large-scale structures. For this purpose, the focus is laid on transferring results and qualification methods from the first funding period to new materials, such as Printdur HSA®. This steel material has been developed specifically for LPBF. And offers higher strength and a …
Research Summary Report of A05
Category: Research Summary Report
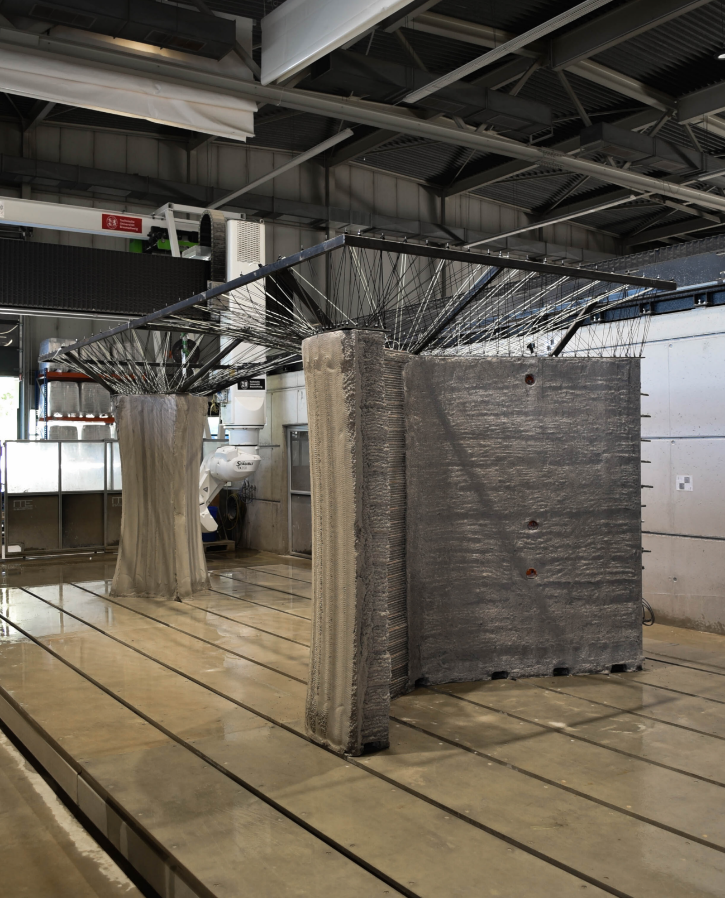
Integration of Individualized Prefabricated Fibre Reinforcement in Additive Manufacturing with Concrete [13.03.2024] Gantner, Stefan; Scientific Researcher, stefan.gantner@tu-bs.de Hack, Norman; Project Leader, n.hack@tu-braunschweig.de Collaboration: Amiri, Fatemeh; Scientific Researcher, fatemeh.amiri@tu-braunschweig.de all: TU BS, Institute of Structural Design (ITE) Main Goal Cement-based additive manufacturing techniques need to be enhanced by the ability of integrating reinforcement, in order to fulfil requirements of construction. This project focuses on non-metallic continuous fibre reinforcement, which is not only corrosion resistant but also flexible in handling. Instead of bending and welding, glass or carbon fibre rovings can be processed robotically by winding onto a support structure. Respective fabrication strategies and their interaction with additive manufacturing of concrete are the main focus of this project. Summary Cement-based …
Research Summary Report of C02
Category: Research Summary Report
3D Structural Puzzle – Numerical Multi Scale Shape and Topology Optimisation Methods to Additively Manufacture Optimal Structures from Optimised Pieces [01.03.2024] Richter, Christiane, M.Sc.; Doctoral Researcher, christiane.richter@tum.de, TUM, Professorship of Structural Design (SD) Prof. Dr. D’Acunto, Pierluigi; Project Leader, pierluigi.dacunto@tum.de, TUM, Professorship of Structural Design (SD) Main Goal Current building practices often adopt a sequential design approach, where architectural, structural, and fabrication aspects are addressed independently, resulting in excessive material consumption. The CO2 project aims to establish a Holistic Design Framework (HDF) integrating the above-mentioned aspects. Within this framework, additive manufacturing facilitates structural optimization by enabling the production of bespoke geometries for an effective use of material resources. Departing from the conventional sequential approach, the HDF concurrently …
Research Summary Report of A04
Category: Research Summary Report
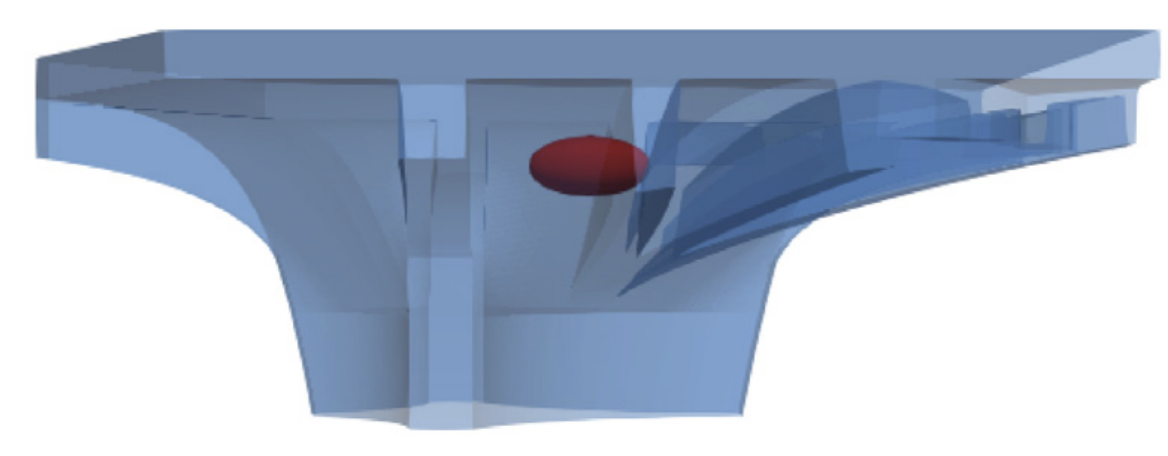
Integrated Additive Manufacturing Processes for Reinforced Shotcrete 3D Printing (SC3DP) Elements with Precise Surface Quality [23.02.2024] Dörrie, Robin Phd candidate r.doerrie@tu-braunschweig.de Technische Universität Braunschweig ITE Institut für Tragwerksentwurf Main Goal The project aims to fundamentally understand SC3DP technology to manufacture sustainable, multi-objective optimised, reinforced concrete components with precise surface quality and improved building physics via functional integration. It seeks to minimise carbon footprint by exploring varied material strategies, such as reducing cement content and design methods to decrease overall concrete volume. Additionally, it focuses on establishing reliable material and process control, emphasising fresh material laws for printability and durability, real-time monitoring of concrete properties, and component build-up strategies. Integration of large-scale reinforcement enhances structural suitability, while precise surface finishing …
Research Summary Report of B04
Category: Research Summary Report
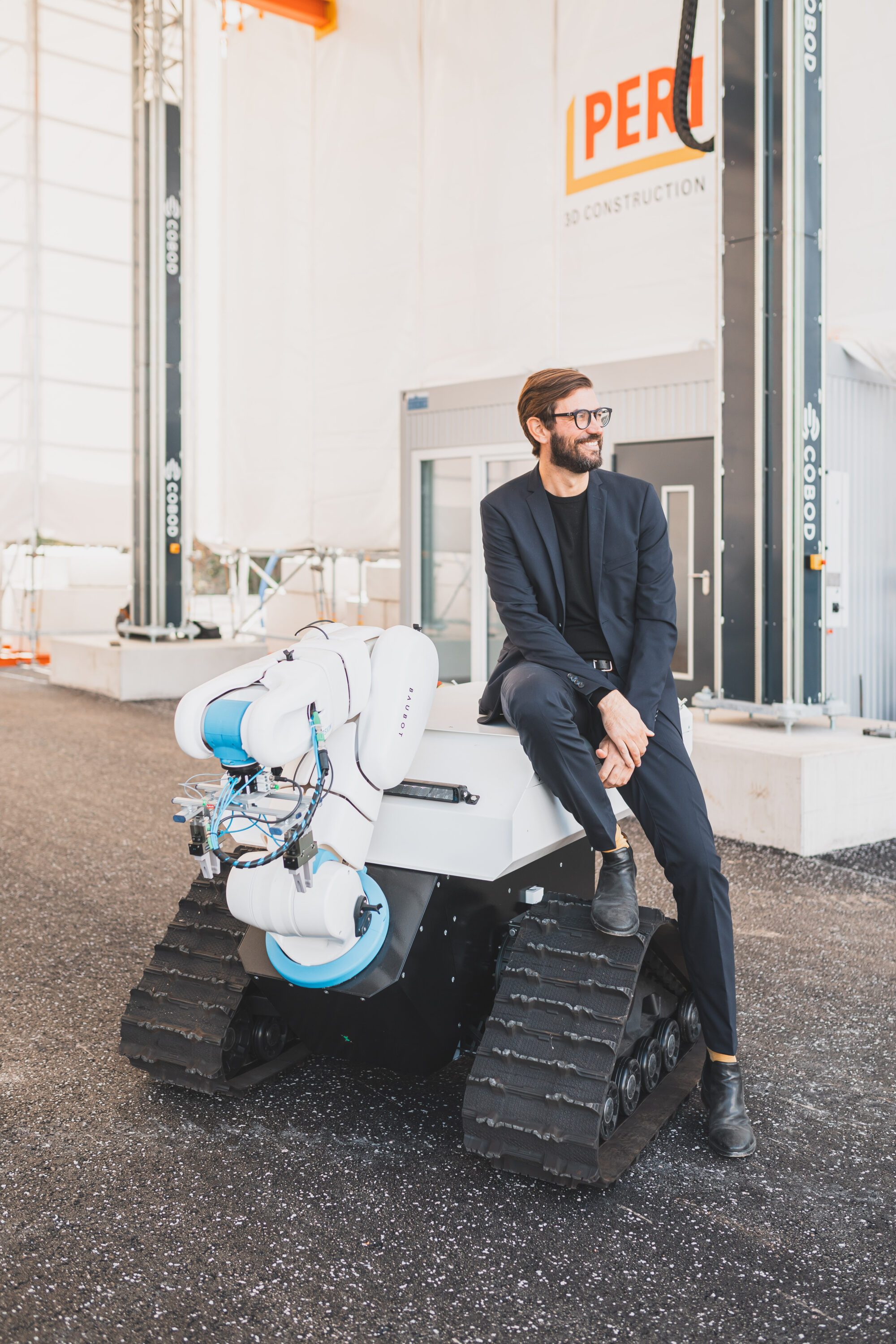
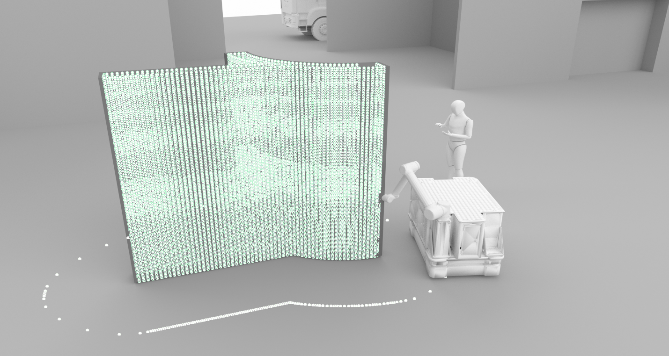
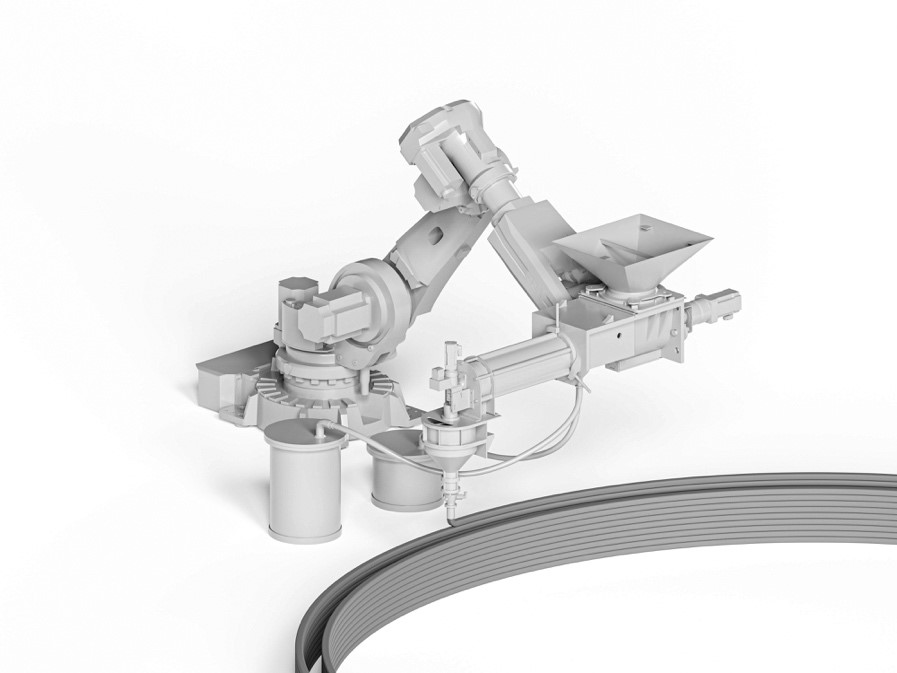
Process Control and Adaptive Path Planning for Additive Manufacturing Processes Based on Industrial Robots with an Extended Degree of Freedom [07.02.2024] Raatz, Annika; raatz@match.uni-hannover.de LUH, Institute of Assembly Technology and Robotics Lachmayer, Lukas; lachmayer@match.uni-hannover.de LUH, Institute of Assembly Technology and Robotics Heeren, Hauke; heeren@match.uni-hannover.de LUH, Institute of Assembly Technology and Robotics Main Goal The research of project B04 is dedicated to extending the current state-of-the-art path planning and process control algorithms for concrete-based additive manufacturing. The objective is to enable reproducible production of multi-material components utilizing mobile robot systems in motion, known as print-while-driving. Achieving this requires precise localization, considering system dynamics, such as acceleration and jerk limitations, as well as accounting for varying material properties and building installation …
Research Summary Report of C01
Category: Research Summary Report
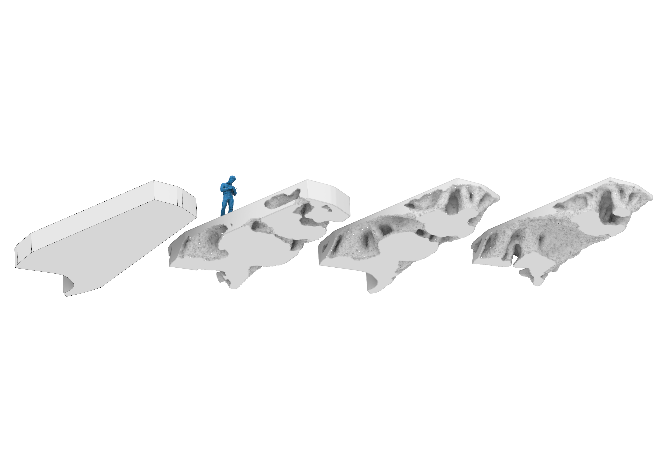
Bridging Scales – From Geometric Part Details to Construction Elements [02.02.2024] Kollmannsberger, Stefan; stefan.kollmannsberger@tum.de TUM, Computational Modeling and Simulation Bürchner, Tim; tim.buerchner@tum.de TUM, Computational Modeling and Simulation Rank, Ernst; ernst.rank@tum.de TUM, Institute for Advanced Study Digital models for Additive Manufacturing (AM) must consider many different geometric scales. The scales range from micrometers up to tens of meters for metal- or concrete-based processes and mutually influence each other. Project C01 aims to develop consistent geometric and computational descriptions for the relevant AM products on all these scales. As-built structures naturally deviate from as-designed structures in geometry, topology, and material properties especially in additive manufacturing. The consequences of such deviations upon the structural behaviour are commonly termed the effect of defect. …
Research Summary Report of A03
Category: Research Summary Report
Extrusion of Near-Nozzle Mixed Concrete – Individually Graded in Density and in Rate of 3D Fibre Reinforcement [1.12.2023] Hechtl, Christian Maximilian, TP editor, m.hechtl@tum.de, TUM, cbm Dr.-Ing. Kränkel, Thomas, PL, thomas.kraenkel@tum.de, TUM, cbm Prof. Dr.-Ing. Gehlen, Christoph, PL, gehlen@tum.de, TUM, cbm The goal of A03 is to establish a concrete extrusion process using a near nozzle mixing (NNM) approach to enable the gradual variation of material properties during printing (gradation). This approach allows for the creation of multifunctional components, such as structures merging both load bearing and thermally insulating zones, by precisely altering material properties as required throughout the printing process. Summary and Current State of Research GRES V1 is a gradation-ready extrusion system that demonstrates the potential …
The AMC at parliamentary evening in Berlin
Future Mobility Under the motto ‘Future Mobility – autonomous and digital,’ the city of Braunschweig, along with TU Braunschweig, presents itself to the capital’s politics and press. Bundled in one evening, participants get to know, among other things, the connection between a functioning infrastructure and a digital and 3D-printed construction industry. More information at TUBraunschweig -future mobility About TRR 277 AMC: The Collaborative Research Center TRR 277 Additive Manufacturing in Construction (AMC) is dedicated to advancing research in the field of construction, with a focus on leveraging 3D printing technology to revolutionize sustainable and energy-efficient building practices. Through innovation and collaboration, the center aims to usher in a new era for the construction industry. In the interdisciplinary, cross-location and …
Research Summary Report of A02
Category: Research Summary Report
Particle-Bed 3D Printing by Selective Cement Paste Intrusion (SPI) – Particle Surface Functionalisation, Particle Synthesis and Integration of WAAM Reinforcement [17.11.2023] Straßer, Alexander, TP editor, alexander.strasser@tum.de, TUM, Chair of Materials Science and Testing Kränkel, Thomas, TP editor, thomas.kraenkel@tum.de, TUM, Chair of Materials Science and Testing Gehlen, Christoph, PL, gehlen@tum.de, TUM, Chair of Materials Science and Testing The goal of A02 is to implement reinforcement by Wire and Arc Additive Manufacturing (WAAM) in concrete elements produced by Selective Paste Intrusion (SPI), see Figure 1. Since the cement paste is applied to the aggregates and must penetrate the cavities between the aggregates by gravity, consistent rheological properties of the cement paste are essential. The welding process with WAAM generates high temperatures …
A New Era for Sustainable Construction
AMC Enters Second Funding Phase The collaborative project “Additive Manufacturing in Construction” (AMC), explores new perspectives for the construction industry. Research on 3D printing in construction at the Technical University of Braunschweig and the Technical University of Munich receives four more years of funding from the German Research Foundation (DFG). 3D printing methods for building with clay and flood protection Challenges in Traditional Construction: Conventional construction processes are characterized by inefficient material usage, high environmental impact, and stagnant productivity. With a growing global population and an increasing demand for housing, the construction industry is reaching its limits. Faced with these challenges and the global significance of the construction sector as a major contributor to CO2 emissions with substantial resource …
Research Summary Report of B03
Category: Research Summary Report
Modelling and Simulation of Shotcrete 3D Printing (SC3DP) Based on a Massively Parallel Multi-Phase, Multi-Component Coupled LBM-DEM Approach [10.11.2023] Kutscher (PostDoc), M. Geier (PI), M. Krafczyk (PI) TU Braunschweig, IRMB The primary aim of the project is to understand and quantify the dynamic distribution of material components (fluid, air and particles) and kinetic energy inside the jet of liquid concrete present in the shotcrete process. The information is required as a basis for future optimization of the process with regards to process and material parameters as well as for the prediction of material inhomogeneities. Summary In order to overcome the numerical difficulties arising from sustaining a high-density ratio in the diffuse interface lattice Boltzmann model we developed a new …
Research Highlights of the 1st funding period (2020-2023)
Take a look at all the highlights of the TRR 277 AMC projects. The videos show the project and their achievements of the entire first four years at a glance. In short presentations you will learn about the main findings, collaborations and gain an overview of the publications and the people behind the projects. This overview was produced at the last AMC Conference in October 2023. The AMC Conference focused on the future of construction with 3D printing technologies. Researchers from the Technical University of Braunschweig and the Technical University of Munich, part of TRR 277 AMC, aim to make construction more resource-efficient, lower-emission, and economical through innovative 3D printing processes. The conference provided insights into AMC’s research areas, including …
Research Summary Report of A01
Category: Research Summary Report
Particle bed 3D printing by selective cement activation: Particle surface functionalization, particle bed compaction and reinforcement integration [03.11.2023] Herding, Friedrich; Researcher, f.herding@ibmb.tu-bs.de Lowke, Dirk; Project leader, lowke@tum.de TU Braunschweig, Institute of Building Materials, Concrete Construction and Fire Safety / Technical University of Munich, Department of Materials Engineering Our main research objective is the fundamental understanding of the material-process interactions in particle bed 3D printing (PB3DP) by Selective Cement Activation (SCA). This will allow for the manufacturing of concrete elements with high mechanical strength and dimensional accuracy. Besides we also investigate different ways of reinforcement integration, which is crucial for the manufacturing of load-bearing building components. Summary In particle bed 3D printing by Selective Cement Activation, the particle mixture mainly …
Code.Craft.Construct. Navigating the Digital Transformation in Architecture and Construction
Inaugural lecture by Prof. Dr. Norman Hack Code.Craft.Construct. Navigating the Digital Transformation in Architecture and Construction Wednesday, 8. November 2023, 5.00 pm | Pockelsstr. 11, TU Braunschweig, Aula, Haus der Wissenschaft As of today, the computer and the digitally controlled machine have a 70-year history in the architectural discourse. Over the years, the fields of application and the potentials of the computer in architecture have been constantly reinterpreted and implemented, whereby the natural sciences, philosophy and art have always had a significant influence on this discourse. In the inaugural lecture „Code.Craft.Construct. Navigating the Digital Transformation in Architecture and Construction“, Professor Hack gives an overview of the influential developments in the discourse of digital architecture and locates his own research on …
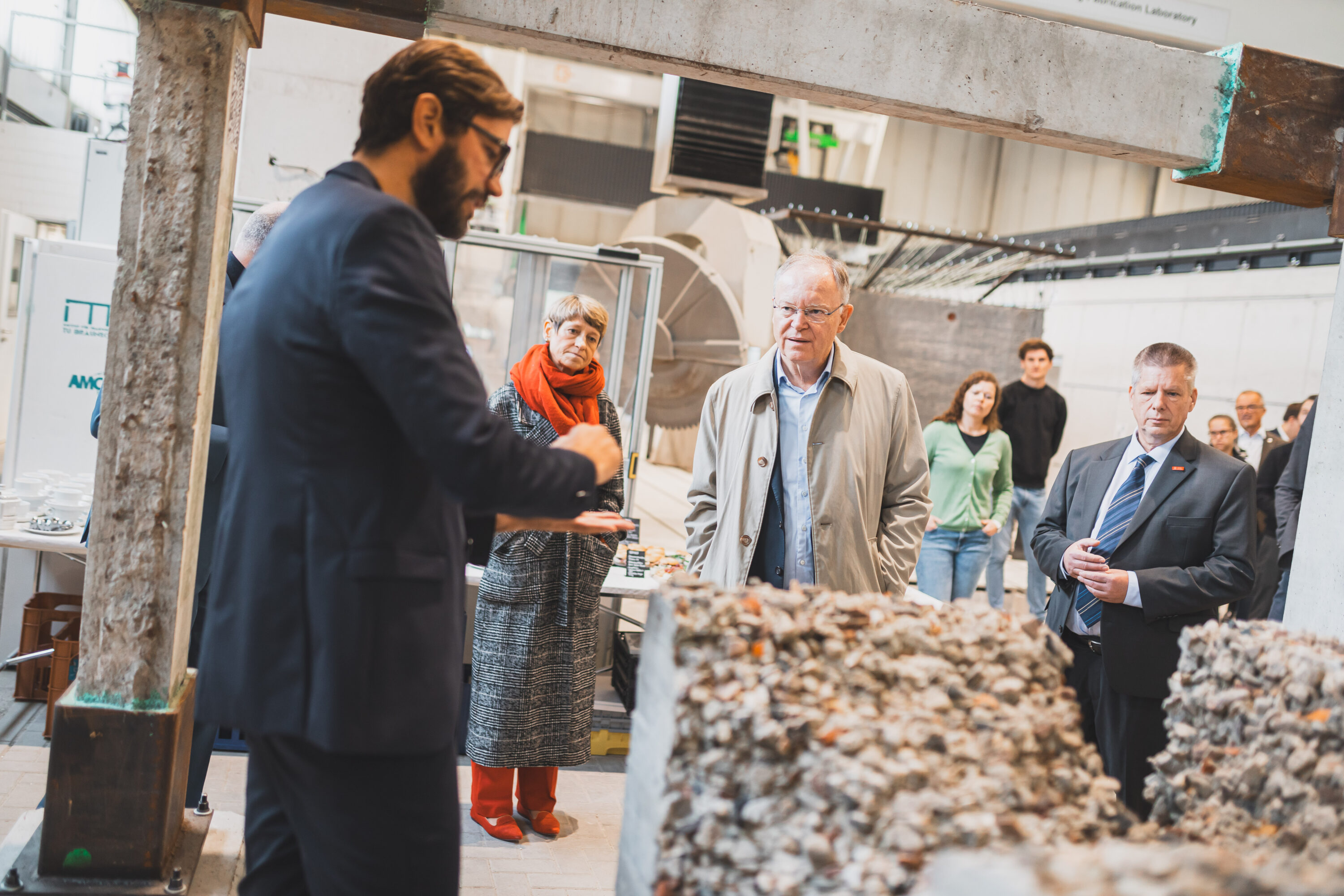
Build with the 3D printer: Stephan Weil visits TU Braunschweig
Buildings are part of our cultural development. New technologies are now needed to make construction more environmentally friendly, faster and more economical. Scientists at the AMC Collaborative Research Centre see additive manufacturing, or 3D printing, as a key digital technology for the construction of the future. On 23 October, the scientists showed Lower Saxony’s Minister President Stephan Weil how they are conducting fundamental research into 3D printing together. “Research from Lower Saxony is a real driver of innovation, as I was once again able to see for myself today at the TU Braunschweig. New technologies are being developed here that make construction more environmentally friendly, faster and more economical – a real milestone,” says Stephan Weil, Minister President of Lower …
Digital Construction – Conference with visionaries for the construction of the future
Instead of brick on brick built by hand, layer by layer 3D printed with a robot. This is what the future of building could look like. The first buildings in Germany are already standing, and the largest printed building in Europe was recently completed in Heidelberg. At the Technical University of Braunschweig and the Technical University of Munich, scientists of TRR 277 AMC are researching new 3D printing processes to make the construction of the future more resource-efficient, lower-emission and more economical. The AMC had now presented its research results. The keynote speaker was Leibniz Prize winner Professor Achim Menges, spokesperson for the IntCDC Cluster of Excellence (Digital Technologies for Design and Construction of the Future) at the University of …