Research Summary Report
Research Summary Report of A03
Category: Research Summary Report
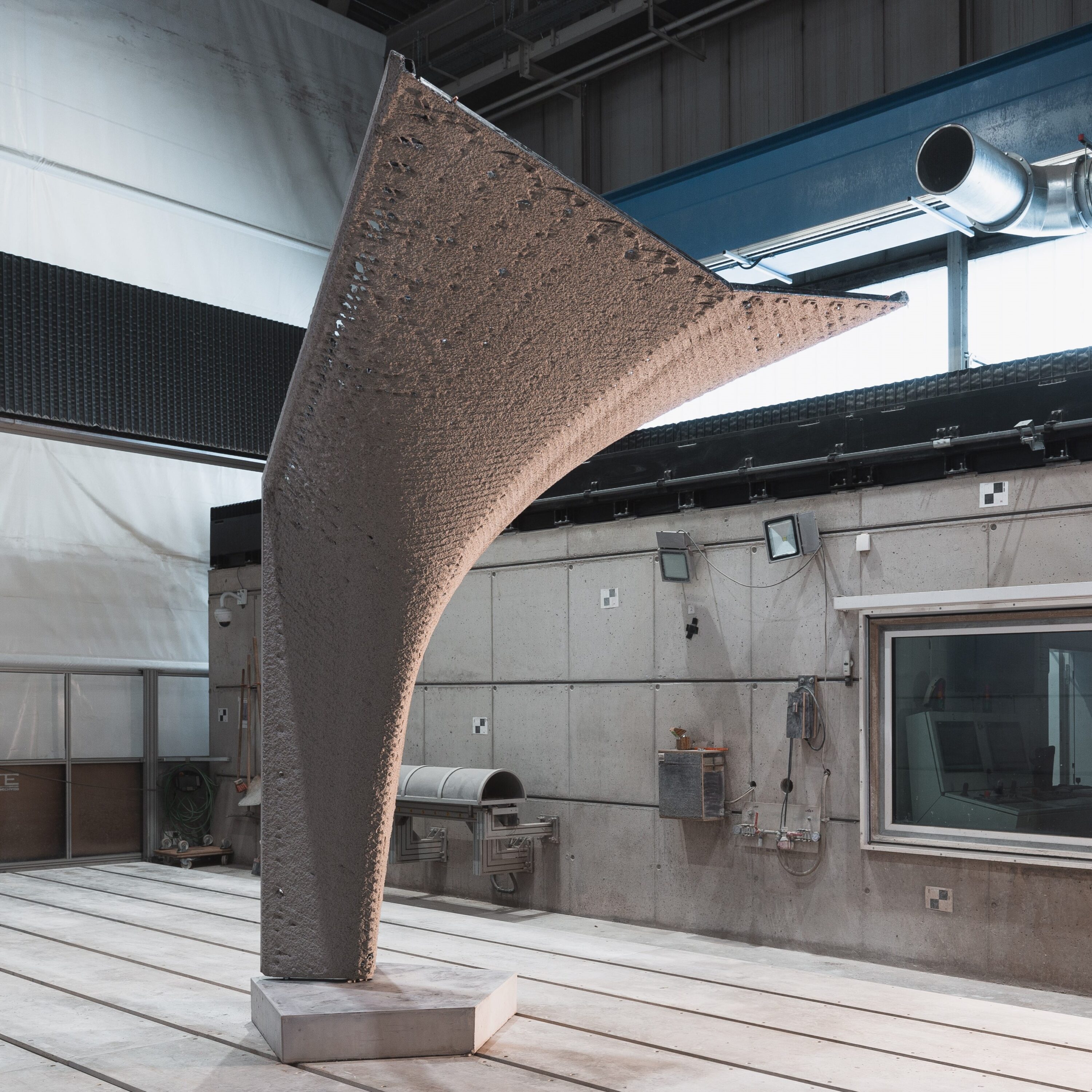
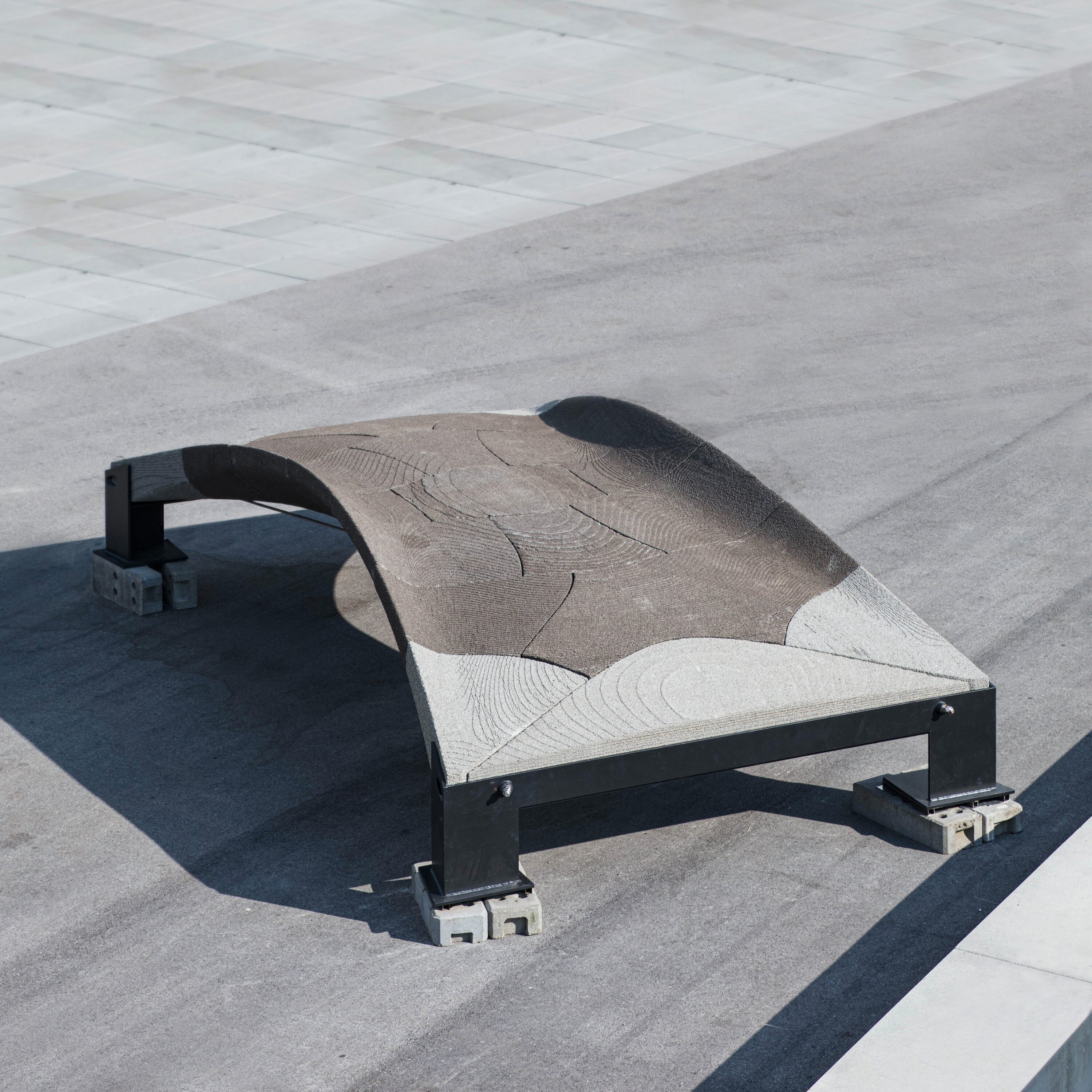
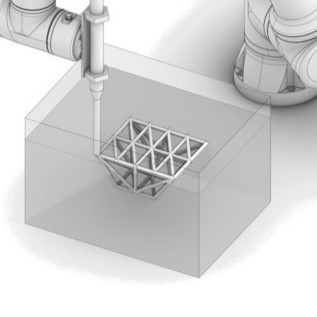
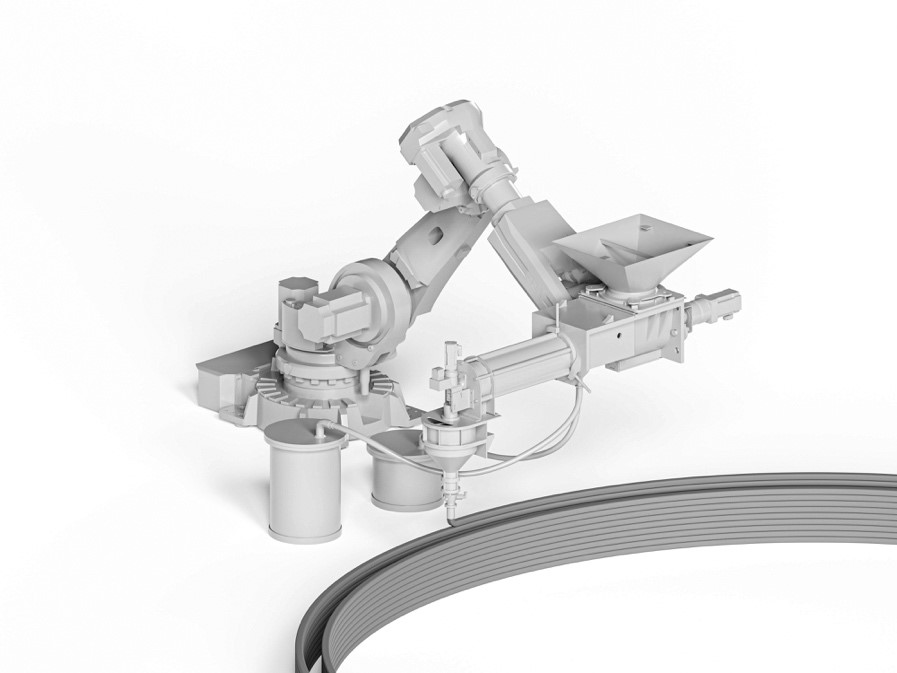
Extrusion of Near-Nozzle Mixed Concrete – Individually Graded in Density and in Rate of 3D Fibre Reinforcement [03.07.2024] M.Sc. Dahlenburg, Maximilian; maximilian.dahleburg@tum.de Prof. Dr.-Ing. Fottner, Johannes; j.fottner@tum.de TUM, Chair of Materials Handling, Material Flow, Logistics Main Goal In the first funding period the feasibility of multiple Near-Nozzle-Mixing approaches (NNM) were studied by iteratively developing a working prototype: the Gradation-Ready-Extrusion-System (GRES). The latest process mixes paste and aggregates at the end-effector, eliminating the challenging long pumping distances of State-of-the-art Extrusion based 3D Concrete Printing systems (E3DCP). This solves the process- and material development conflict of having a highly workable material for pumping and the contrasting need for a highly buildable material after strand deposition. Furthermore, this process type enables …
Research Summary Report of C06
Category: Research Summary Report
Integration of Additive Manufacturing in the Construction Process [13.06.2024] Mawas, Karam; Doctoral researcher, k.mawas@tu-braunschweig.de, TU Braunschweig, Institute of Geodesy and Photogrammetry (IGP) Gerke, Markus; Project leader, m.gerke@tu-braunschweig.de, TU Braunschweig, Institute of Geodesy and Photogrammetry (IGP) Maboudi, Mehdi; Associated scientist, m.maboudi@tu-braunschweig.de, TU Braunschweig, Institute of Geodesy and Photogrammetry (IGP) Quality control plays a pivotal role in enabling the seamless integration of components into objects. To ensure adherence to a resilient process and the faithful realization of the designed model in the printed object, it is essential to implement continuous and automated data capture and process inspection. Based on the outcomes of our quality control measures, we investigated how to integrate these practices into Construction Industry 4.0. We will continue …
Research Summary Report of A01
Category: Research Summary Report
Particle-Bed 3D Printing by Selective Cement Activation (SCA) – Particle Surface Functionalisation, Particle-Bed Compaction and Reinforcement Implementation [14.06.2024] Meier, Niklas; Researcher, niklas.meier@tu-braunschweig.de Zetzener, Harald; Leading researcher, h.zetzener@tu-braunschweig.de Kwade, Arno; Project Leader, a.kwade@tu-braunschweig.de all: TU Braunschweig, Institute for particle technology The fundamental goal of project A01 is to understand material process interactions in particle-bed 3D printing by Selective Cement Activation (SCA). In SCA, a particle-bed consisting of fine aggregates and cement is applied layerwise. Inbetween the layerwise application, a liquid is applied selectively on the upper layer of the particle-bed. Thereby, a the cement hydration reaction is induced locally and the particle-bed hardens at the desired places. In the second funding period of this project, there is a focus on …
Research Summary Report of C04
Category: Research Summary Report
Integrating Digital Design and Additive Manufacturing through BIM-Based Decision Support and Digital Twin Methods [07.06.2024] Li, Chao; doctoral researcher, chao1.li@tum.de Petzold, Frank; PL, petzold@tum.de Technical University of Munich, TUM School of Engineering and Design, Chair of Architectural Informatics Project C04-WP1 aims to conceive a design decision support system (DDSS) to integrate AM technologies in the early design phase. Project C04 has formalized a ontology-based knowledge base, enabling analysis of AM for building design regarding geometric and functional conformity. The DDSS will be strengthened by implementing the case-based reasoning (CBR) method to integrate AM experts’ know-how, experience, and practical examples into the architectural design process. Summary How to capitalize multi-domain expertise in a BIM-based design workflow, and how to …
Research Summary Report of C03
Category: Research Summary Report
Integration of Passive and Active Functions in Additively Manufactured Construction Elements [29.05.2024] Auer, Thomas; PL, thomas.auer@tum.de * Briels, David; doctoral researcher, david.briels@tum.de * Nouman, Ahmad; doctoral researcher, ahmad.nouman@tum.de * * Technical University of Munich, TUM School of Engineering and Design, Chair of Building Technology and Climate Responsive Design In engineering advancements, Additive Manufacturing in Construction (AMC) represents a significant paradigm shift. To fully harness the capabilities of AMC, our project, C03, is dedicated to fundamentally transforming the design of building elements. Additive Manufacturing (AM) facilitates the creation of highly specialized components that enhance both passive and active functionalities within buildings. It includes aspects of building physics, such as heat transfer and acoustics, and building services, such as heating, cooling, …
Research Summary Report of A04
Category: Research Summary Report
Integrated Additive Manufacturing Processes for Reinforced Shotcrete 3D Printing (SC3DP) Elements with Precise Surface Quality [24.05.2024] Böhler, David1; doctoral researcher, d.boehler@ibmb.tu-bs.de Rudolph, Jennifer1; doctoral researcher, j.rudolph@ibmb.tu-bs.de Freund, Niklas1; doctoral researcher, n.freund@ibmb.tu-bs.de Lowke, Dirk2; project leader, lowke@tum.de 1TU Braunschweig, Institute of Building Materials and Concrete Construction and Fire Safety (iBMB) 2TU Munich, Department of Materials Engineering Main Goal Project A04 investigates cooperative Additive Manufacturing (AM) processes based on Shotcrete 3D Printing (SC3DP). The aim of this project is a fundamental understanding of the SC3DP technology to manufacture sustainable, multi-objective optimised, reinforced concrete components with geometrically precise surface quality and improved building physics by functional integration. Current state of research 3D concrete printing (3DCP) has the potential to significantly …
Research Summary Report of A02
Category: Research Summary Report
Particle-Bed 3D Printing by Selective Cement Paste Intrusion (SPI) – Particle Surface Functionalisation, Particle Synthesis and Integration of WAAM Reinforcement [02.05.2024] Riegger, Felix; Doctoral researcher; Felix.Riegger@iwb.tum.de Baehr, Siegfried; Head of the research group; Siegfried.Baehr@iwb.tum.de All: Technical University of Munich, Institute for Machine Tools and Industrial Management Main Goal To enable selective paste intrusion (SPI) for practical applications, the inclusion of reinforcement is mandatory. The focus of the first funding period was set on implementing reinforcements in SPI parts by using wire arc additive manufacturing (WAAM). During the first funding period, two main issues were identified: the need for increased ecological sustainability for the combined process of SPI+WAAM and accelerated process velocities to improve the economic efficiency. Therefore, the main …
Research Summary Report of B05
Category: Research Summary Report
Principles of Mobile Robotics for Additive Manufacturing in Construction [02.05.2024] Dielemans, Gido; PhD Researcher, gido.dielemans@tum.de Technical University of Munich, TT Professorship of Digital Fabrication. Main Goal InjeIn this research, we investigate the deployment of mobile robots in construction scenarios for the additive manufacturing of building components through deposition-based 3D printing techniques. Our objective is to enhance on-site precision by enabling these robots to adjust their 3D printing operations autonomously in response to their immediate environment, facilitating the in-situ fabrication of building elements. We further aim to provide scalability via the parallelisation of tasks among multiple mobile robots, thereby increasing efficiency and expanding geometric possibilities. Summary Our approach utilises a method termed “print-drive-print,” which separates navigation and manipulation routines …
Research Summary Report of A09
Category: Research Summary Report
Injection 3D Concrete Printing (I3DCP) – Material Efficient Lightweight Reinforced Concrete Structures based on Spatially Complex Strut-and-Tie Models [20.04.2024] Mai, Inka, Project leader, mai@tu-berlin.de, TU Berlin, institute of civil engineering, chair of robot assisted manufacturing of the built environment. Main Goal Injection 3D Concrete Printing (I3DCP) is a new additive manufacturing process where a fluid of material A is robotically injected into another fluid of another material B. The role of material B is to support material A such that material A maintains a stable position. In general, I3DCP can be categorized into sub-categories, whereby the following two subcategories are addressed within this project: Concrete in Suspension (CiS) where concrete is injected into a non-hardening carrier liquid and …
Research Summary Report of C06
Category: Research Summary Report
Integration of Additive Manufacturing into a Cyber-Physical Construction System [16.04.2024] Placzek, Gerrit; Doctoral researcher, g.placzek@tu-braunschweig.de, Schwerdtner, Patrick; Project Leader, patrick.schwerdtner@tu-braunschweig.de both: TU Braunschweig, IBB Main Goal The integration of additive manufacturing into construction requires an interdisciplinary approach. The different competences of the team – digital fabrication in architecture (Hack), geodesy and photogrammetry (Gerke) and construction management (Schwerdtner) – lead to research from diverse perspectives on the various scalar levels of construction to be viewed holistically: component, building and industry scale. Within Subproject C06, the goal of the first phase was to create a continuous digital and lean-based process chain from design (using BIM method) to fabrication (using AM method). Based on process models und strategic decisions, we investigated …
Research Summary Report of A07
Category: Research Summary Report
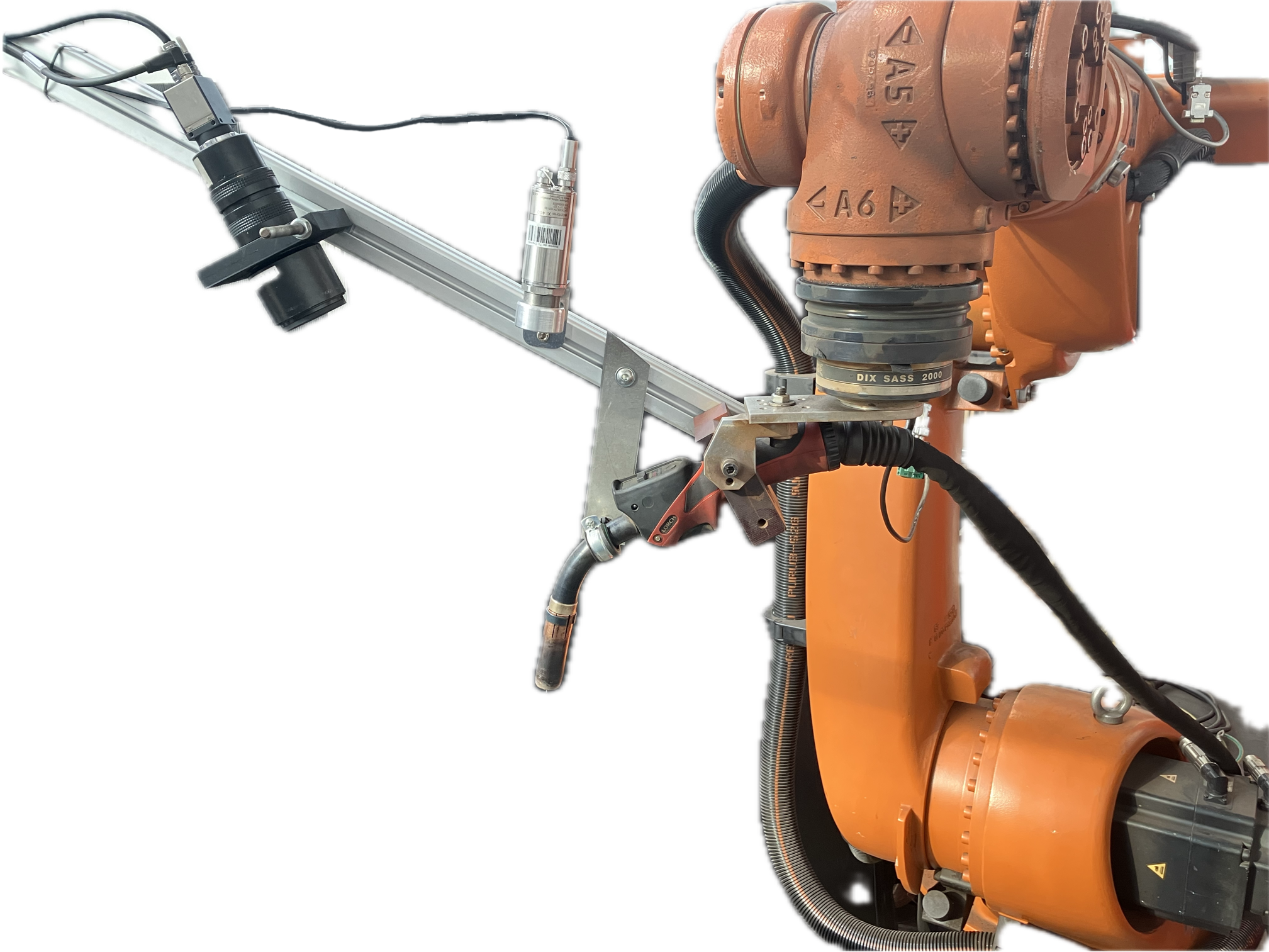
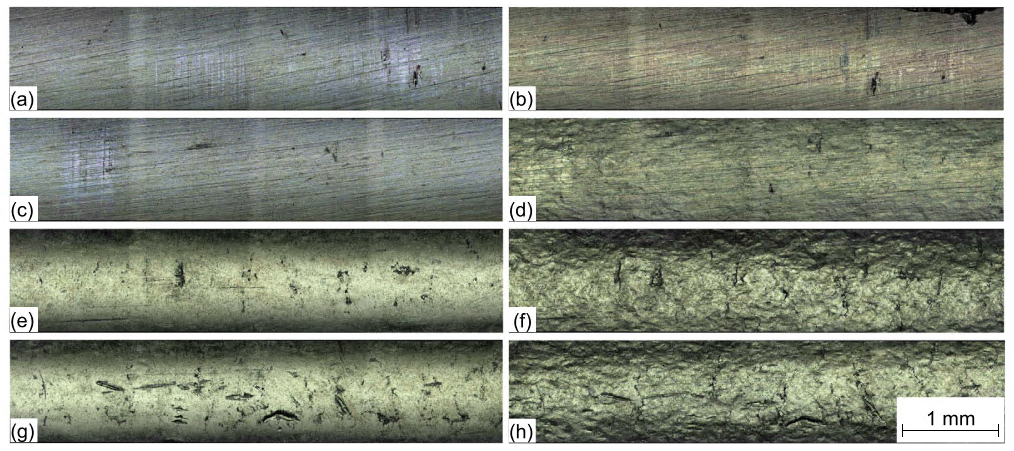
Wire Arc Additive Manufacturing (WAAM) of High Strength and Individualized Steel Components [05.04.2024] Jurke, Florian; Research Assistant, florian.jurke@mb.tu-chemnitz.de Kevin Hoefer, Research Assistant, kevin.hoefer@mb.tu-chemnitz.de Hensel, Jonas; Project Leader, jonas.hensel@mb.tu-chemnitz.de Main Goal A07 focuses on understanding the interaction between DED-arc components and existing structures, developing load-specific strengthening solutions and designing welding strategies. A design framework will incorporate manufacturing constraints and optimization tools for efficient structural components. Additionally, online-process control will be implemented to compensate deviations in component geometry and temperature within the process, using a “Learning-by-Printing” approach. Overall, the project seeks to advance DED-arc application in construction by improving efficiency, reducing material usage and enhancing structural performance. Summary Before Johanna Müller left from the TRR after four years, she constructed …
Research Summary Report of A06
Category: Research Summary Report
Laser Powder-Bed Fusion (LPBF) of Steel Elements for Construction – Basics of Design and Mechanical Resilience [19.03.2024] Blankenhagen, Jakob; doctoral researcher; Jakob.blankenhagen@tum.de Technical University of Munich, Chair of Metal Structures Wenzler, David; doctoral researcher; david.wenzler@tum.de Technical University of Munich, Institute for Machine Tools and Industrial Management Summary The project A06 aims to develop a methodology for producing safe and functional structural steel elements for construction using LPBF. This involves integrating complex LPBF parts into large-scale structures. For this purpose, the focus is laid on transferring results and qualification methods from the first funding period to new materials, such as Printdur HSA®. This steel material has been developed specifically for LPBF. And offers higher strength and a …
Research Summary Report of A05
Category: Research Summary Report
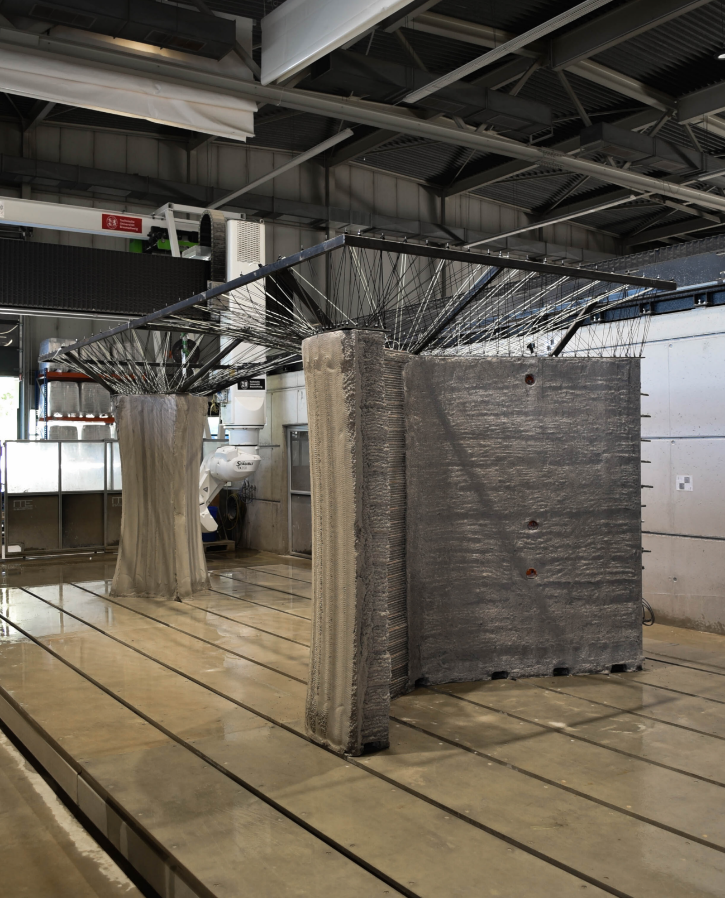
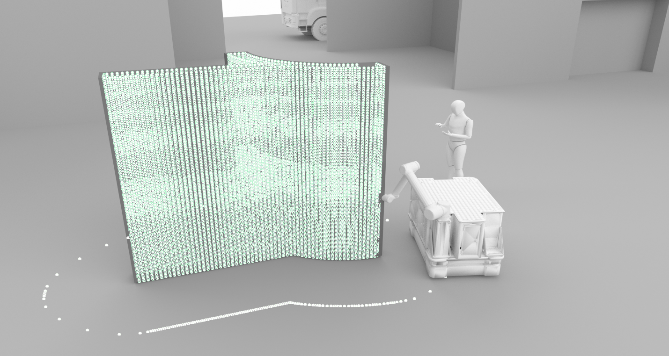
Integration of Individualized Prefabricated Fibre Reinforcement in Additive Manufacturing with Concrete [13.03.2024] Gantner, Stefan; Scientific Researcher, stefan.gantner@tu-bs.de Hack, Norman; Project Leader, n.hack@tu-braunschweig.de Collaboration: Amiri, Fatemeh; Scientific Researcher, fatemeh.amiri@tu-braunschweig.de all: TU BS, Institute of Structural Design (ITE) Main Goal Cement-based additive manufacturing techniques need to be enhanced by the ability of integrating reinforcement, in order to fulfil requirements of construction. This project focuses on non-metallic continuous fibre reinforcement, which is not only corrosion resistant but also flexible in handling. Instead of bending and welding, glass or carbon fibre rovings can be processed robotically by winding onto a support structure. Respective fabrication strategies and their interaction with additive manufacturing of concrete are the main focus of this project. Summary Cement-based …
Research Summary Report of C02
Category: Research Summary Report
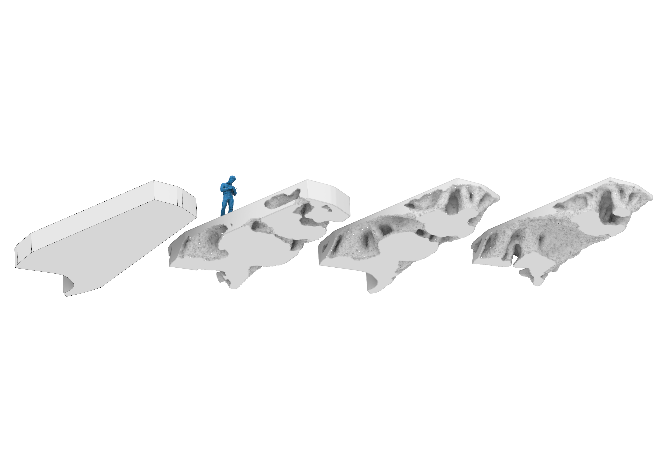
3D Structural Puzzle – Numerical Multi Scale Shape and Topology Optimisation Methods to Additively Manufacture Optimal Structures from Optimised Pieces [01.03.2024] Richter, Christiane, M.Sc.; Doctoral Researcher, christiane.richter@tum.de, TUM, Professorship of Structural Design (SD) Prof. Dr. D’Acunto, Pierluigi; Project Leader, pierluigi.dacunto@tum.de, TUM, Professorship of Structural Design (SD) Main Goal Current building practices often adopt a sequential design approach, where architectural, structural, and fabrication aspects are addressed independently, resulting in excessive material consumption. The CO2 project aims to establish a Holistic Design Framework (HDF) integrating the above-mentioned aspects. Within this framework, additive manufacturing facilitates structural optimization by enabling the production of bespoke geometries for an effective use of material resources. Departing from the conventional sequential approach, the HDF concurrently …
Research Summary Report of A04
Category: Research Summary Report
Integrated Additive Manufacturing Processes for Reinforced Shotcrete 3D Printing (SC3DP) Elements with Precise Surface Quality [23.02.2024] Dörrie, Robin Phd candidate r.doerrie@tu-braunschweig.de Technische Universität Braunschweig ITE Institut für Tragwerksentwurf Main Goal The project aims to fundamentally understand SC3DP technology to manufacture sustainable, multi-objective optimised, reinforced concrete components with precise surface quality and improved building physics via functional integration. It seeks to minimise carbon footprint by exploring varied material strategies, such as reducing cement content and design methods to decrease overall concrete volume. Additionally, it focuses on establishing reliable material and process control, emphasising fresh material laws for printability and durability, real-time monitoring of concrete properties, and component build-up strategies. Integration of large-scale reinforcement enhances structural suitability, while precise surface finishing …
Research Summary Report of B04
Category: Research Summary Report
Process Control and Adaptive Path Planning for Additive Manufacturing Processes Based on Industrial Robots with an Extended Degree of Freedom [07.02.2024] Raatz, Annika; raatz@match.uni-hannover.de LUH, Institute of Assembly Technology and Robotics Lachmayer, Lukas; lachmayer@match.uni-hannover.de LUH, Institute of Assembly Technology and Robotics Heeren, Hauke; heeren@match.uni-hannover.de LUH, Institute of Assembly Technology and Robotics Main Goal The research of project B04 is dedicated to extending the current state-of-the-art path planning and process control algorithms for concrete-based additive manufacturing. The objective is to enable reproducible production of multi-material components utilizing mobile robot systems in motion, known as print-while-driving. Achieving this requires precise localization, considering system dynamics, such as acceleration and jerk limitations, as well as accounting for varying material properties and building installation …
Research Summary Report of C01
Category: Research Summary Report
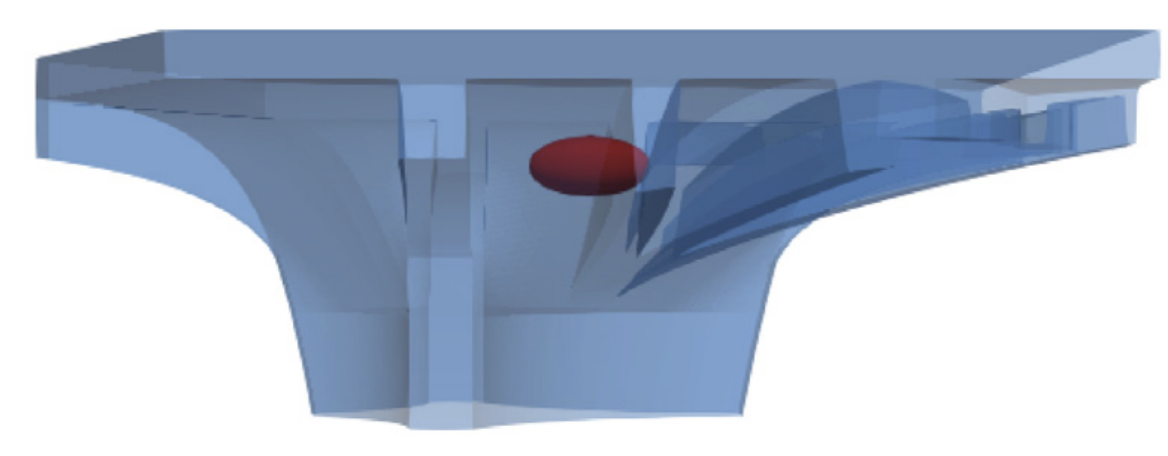
Bridging Scales – From Geometric Part Details to Construction Elements [02.02.2024] Kollmannsberger, Stefan; stefan.kollmannsberger@tum.de TUM, Computational Modeling and Simulation Bürchner, Tim; tim.buerchner@tum.de TUM, Computational Modeling and Simulation Rank, Ernst; ernst.rank@tum.de TUM, Institute for Advanced Study Digital models for Additive Manufacturing (AM) must consider many different geometric scales. The scales range from micrometers up to tens of meters for metal- or concrete-based processes and mutually influence each other. Project C01 aims to develop consistent geometric and computational descriptions for the relevant AM products on all these scales. As-built structures naturally deviate from as-designed structures in geometry, topology, and material properties especially in additive manufacturing. The consequences of such deviations upon the structural behaviour are commonly termed the effect of defect. …
Research Summary Report of A03
Category: Research Summary Report
Extrusion of Near-Nozzle Mixed Concrete – Individually Graded in Density and in Rate of 3D Fibre Reinforcement [1.12.2023] Hechtl, Christian Maximilian, TP editor, m.hechtl@tum.de, TUM, cbm Dr.-Ing. Kränkel, Thomas, PL, thomas.kraenkel@tum.de, TUM, cbm Prof. Dr.-Ing. Gehlen, Christoph, PL, gehlen@tum.de, TUM, cbm The goal of A03 is to establish a concrete extrusion process using a near nozzle mixing (NNM) approach to enable the gradual variation of material properties during printing (gradation). This approach allows for the creation of multifunctional components, such as structures merging both load bearing and thermally insulating zones, by precisely altering material properties as required throughout the printing process. Summary and Current State of Research GRES V1 is a gradation-ready extrusion system that demonstrates the potential …
Research Summary Report of A02
Category: Research Summary Report
Particle-Bed 3D Printing by Selective Cement Paste Intrusion (SPI) – Particle Surface Functionalisation, Particle Synthesis and Integration of WAAM Reinforcement [17.11.2023] Straßer, Alexander, TP editor, alexander.strasser@tum.de, TUM, Chair of Materials Science and Testing Kränkel, Thomas, TP editor, thomas.kraenkel@tum.de, TUM, Chair of Materials Science and Testing Gehlen, Christoph, PL, gehlen@tum.de, TUM, Chair of Materials Science and Testing The goal of A02 is to implement reinforcement by Wire and Arc Additive Manufacturing (WAAM) in concrete elements produced by Selective Paste Intrusion (SPI), see Figure 1. Since the cement paste is applied to the aggregates and must penetrate the cavities between the aggregates by gravity, consistent rheological properties of the cement paste are essential. The welding process with WAAM generates high temperatures …
Research Summary Report of B03
Category: Research Summary Report
Modelling and Simulation of Shotcrete 3D Printing (SC3DP) Based on a Massively Parallel Multi-Phase, Multi-Component Coupled LBM-DEM Approach [10.11.2023] Kutscher (PostDoc), M. Geier (PI), M. Krafczyk (PI) TU Braunschweig, IRMB The primary aim of the project is to understand and quantify the dynamic distribution of material components (fluid, air and particles) and kinetic energy inside the jet of liquid concrete present in the shotcrete process. The information is required as a basis for future optimization of the process with regards to process and material parameters as well as for the prediction of material inhomogeneities. Summary In order to overcome the numerical difficulties arising from sustaining a high-density ratio in the diffuse interface lattice Boltzmann model we developed a new …