Research Summary Report
Research Summary Report of A03
Category: Research Summary Report
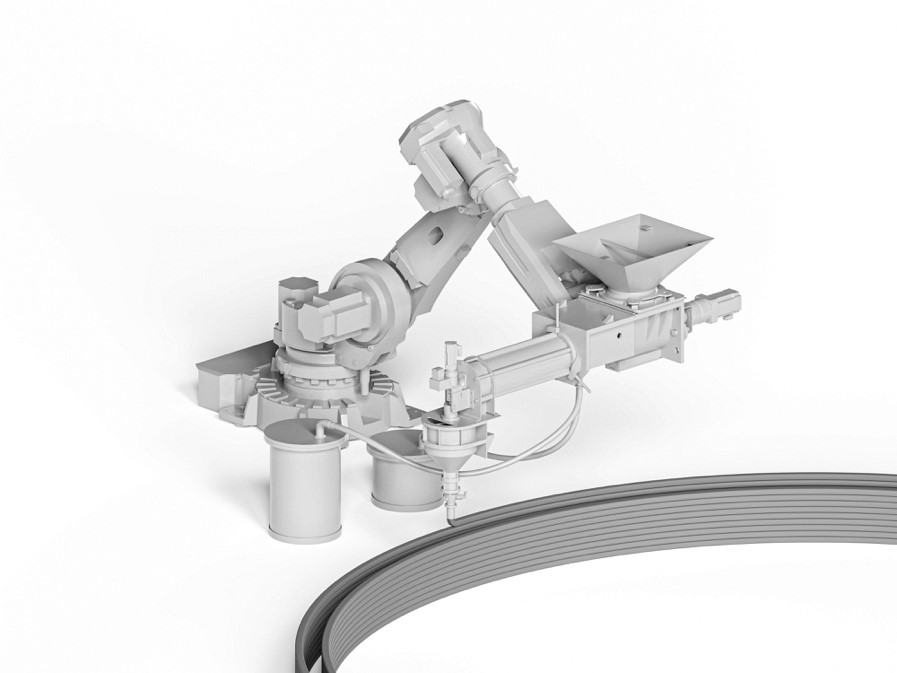
Extrusion of Near-Nozzle Mixed Concrete – Individually Graded in Density and in Rate of 3D Fibre Reinforcement [06.08.2023] M.Sc. Dahlenburg, Maximilian; TP editor, maximilian.dahleburg@tum.de, TUM, Chair of Materials Handling, Material Flow, Logistics Prof. Dr.-Ing. Fottner, Johannes; Project leader, j.fottner@tum.de, TUM, Chair of Materials Handling, Material Flow, Logistics Main Goal The main goal of A03 is to establish a novel concrete extrusion process using a near nozzle mixing (NNM) process to enable the change and non-discrete gradation of material and its properties during printing. With this approach, multi-functional and multi-material parts can be printed, with an overall higher building rate due to a lower workability demand of the process and higher structuration rates of the used materials. Printed parts can thus simultaneously fulfil load-bearing …
Research Summary Report of A01
Category: Research Summary Report
Particle-bed 3D printing by selective cement activation: Particle surface functionalization, particle bed compaction and reinforcement [21.07.2023] Meier, Niklas; Researcher, niklas.meier@tu-braunschweig.de Zetzener, Harald; Leading researcher, h.zetzener@tu-braunschweig.de Kwade, Arno; Project Leader, a.kwade@tu-braunschweig.de all: TU Braunschweig, Institute for particle technology The main goal of our research in project A01 is to improve the mechanical strength and shape accuracy of the printed concrete parts as well as the printing speed. While our work at the iPAT is improving the powder properties the project partner iBMB focuses on the material-process interaction. Summary Previous research has shown, that a higher packing density of the particle bed leads to an increase in compressive strength. On the one side the process parameter during printing e.g. compaction heigt …
Research Summary Report of C04
Category: Research Summary Report
Integrating Digital Design and Additive Manufacturing through BIM-Based Decision Support and Digital Twin Methods [14.07.2023] Li, Chao; doctoral researcher, chao1.li@tum.de Petzold, Frank; PL, petzold@tum.de Technical University of Munich, TUM School of Engineering and Design, Chair of Architectural Informatics The application of Additive Manufacturing (AM) technology requires careful consideration of AM methods‘ boundary conditions. Determining suitable AM methods is critical during the early design stages since changes in design are costly when design becomes more mature. To this end, WP1 of sub-project C04 aims to develop a design decision support system (DDSS) that assists architects and engineers in choosing feasible AM methods for BIM-based design. To achieve this, a knowledge base is formalized, which consists of information on different AM …
Research Summary Report of A04
Category: Research Summary Report
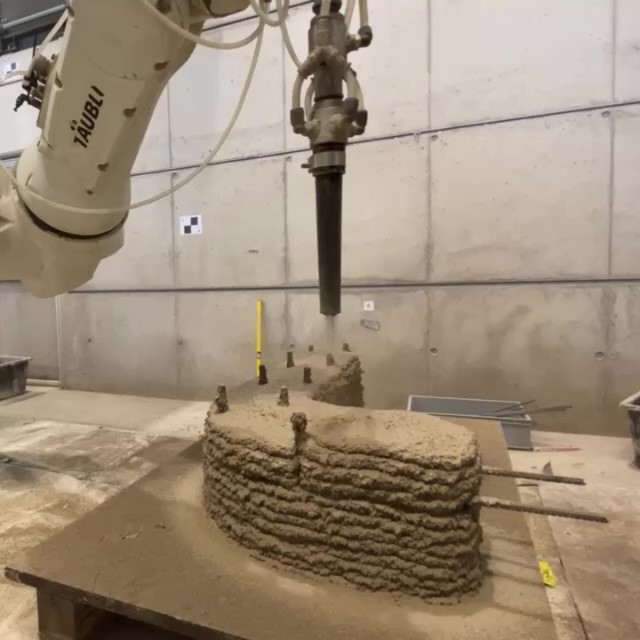
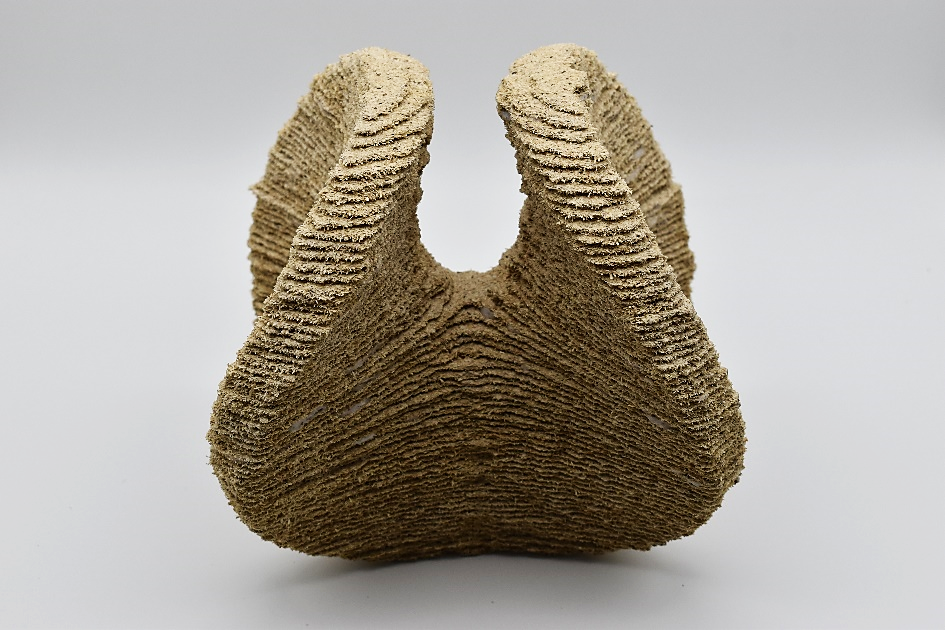
Integrated Additive Manufacturing Processes for Reinforced Shotcrete 3D Printing (SC3DP) Elements with Precise Surface Quality [07.07.2023] Rudolph, Jennifer; doctoral researcher, j.rudolph@ibmb.tu-bs.de Freund, Niklas; doctoral researcher, n.freund@ibmb.tu-bs.de Lowke, Dirk; project leader, d.lowke@ibmb.tu-bs.de all: TU Braunschweig, Institute of Building Materials and Concrete Construction and Fire Safety (iBMB) Summary Project A04 investigates cooperative Additive Manufacturing (AM) processes based on Shotcrete 3D Printing (SC3DP) for the production of material-efficient, force-optimised, reinforced, load-bearing concrete components with precise surface quality and high geometric precision. The goal is to produce large-scale concrete elements using significantly lower amounts of reinforcement and concrete as compared to standard concrete construction principles. Current state of research Reinforcement integration is one of the key topics of current research in the field …
Research Summary Report of C05
Category: Research Summary Report
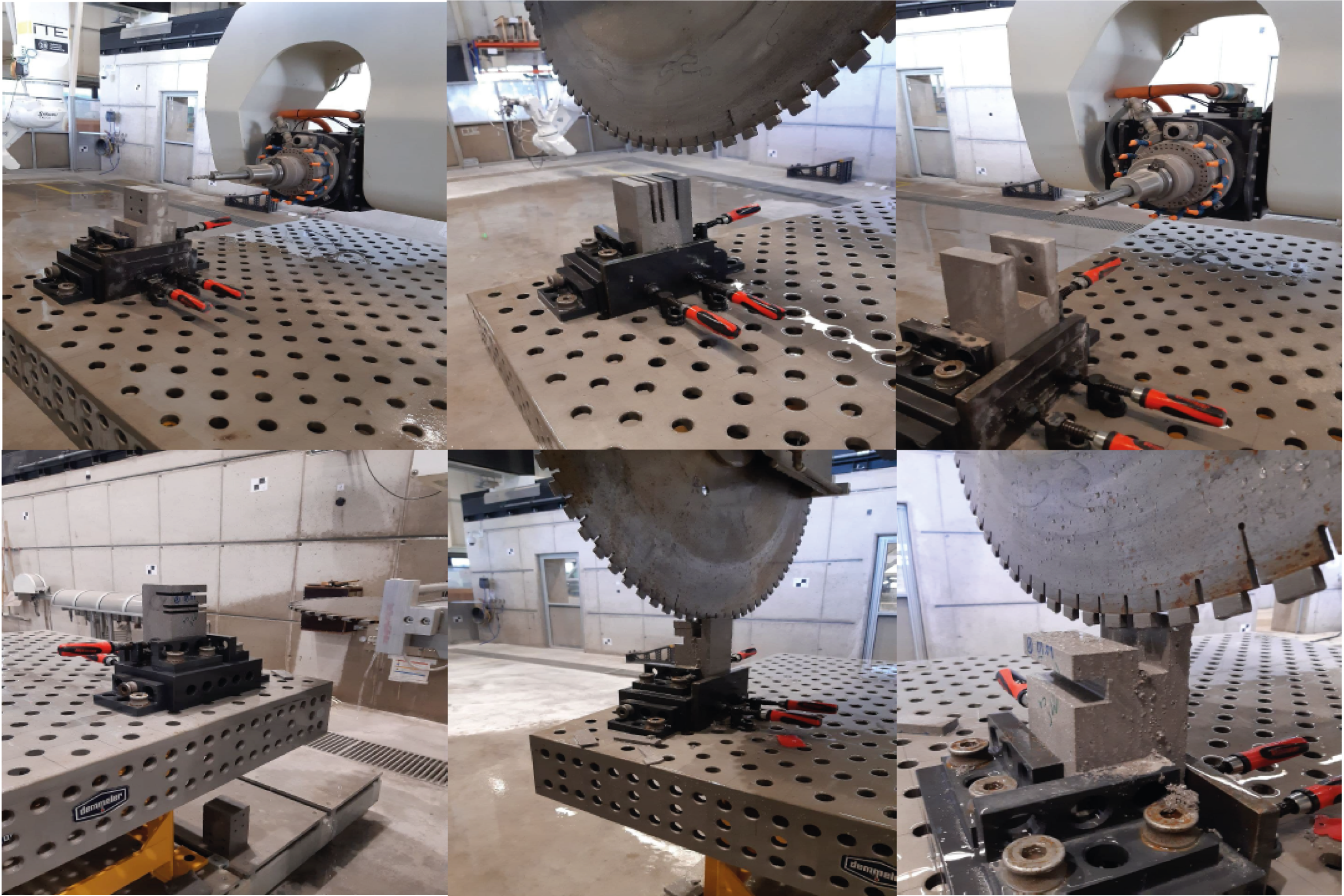
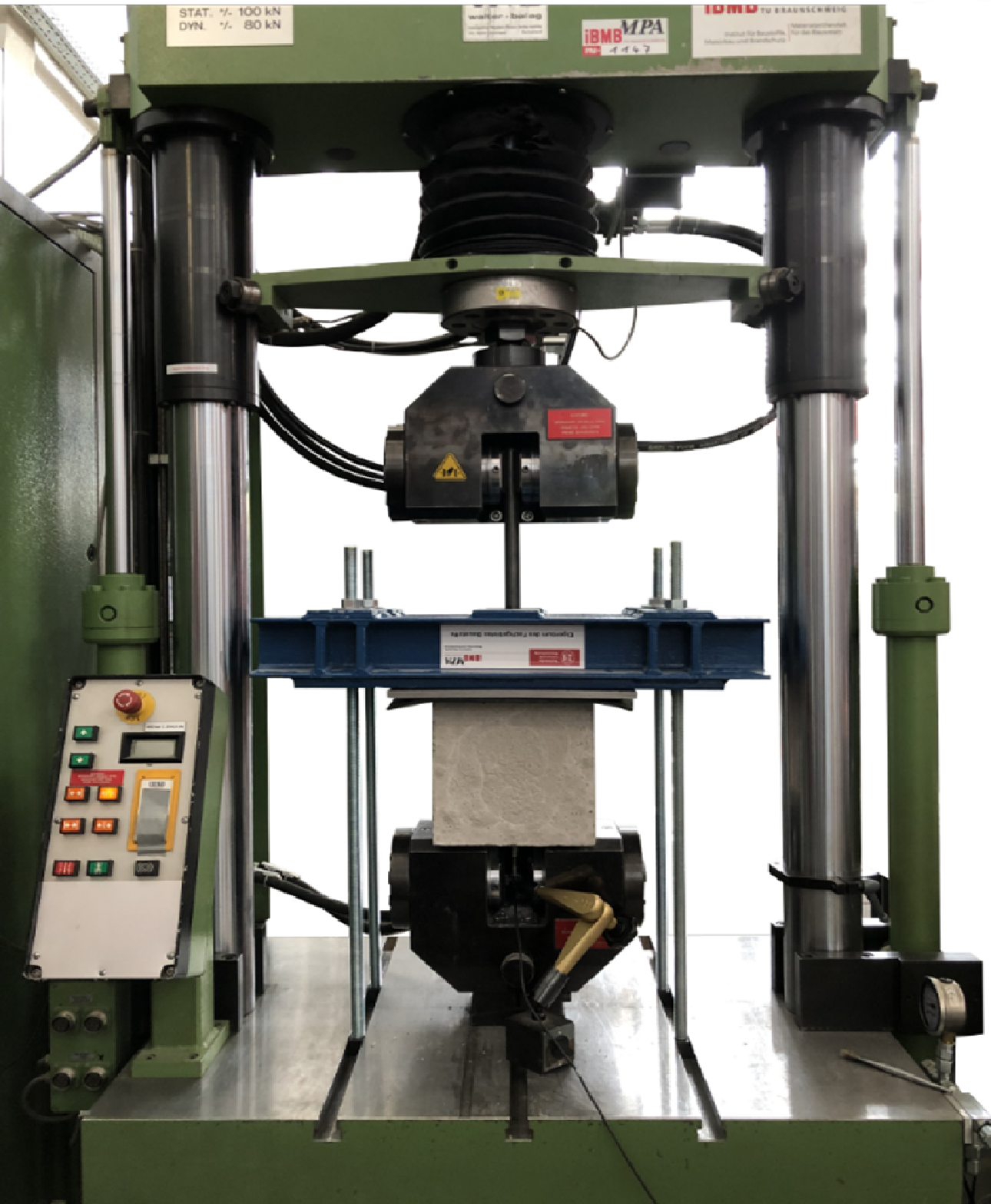
Jointing Principles for Combination of Concrete Elements Produced by Different Additive Manufacturing Processes [19.05.2023] Empelmann, Martin; Project Leader, m.empelmann@ibmb.tu-bs.de Lanwer, Jan-Paul; Doctoral Researcher, j.lanwer@ibmb.tu-bs.de TU Braunschweig, Institute of Building Materials, Concrete Construction and Fire Safety (iBMB), Division of Concrete Construction The C05 project deals with the design, the manufacturing and the calculation of suitable connections for segmental AM-components. Principally, the connections should be based on the dry joint approach manufactured by subtractive post-processing. Alternatively, they could be also directly printed with the segment. The joint design should be efficient in production, apply for all AM-processes (SC3DP, Extrusion, Particle bed) and bear combined normal and shear stresses. Summary The selected joint profiles from the so-called joint catalogue (see Reference) …
Research Summary Report of C06
Category: Research Summary Report
Integration of Additive Manufacturing in the Construction Process [16.06.2023] Placzek, Gerrit; Doctoral researcher, g.placzek@tu-braunschweig.de, TU Braunschweig, IBB The integration of additive manufacturing into construction requires an interdisciplinary approach. The different competences of the team – digital fabrication in architecture (Hack), geodesy and photogrammetry (Gerke) and construction management (Schwerdtner) – lead to research from diverse perspectives on the various scalar levels of construction to be viewed holistically: component, building and industry scale. Within Subproject C06, our goal is to create a continuous digital and lean-based process chain from design (using BIM method) to fabrication (using AM method). Based on process models und strategic decisions, we investigate construction processes and how to change them into a construction industry 4.0. Summary In …
Research Summary Report of A08
Category: Research Summary Report
Structural Timber by Individual Layer Fabrication (ILF) [09.06.2023] Buschmann, Birger; Doctoral researcher, birger.buschmann@tum.de, Talke, Daniel; Doctoral researcher, talke@tum.de Henke, Klaudius; Project leader, henke@tum.de Technical University of Munich, Chair of Timber Structures and Building Construction Summary The main goal of the project ‘A08 -Structural Timber by Individual Layer Fabrication (ILF)’ is to develop a process to additively manufacture large-scale, wood composite objects with a maximum content of wood material and strength values suited for applications in construction. In the course of the project multiple process variants and material combinations are explored. For this, the necessary machinery is developed in iterative steps and the mechanical properties of the resulting objects as well as the geometric capacity of the processes are investigated. Finally, …
Research Summary Report of A07
Category: Research Summary Report
Wire and Arc Additive Manufacturing (WAAM) of Complex Individualized Steel Components [26.05.2023] Müller, Johanna; doctoral researcher, johanna.mueller@mb.tu-chemnitz.de TU Chemnitz, Institute of Joining and Assembly The aim of TP A07 is the design, the manufacturing and the testing of complex individualized steel components by means of WAAM. That contains the fundamental investigation of design and the design process for WAAM components. For the manufacturing of steel components by WAAM, stable and reliable processes for basic geometries are qualified and based on that, case study demonstrators for the identification of manufacturing constraints are fabricated. Furthermore, a novel approach for material and component testing is developed to identify local material and component properties. Summary The aim of WG Hensel within the …
Research Summary Report of A06
Category: Research Summary Report
Laser Powder-Bed Fusion (LPBF) of Steel Elements for Construction – Basics of Design and Mechanical Resilience. [12.05.2023] Diller, Johannes; Doctoral researcher; johannes.diller@tum.de, Siebert, Dorina; Doctoral researcher; dorina.siebert@tum.de Technical University of Munich, Chair of Metal Structures Wenzler, David; Doctoral researcher; david.wenzler@tum.de Technical University of Munich, Institute for Machine Tools and Industrial Management Summary The project A06 aims to explore and evaluate the factors influencing the manufacturing of safe and durable structural steel elements by Powder Bed Fusion of Metals using a Laser Beam (PBF-LB/M). Thereby, the PBF-LB/M process, the post-treatment, and the geometrical aspects in terms of microstructure and mechanical properties were investigated and correlations determined. In the first funding period, it is focused on analyzing small-scale specimens …
Research Summary Report of A04
Category: Research Summary Report
Integrated Additive Manufacturing Processes for Reinforced Shotcrete 3D Printing (SC3DP) Elements with Precise Surface Quality [21.03.2023] Robin Dörrie; phd candidate, r.doerrie@tu-braunschweig.de, Technische Universität Braunschweig, Institute of Structural Design Main goal Within this project, basic research on various Shotcrete 3D Printing (SC3DP) strategies, materials, tools and methods will be conducted with regard to enhanced material and process control, reinforcement integration, surface quality and automation. To that end, different reinforcement materials in combination with suitable reinforcement manufacturing and integration concepts will be investigated based on force-flow oriented reinforcement alignment. Besides, design strategies as well as material and process control will be researched in detail. Furthermore, tools and strategies for precise control of the surface quality and geometric resolution of SC3DP elements …
Research Summary Report of B04
Category: Research Summary Report
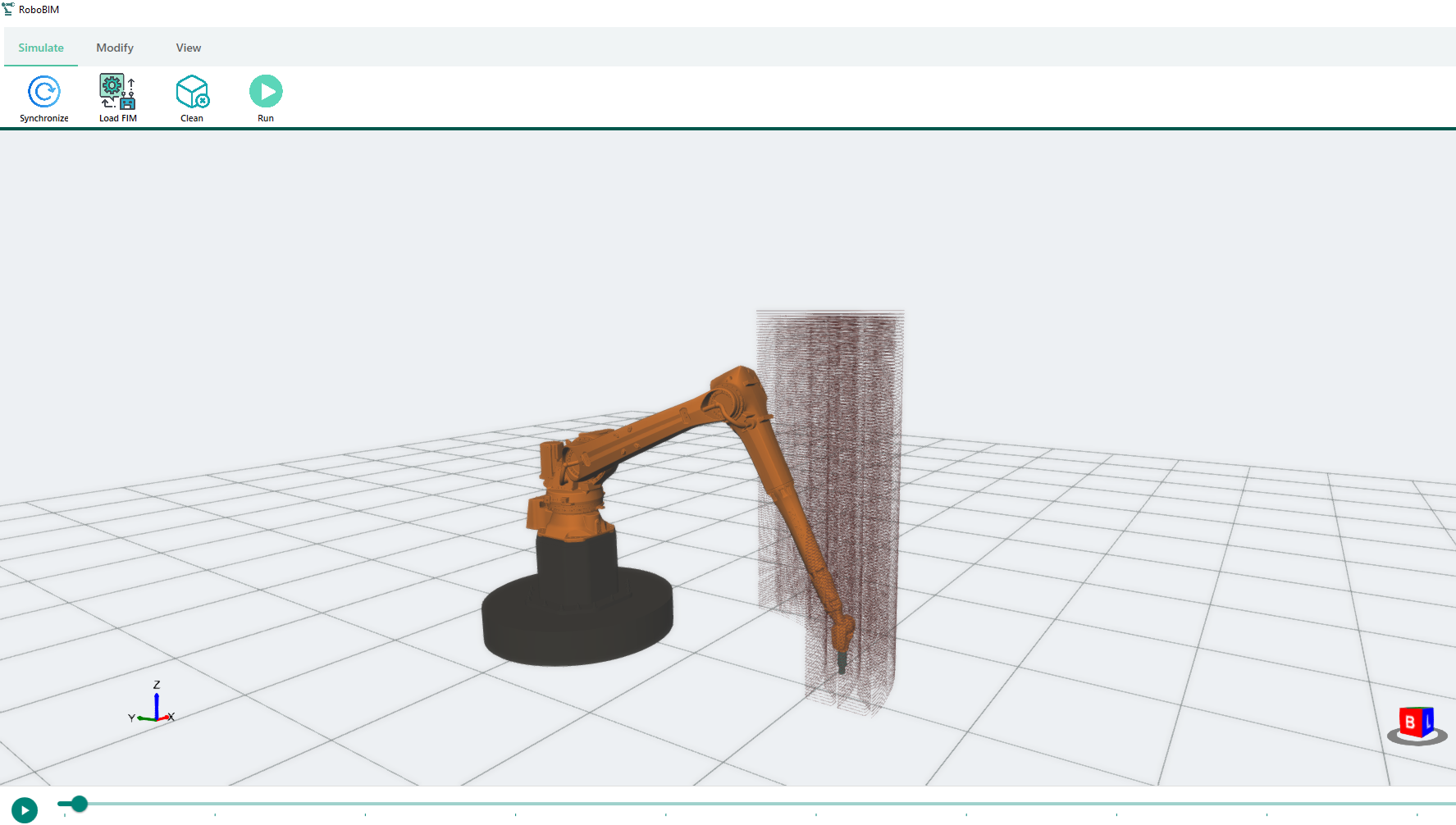
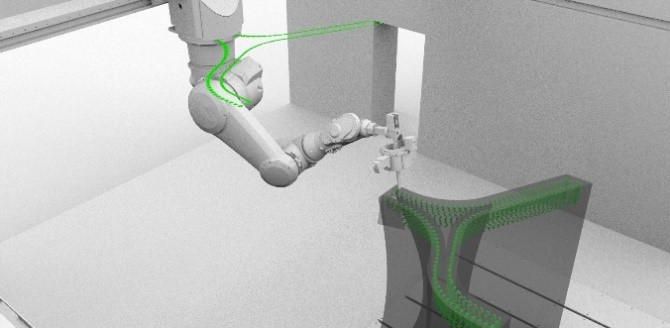
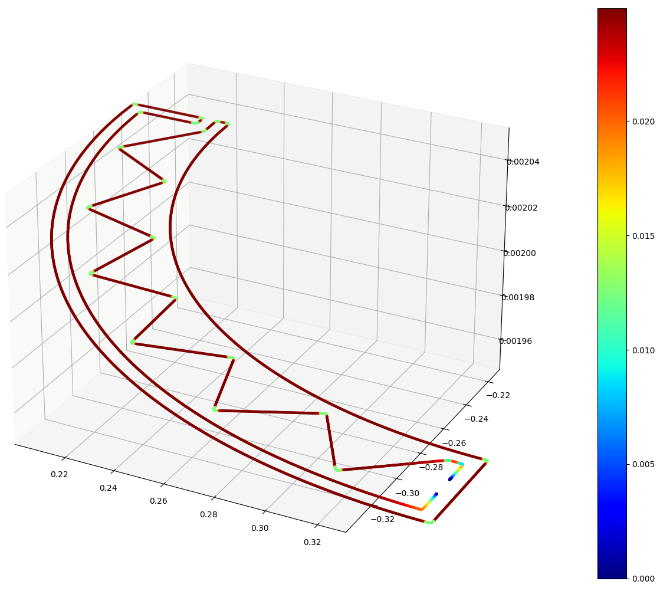
Process Control and Adaptive Path Planning for Additive Manufacturing Processes Based on Industrial Robots with an Extended Degree of Freedom [14.04.2023] Lachmayer, Lukas; Doctoral researcher, lachmayer@match.uni-hannover.de, Leibniz Universität Hannover, Institute of Assembly Technology (match) Main goal The main objective of project B04 is to achieve repeatability in concrete-based robot-guided additive manufacturing processes, which is crucial for enhancing productivity, sustainability and safety in the construction industry. While additive manufacturing processes offer several benefits such as reduced workload, decreased material usage, and minimized manual labor, the time- and environment-dependent material properties of fresh concrete can lead to unpredictable outcomes and component collapses. By achieving stability and accuracy in these processes, we can ensure consistent and predictable results, thereby increasing minimizing the …
Research Summary Report of A03
Category: Research Summary Report
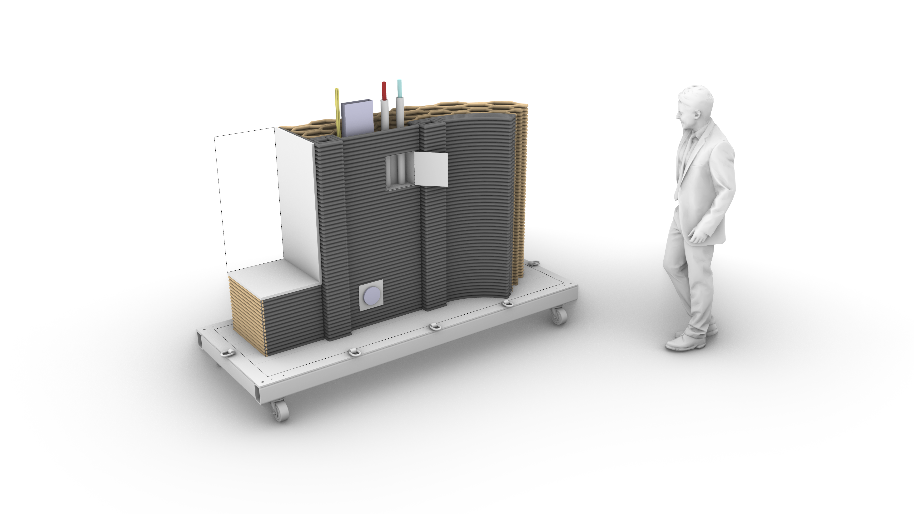
Extrusion of Near-Nozzle Mixed Concrete –Individually Graded in Density and in Rate of 3D Fibre Reinforcement [07.04.2023] Hechtl, Christian Maximilian, TP editor, m.hechtl@tum.de, TUM, Chair of Materials Science and Testing (cbm) Dr.-Ing. Kränkel, Thomas, PL, thomas.kraenkel@tum.de, TUM, cbm Prof. Dr.-Ing. Gehlen, Christoph, PL, gehlen@tum.de, TUM, cbm Main goal The goal of A03 is to establish a concrete extrusion process using a near-nozzle mixing (NNM) approach to enable a quick change of material properties during printing (gradation). This approach allows for the creation of multifunctional components, such as combined load-bearing and thermally insulating structures, by precisely altering material properties as required throughout the printing process. Summary and current state of research GRES V1 is a gradation-capable extrusion system that demonstrates …
Research Summary Report of A02
Category: Research Summary Report
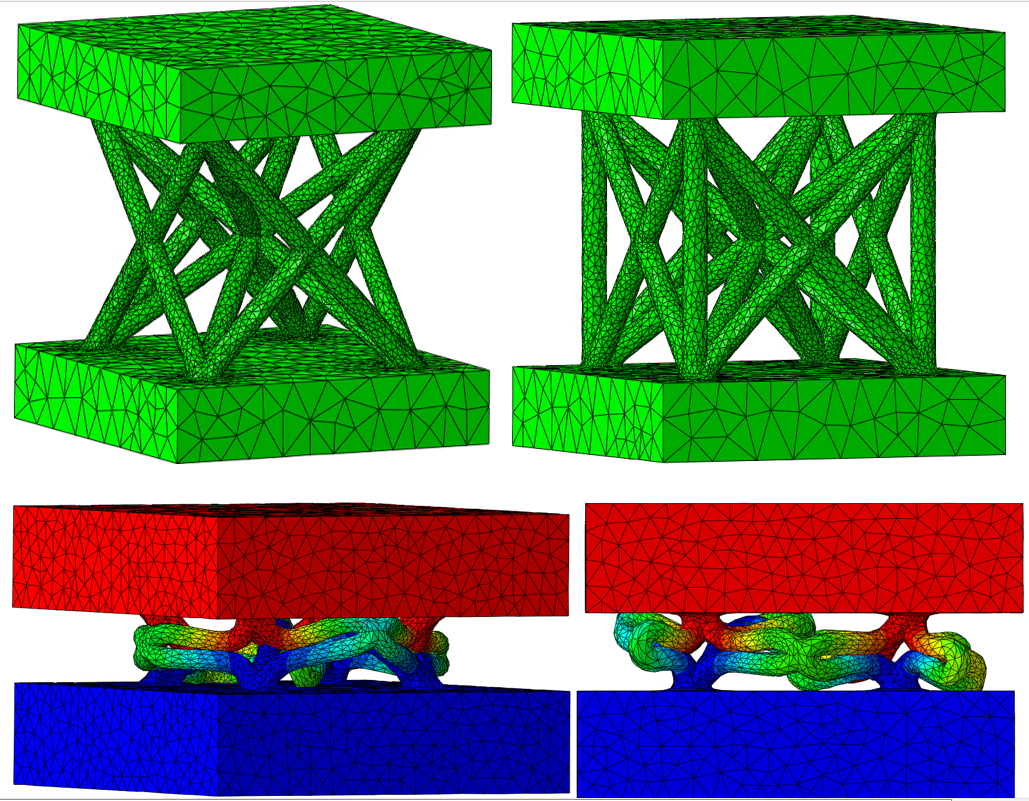
Particle-Bed 3D Printing by Selective Cement Paste Intrusion (SPI) – Particle Surface Functionalisation, Particle Synthesis and Integration of WAAM Reinforcement [24.03.2023] Straßer, Alexander, TP editor, alexander.strasser@tum.de, TUM, Chair of Materials Science and Testing Kränkel, Thomas, TP editor, thomas.kraenkel@tum.de, TUM, Chair of Materials Science and Testing Gehlen, Christoph, PL, gehlen@tum.de, TUM, Chair of Materials Science and Testing Main goal The goal of A02 is to implement reinforcement by Wire and Arc Additive Manufacturing (WAAM) in concrete elements produced by Selective Paste Intrusion (SPI), see Figure 1. Since the cement paste is applied to the aggregates and must penetrate the cavities between the aggregates by gravity, consistent rheological properties of the cement paste are essential. The welding process with WAAM generates …
Research Summary Report of A01
Category: Research Summary Report
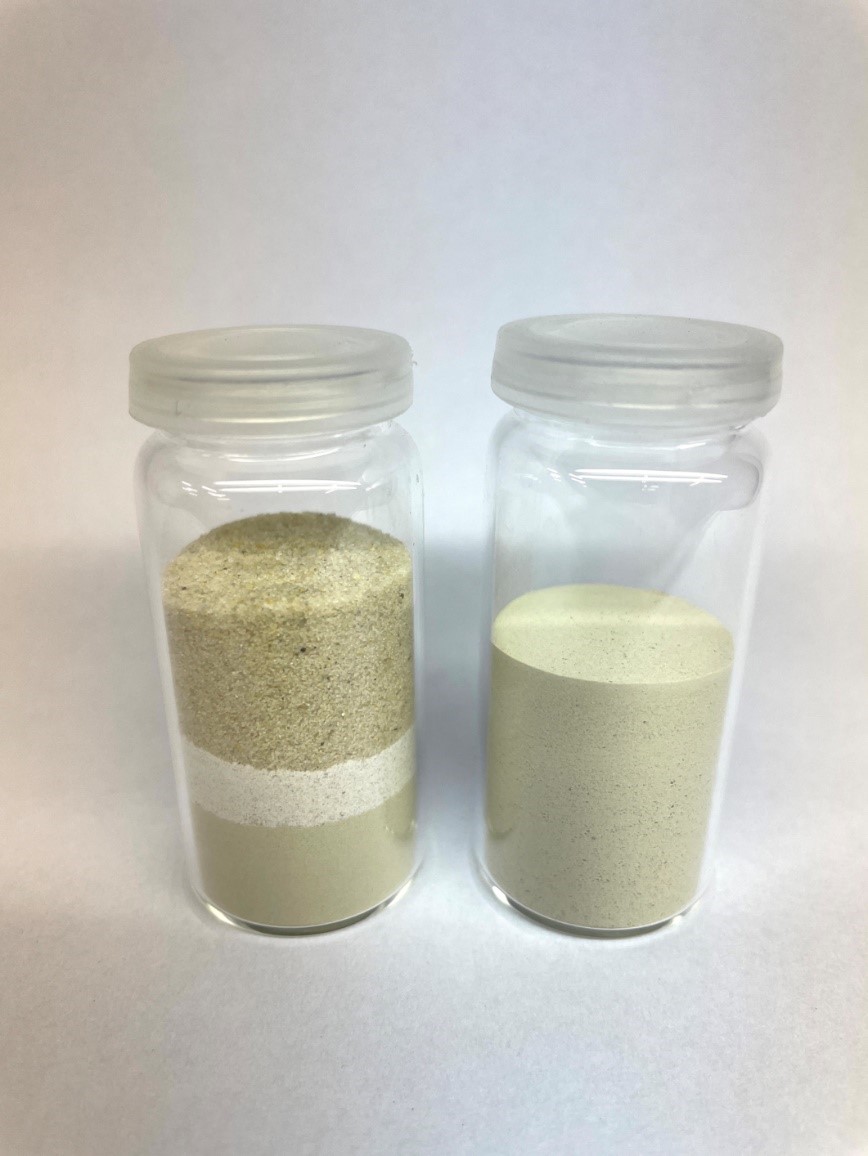
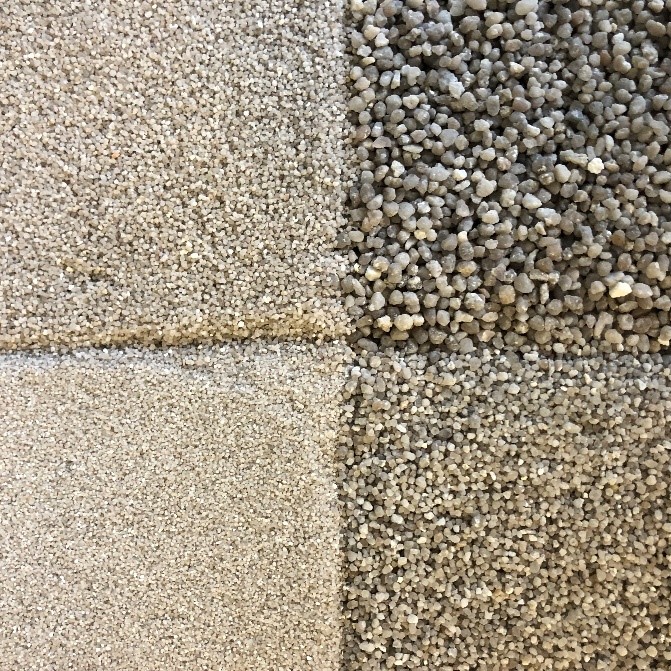
Particle-Bed 3D Printing by Selective Cement Activation (SCA) – Particle Surface Functionalisation, Particle-Bed Compaction and Reinforcement Implementation [10.03.2023] Herding, Friedrich; Researcher, f.herding@ibmb.tu-bs.de Mai, Inka; Researcher, mai@tu-berlin.de Lowke, Dirk; Project leader, d.lowke@ibmb.tu-bs.de TU Braunschweig, Institute of Building Materials, Concrete Construction and Fire Safety (iBMB) The main objective of our research is to understand the material-process interactions in particle-bed 3D printing (PB3DP) by Selective Cement Activation (SCA) in order to produce concrete elements with high mechanical strength and geometric precision. Besides, we are also investigating different ways of reinforcement integration, which is crucial for the manufacturing of load-bearing building components. Summary In particle-bed 3D printing by Selective Cement Activation the particle-bed consists mainly of a mixture of sand and …
Research Summary Report of C05
Category: Research Summary Report
Jointing Principles for Combination of Concrete Elements Produced by Different Additive Manufacturing Processes [24.03.2023] Prof. Dr. Martin Empelmann (iBMB) Prof. Dr. Harald Kloft (ITE) Abtin Baghdadi, a.baghdadi@tu-braunschweig.de Jan-Paul Lanwer, Hendrik Weigel (iBMB) The Technical University of Braunschweig, Institute of Structural Design (ITE) Institute of Building Materials, Concrete Construction and Fire Safety (iBMB) This collaborative project between ITE and iBMB (Concrete-Construction Division) focuses on investigating the combination of different additively manufactured elements using subtractive robotic processes. The primary objective of this project is to examine the jointing principle to determine the execution process and the load-bearing capacity of concrete joints, utilizing several concrete printing techniques for prefabricated structures. Specifically, the research in C05 explores the potential application of post-processing …
Research Summary Report of B03
Category: Research Summary Report
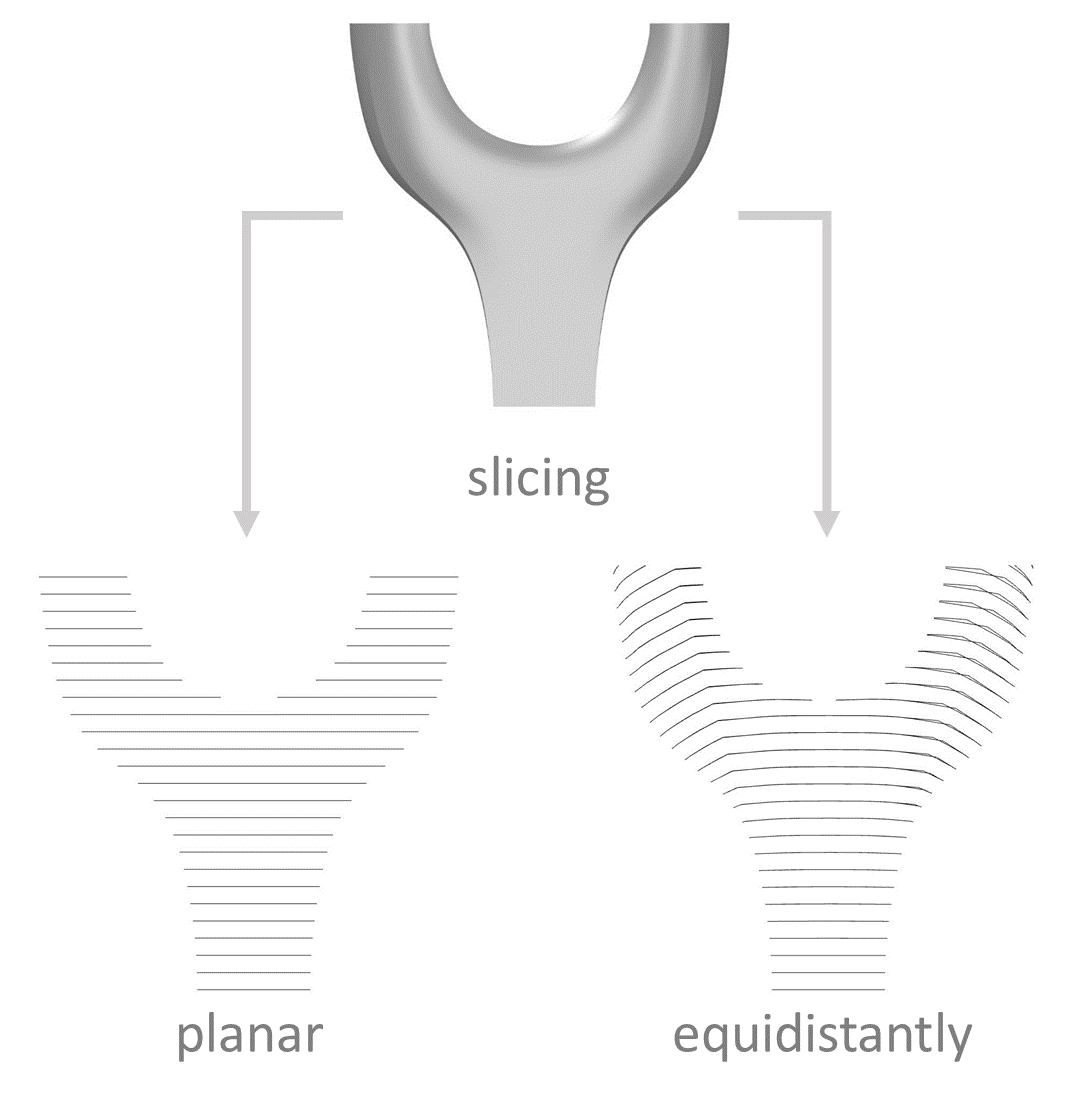
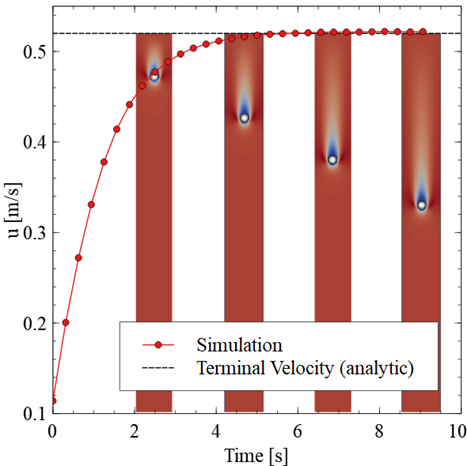
Modelling and Simulation of Shotcrete 3D Printing (SC3DP) Based on a Massively Parallel Multi-Phase, Multi-Component Coupled LBM-DEM Approach [17.03.2023] K. Kutscher (PostDoc), kutscher@irmb.tu-bs.de M. Geier (PI), geier@irmb.tu-bs.de M. Krafczyk (PI), kraft@irmb.tu-bs.de TU Braunschweig, IRMB The primary aim of the project is to understand and quantify the dynamic distribution of material components (fluid, air and particles) and kinetic energy inside the jet of liquid concrete present in the shotcrete process. The information is required as a basis for future optimization of the process with regards to process and material parameters as well as for the prediction of material inhomogeneities. Summary For the modeling of the shotcrete process, the project currently proceeds with the development of several model components. The coupling …
Research Summary Report of C04
Category: Research Summary Report
Integrating Digital Design and Additive Manufacturing through BIM-Based Decision Support and Digital Twin Methods [17.02.2023] Borrmann, André, Project leader,andre.borrmann@tum.de, Slepicka, Martin, Researcher,martin.slepicka@tum.de, Technical University of Munich,Chair of Computational Modeling and Simulation Summary Computer Aided Manufacturing (CAM) methods, such as Additive Manufacturing (AM), are becoming increasingly popular in the construction industry since they offer more geometrical freedom than conventional methods. However, more complex data preparation is required for these methods and thus they have been considered separately from digital design so far. To increase the usefulness of AM for the industry, this project aims to integrate AM methods into the digital design methodology BIM. To achieve this, a framework is being implemented that acts as an intermediate layer between design …
Research Summary Report of A02
Category: Research Summary Report
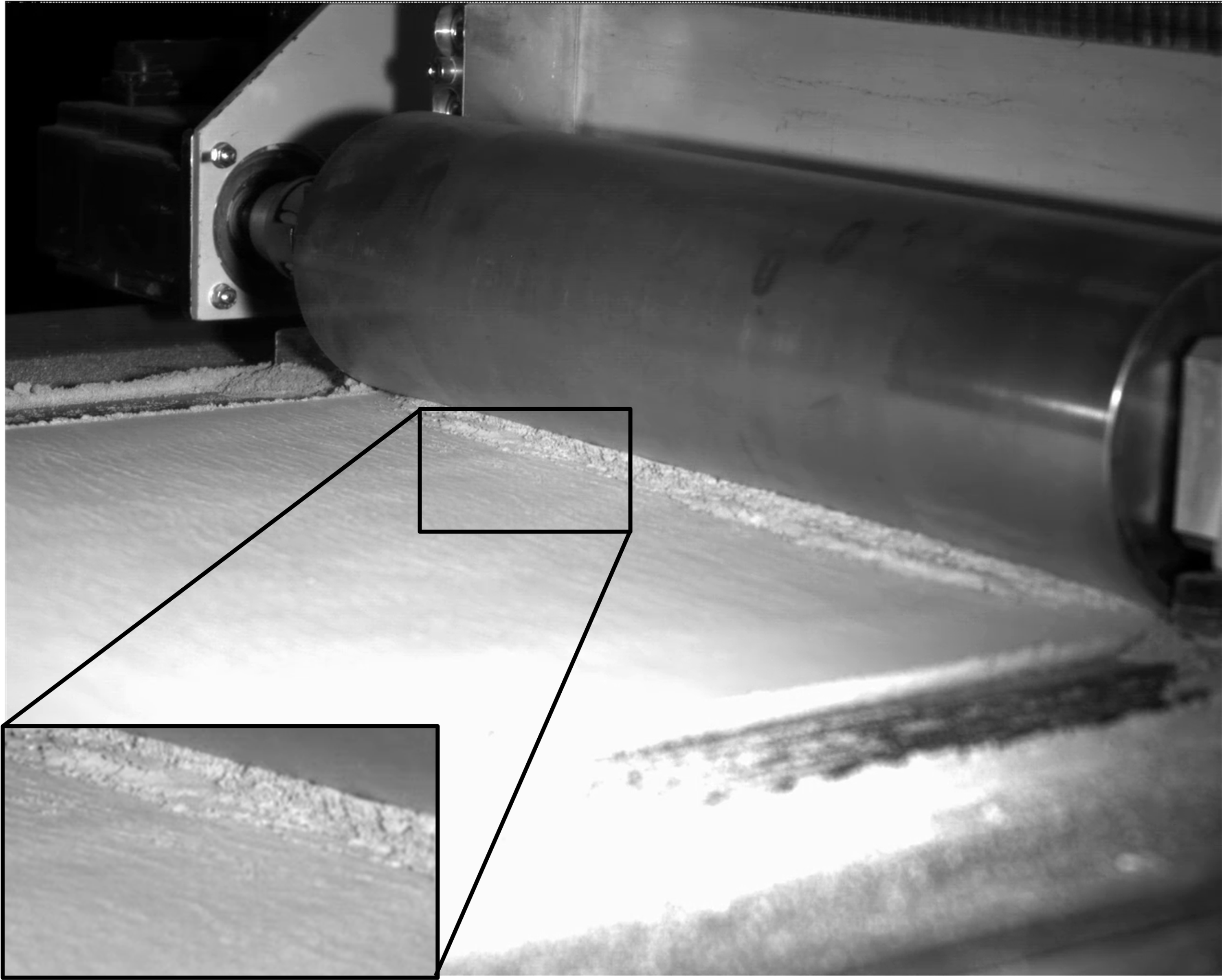
Particle-Bed 3D Printing by Selective Cement Paste Intrusion (SPI) – Particle Surface Functionalisation, Particle Synthesis and Integration of WAAM Reinforcement [10.02.2023] Hamilton, Leigh Duncan; Researcher; Leigh-Duncan.Hamilton@tu-braunschweig.de Zetzener, Harald; Leading researcher; H.Zetzener@tu-braunschweig.de Kwade, Arno; Project leader; A.Kwade@tu-braunschweig.de All: TU Braunschweig, Institute for Particle Technology Our main goal within project A02 is to unite two additive manufacturing (AM) processes, thereby, creating a hybrid AM process for structural concrete. The foundation of A02 is formed around the concrete 3D printing process Selective Paste Intrusion (SPI). SPI creates components in layers by first spreading coarse aggregates (usually quartz) on a surface or previous layer. Subsequently, the cement slurry is applied onto designated areas, where it fills void volumes between aggregate particles. The second …
Research Summary Report of A04
Category: Research Summary Report
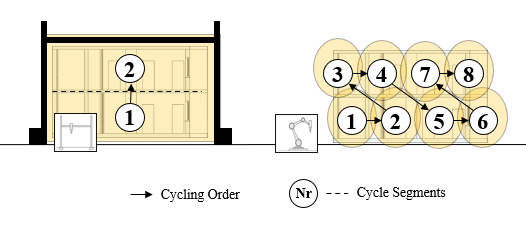
Integrated Additive Manufacturing Processes for Reinforced Shotcrete 3D Printing (SC3DP) Elements with Precise Surface Quality [20.01.2023] David, Martin; Doctoral Researcher, m.david@tu-braunschweig.de, TU Braunschweig, Institute for Machine Tools and Production Technology (IWF) Summary Project A04 aims to investigate cooperative Additive Manufacturing (AM) processes based on Shotcrete 3D Printing (SC3DP) for the production of material-efficient, force-optimised, reinforced, load-bearing concrete components with precise surface quality and geometrical precision. The goal is to produce large-scale concrete elements using significantly lower amounts of reinforcement and concrete as compared to standard concrete construction principles. Hereby, different robot guided end effectors are subject for research in a flexible and automated process chain. Current state of research Currently, there are two focal points in the research …
Research Summary Report of A05
Category: Research Summary Report
Integration of Individualized Prefabricated Fibre Reinforcement in Additive Manufacturing with Concrete [03.02.2023] Rothe, Tom; Doctoral researcher, t.rothe@tu-braunschweig.de, Hühne, Christian; Project Leader, Christian.Huehne@tu-braunschweig.de, TU Braunschweig, Institute for Mechanics and Adaptronics (IMA) The individual integration of fibre reinforcement into large concrete components produced by Additive Manufacturing allows new design freedoms and reduces concrete consumption due to reduced concrete cover. The project A05 develops strategies to integrate freely formable reinforcement strands for the different AM processes. For doing so, a Dynamic Winding Machine is developed and constantly updated. This machine is used to consolidate and impregnate a primary fibre strand and wind a secondary yarn around it as a surface structuring. Thus, these reinforcement strands can be adapted for different purposes and …