Research Summary Report
Research Summary Report of A07
Category: Research Summary Report
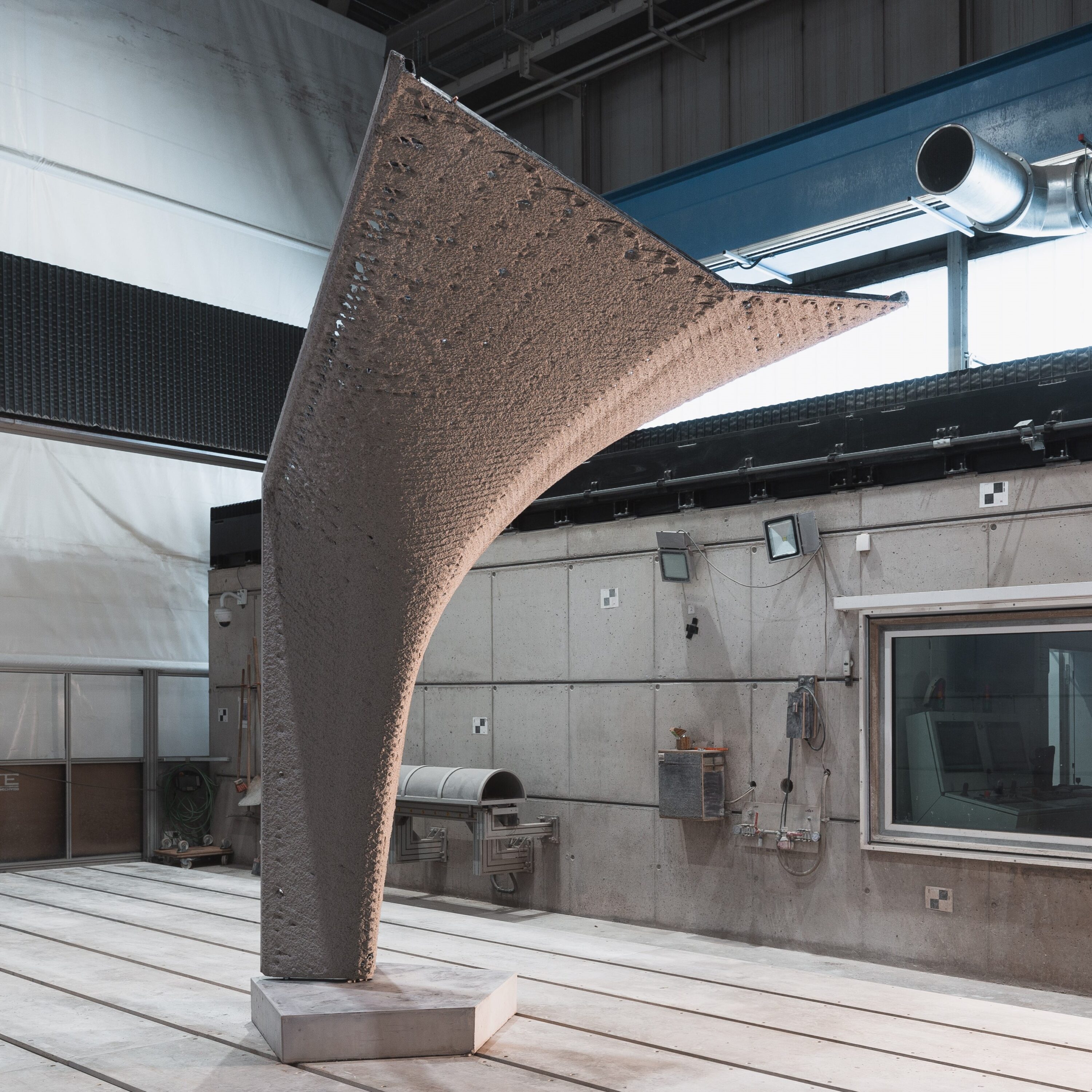
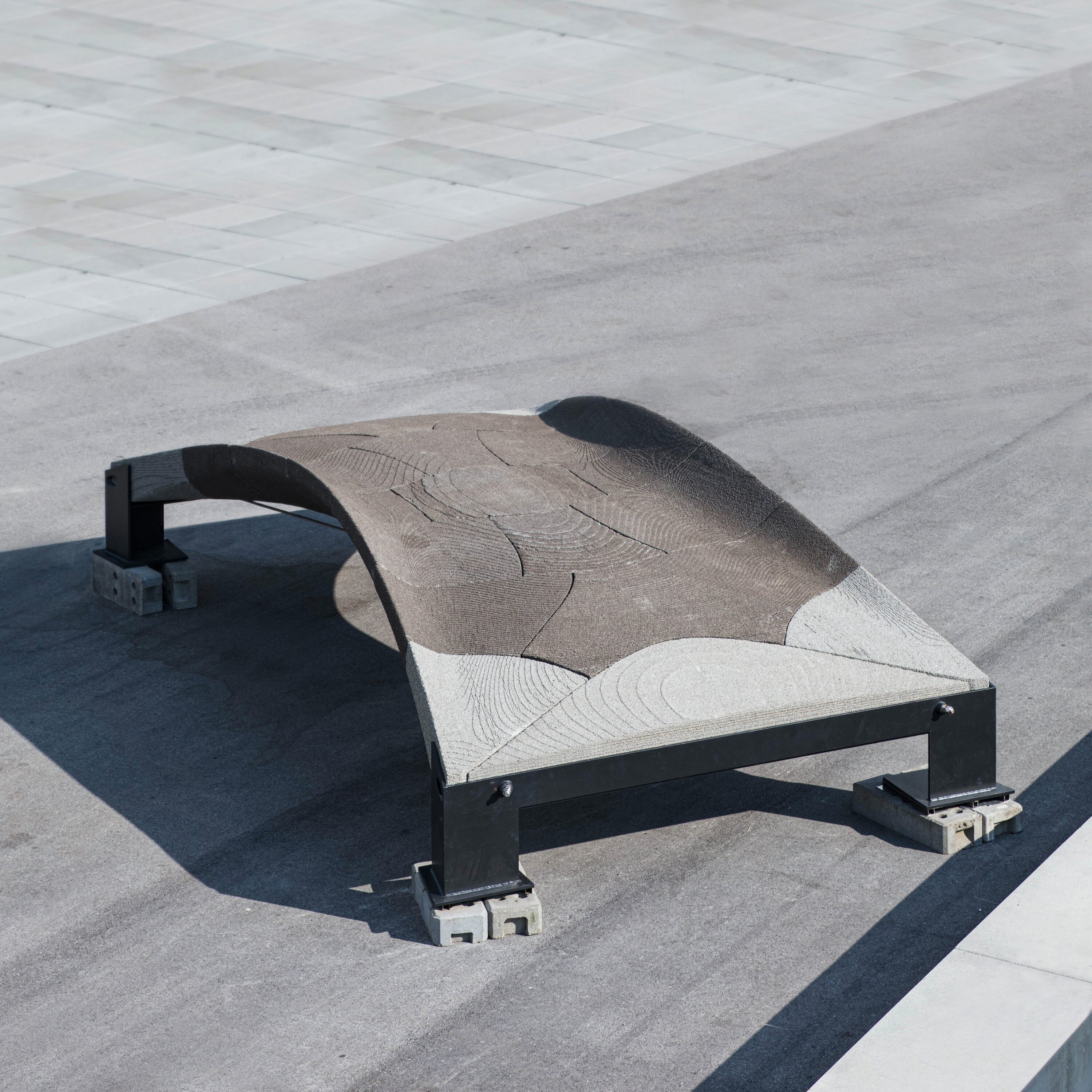
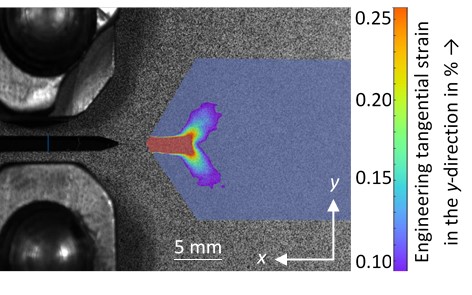
Wire Arc Additive Manufacturing (WAAM) of High Strength and Individualized Steel Components [05.04.2024] Jurke, Florian; Research Assistant, florian.jurke@mb.tu-chemnitz.de Kevin Hoefer, Research Assistant, kevin.hoefer@mb.tu-chemnitz.de Hensel, Jonas; Project Leader, jonas.hensel@mb.tu-chemnitz.de Main Goal A07 focuses on understanding the interaction between DED-arc components and existing structures, developing load-specific strengthening solutions and designing welding strategies. A design framework will incorporate manufacturing constraints and optimization tools for efficient structural components. Additionally, online-process control will be implemented to compensate deviations in component geometry and temperature within the process, using a “Learning-by-Printing” approach. Overall, the project seeks to advance DED-arc application in construction by improving efficiency, reducing material usage and enhancing structural performance. Summary Before Johanna Müller left from the TRR after four years, she constructed …
Research Summary Report of A06
Category: Research Summary Report
Laser Powder-Bed Fusion (LPBF) of Steel Elements for Construction – Basics of Design and Mechanical Resilience [19.03.2024] Blankenhagen, Jakob; doctoral researcher; Jakob.blankenhagen@tum.de Technical University of Munich, Chair of Metal Structures Wenzler, David; doctoral researcher; david.wenzler@tum.de Technical University of Munich, Institute for Machine Tools and Industrial Management Summary The project A06 aims to develop a methodology for producing safe and functional structural steel elements for construction using LPBF. This involves integrating complex LPBF parts into large-scale structures. For this purpose, the focus is laid on transferring results and qualification methods from the first funding period to new materials, such as Printdur HSA®. This steel material has been developed specifically for LPBF. And offers higher strength and a …
Research Summary Report of A05
Category: Research Summary Report
Integration of Individualized Prefabricated Fibre Reinforcement in Additive Manufacturing with Concrete [13.03.2024] Gantner, Stefan; Scientific Researcher, stefan.gantner@tu-bs.de Hack, Norman; Project Leader, n.hack@tu-braunschweig.de Collaboration: Amiri, Fatemeh; Scientific Researcher, fatemeh.amiri@tu-braunschweig.de all: TU BS, Institute of Structural Design (ITE) Main Goal Cement-based additive manufacturing techniques need to be enhanced by the ability of integrating reinforcement, in order to fulfil requirements of construction. This project focuses on non-metallic continuous fibre reinforcement, which is not only corrosion resistant but also flexible in handling. Instead of bending and welding, glass or carbon fibre rovings can be processed robotically by winding onto a support structure. Respective fabrication strategies and their interaction with additive manufacturing of concrete are the main focus of this project. Summary Cement-based …
Research Summary Report of C02
Category: Research Summary Report
3D Structural Puzzle – Numerical Multi Scale Shape and Topology Optimisation Methods to Additively Manufacture Optimal Structures from Optimised Pieces [01.03.2024] Richter, Christiane, M.Sc.; Doctoral Researcher, christiane.richter@tum.de, TUM, Professorship of Structural Design (SD) Prof. Dr. D’Acunto, Pierluigi; Project Leader, pierluigi.dacunto@tum.de, TUM, Professorship of Structural Design (SD) Main Goal Current building practices often adopt a sequential design approach, where architectural, structural, and fabrication aspects are addressed independently, resulting in excessive material consumption. The CO2 project aims to establish a Holistic Design Framework (HDF) integrating the above-mentioned aspects. Within this framework, additive manufacturing facilitates structural optimization by enabling the production of bespoke geometries for an effective use of material resources. Departing from the conventional sequential approach, the HDF concurrently …
Research Summary Report of A04
Category: Research Summary Report
Integrated Additive Manufacturing Processes for Reinforced Shotcrete 3D Printing (SC3DP) Elements with Precise Surface Quality [23.02.2024] Dörrie, Robin Phd candidate r.doerrie@tu-braunschweig.de Technische Universität Braunschweig ITE Institut für Tragwerksentwurf Main Goal The project aims to fundamentally understand SC3DP technology to manufacture sustainable, multi-objective optimised, reinforced concrete components with precise surface quality and improved building physics via functional integration. It seeks to minimise carbon footprint by exploring varied material strategies, such as reducing cement content and design methods to decrease overall concrete volume. Additionally, it focuses on establishing reliable material and process control, emphasising fresh material laws for printability and durability, real-time monitoring of concrete properties, and component build-up strategies. Integration of large-scale reinforcement enhances structural suitability, while precise surface finishing …
Research Summary Report of B04
Category: Research Summary Report
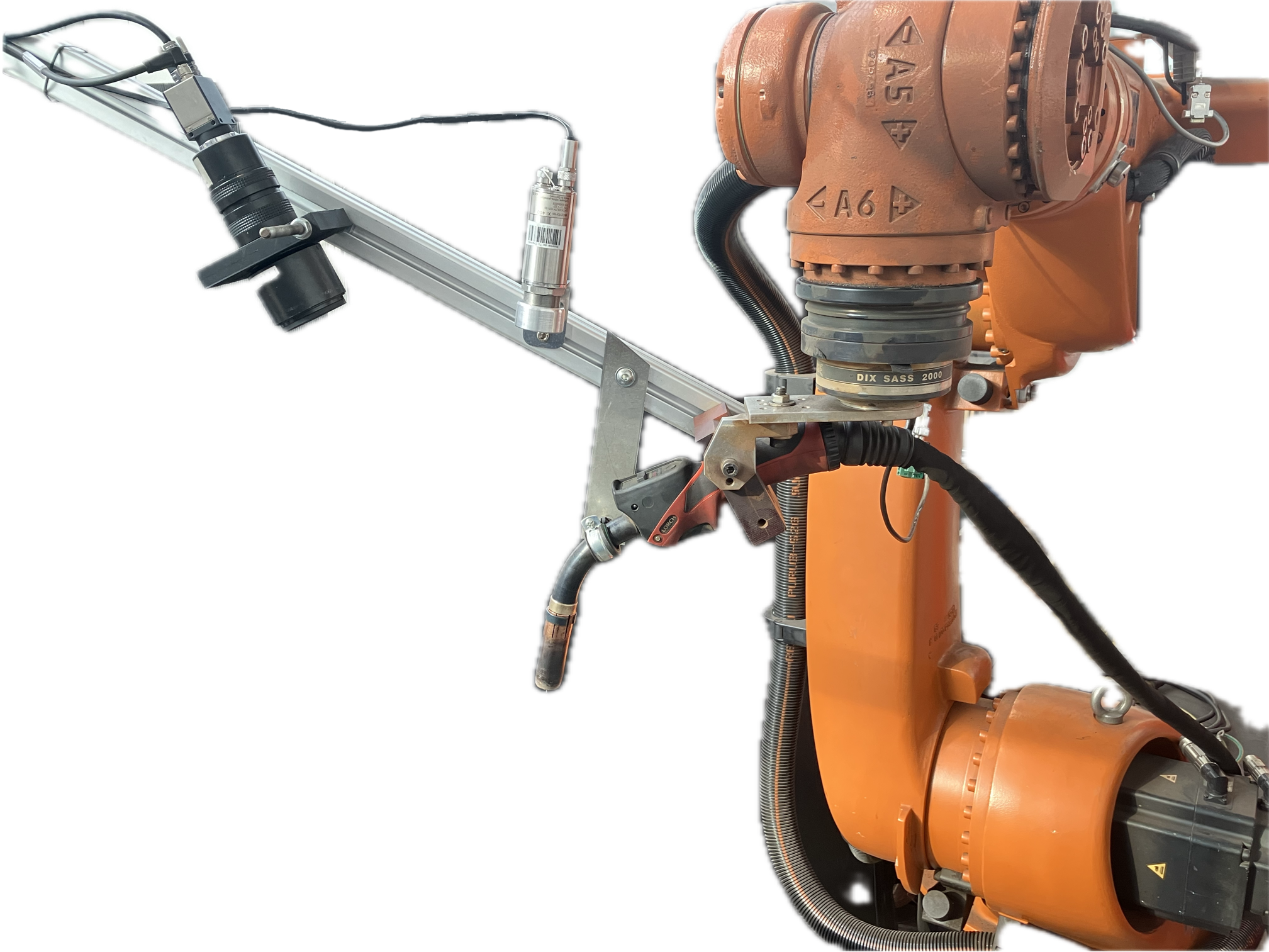
Process Control and Adaptive Path Planning for Additive Manufacturing Processes Based on Industrial Robots with an Extended Degree of Freedom [07.02.2024] Raatz, Annika; raatz@match.uni-hannover.de LUH, Institute of Assembly Technology and Robotics Lachmayer, Lukas; lachmayer@match.uni-hannover.de LUH, Institute of Assembly Technology and Robotics Heeren, Hauke; heeren@match.uni-hannover.de LUH, Institute of Assembly Technology and Robotics Main Goal The research of project B04 is dedicated to extending the current state-of-the-art path planning and process control algorithms for concrete-based additive manufacturing. The objective is to enable reproducible production of multi-material components utilizing mobile robot systems in motion, known as print-while-driving. Achieving this requires precise localization, considering system dynamics, such as acceleration and jerk limitations, as well as accounting for varying material properties and building installation …
Research Summary Report of C01
Category: Research Summary Report
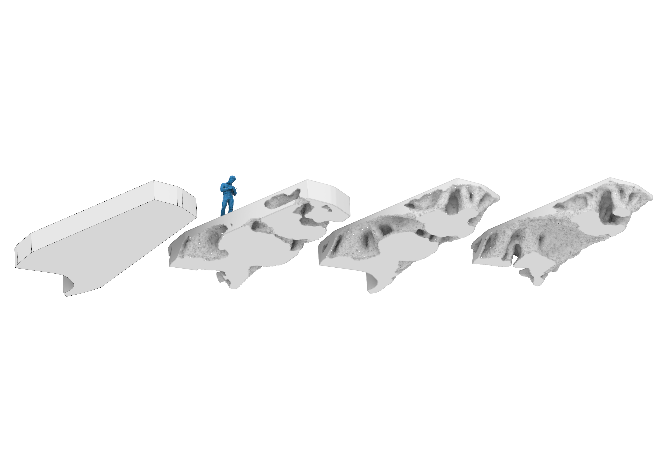
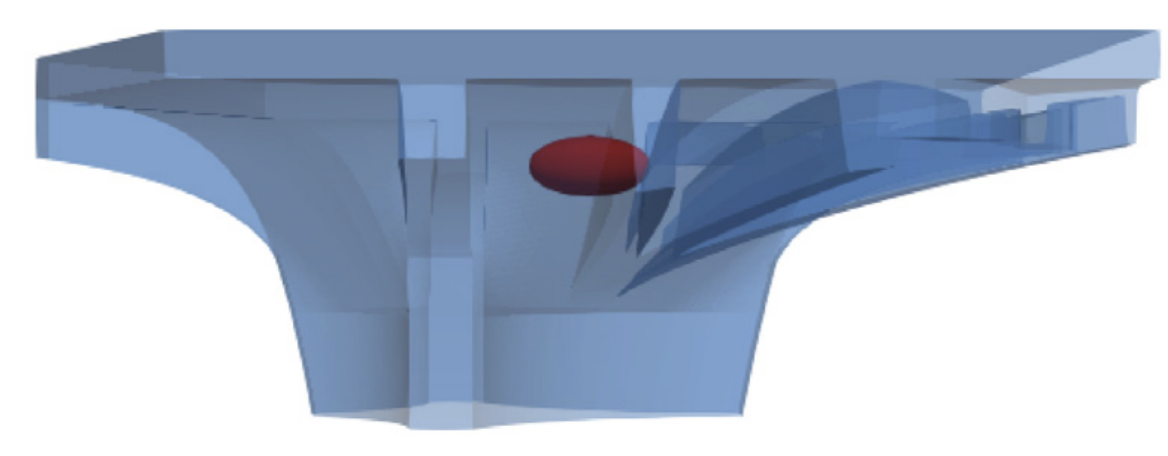
Bridging Scales – From Geometric Part Details to Construction Elements [02.02.2024] Kollmannsberger, Stefan; stefan.kollmannsberger@tum.de TUM, Computational Modeling and Simulation Bürchner, Tim; tim.buerchner@tum.de TUM, Computational Modeling and Simulation Rank, Ernst; ernst.rank@tum.de TUM, Institute for Advanced Study Digital models for Additive Manufacturing (AM) must consider many different geometric scales. The scales range from micrometers up to tens of meters for metal- or concrete-based processes and mutually influence each other. Project C01 aims to develop consistent geometric and computational descriptions for the relevant AM products on all these scales. As-built structures naturally deviate from as-designed structures in geometry, topology, and material properties especially in additive manufacturing. The consequences of such deviations upon the structural behaviour are commonly termed the effect of defect. …
Research Summary Report of A03
Category: Research Summary Report
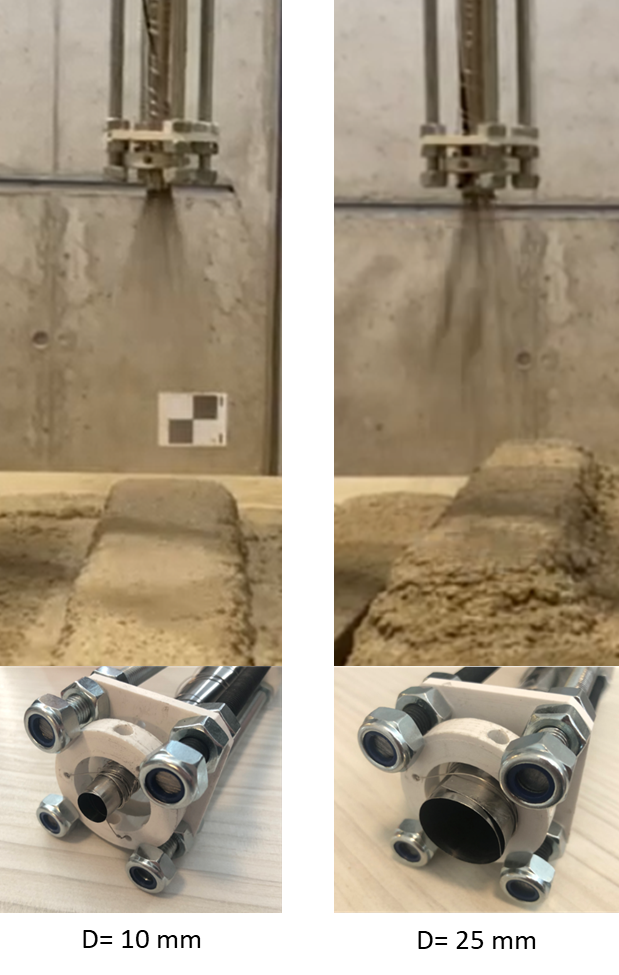
Extrusion of Near-Nozzle Mixed Concrete – Individually Graded in Density and in Rate of 3D Fibre Reinforcement [1.12.2023] Hechtl, Christian Maximilian, TP editor, m.hechtl@tum.de, TUM, cbm Dr.-Ing. Kränkel, Thomas, PL, thomas.kraenkel@tum.de, TUM, cbm Prof. Dr.-Ing. Gehlen, Christoph, PL, gehlen@tum.de, TUM, cbm The goal of A03 is to establish a concrete extrusion process using a near nozzle mixing (NNM) approach to enable the gradual variation of material properties during printing (gradation). This approach allows for the creation of multifunctional components, such as structures merging both load bearing and thermally insulating zones, by precisely altering material properties as required throughout the printing process. Summary and Current State of Research GRES V1 is a gradation-ready extrusion system that demonstrates the potential …
Research Summary Report of A02
Category: Research Summary Report
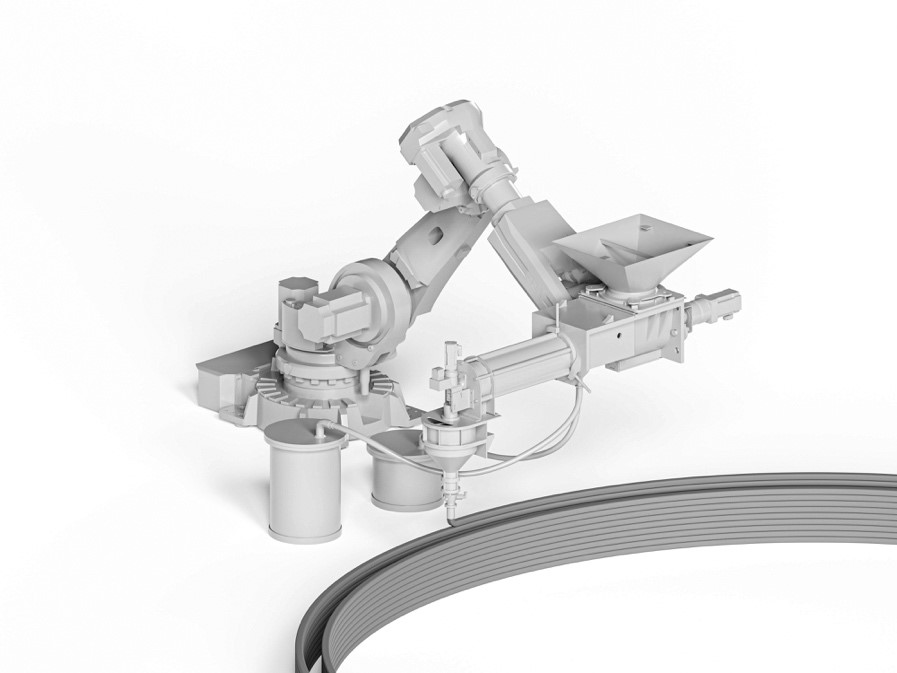
Particle-Bed 3D Printing by Selective Cement Paste Intrusion (SPI) – Particle Surface Functionalisation, Particle Synthesis and Integration of WAAM Reinforcement [17.11.2023] Straßer, Alexander, TP editor, alexander.strasser@tum.de, TUM, Chair of Materials Science and Testing Kränkel, Thomas, TP editor, thomas.kraenkel@tum.de, TUM, Chair of Materials Science and Testing Gehlen, Christoph, PL, gehlen@tum.de, TUM, Chair of Materials Science and Testing The goal of A02 is to implement reinforcement by Wire and Arc Additive Manufacturing (WAAM) in concrete elements produced by Selective Paste Intrusion (SPI), see Figure 1. Since the cement paste is applied to the aggregates and must penetrate the cavities between the aggregates by gravity, consistent rheological properties of the cement paste are essential. The welding process with WAAM generates high temperatures …
Research Summary Report of B03
Category: Research Summary Report
Modelling and Simulation of Shotcrete 3D Printing (SC3DP) Based on a Massively Parallel Multi-Phase, Multi-Component Coupled LBM-DEM Approach [10.11.2023] Kutscher (PostDoc), M. Geier (PI), M. Krafczyk (PI) TU Braunschweig, IRMB The primary aim of the project is to understand and quantify the dynamic distribution of material components (fluid, air and particles) and kinetic energy inside the jet of liquid concrete present in the shotcrete process. The information is required as a basis for future optimization of the process with regards to process and material parameters as well as for the prediction of material inhomogeneities. Summary In order to overcome the numerical difficulties arising from sustaining a high-density ratio in the diffuse interface lattice Boltzmann model we developed a new …
Research Summary Report of A01
Category: Research Summary Report
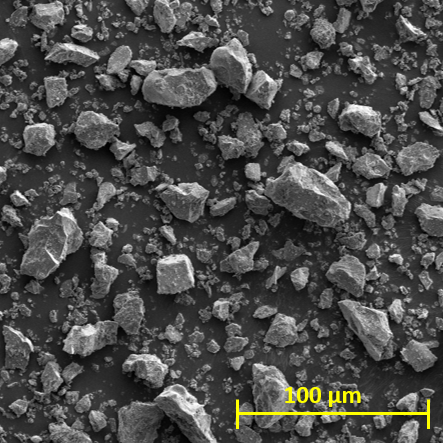
Particle bed 3D printing by selective cement activation: Particle surface functionalization, particle bed compaction and reinforcement integration [03.11.2023] Herding, Friedrich; Researcher, f.herding@ibmb.tu-bs.de Lowke, Dirk; Project leader, lowke@tum.de TU Braunschweig, Institute of Building Materials, Concrete Construction and Fire Safety / Technical University of Munich, Department of Materials Engineering Our main research objective is the fundamental understanding of the material-process interactions in particle bed 3D printing (PB3DP) by Selective Cement Activation (SCA). This will allow for the manufacturing of concrete elements with high mechanical strength and dimensional accuracy. Besides we also investigate different ways of reinforcement integration, which is crucial for the manufacturing of load-bearing building components. Summary In particle bed 3D printing by Selective Cement Activation, the particle mixture mainly …
Research Summary Report of A02
Category: Research Summary Report
Particle-Bed 3D Printing by Selective Cement Paste Intrusion (SPI) – Particle Surface Functionalisation, Particle Synthesis and Integration of WAAM Reinforcement [06.10.2023] Hamilton, Leigh Duncan; Researcher; Leigh-Duncan.Hamilton@tu-braunschweig.de Zetzener, Harald; Leading researcher H.Zetzener@tu-braunschweig.de Kwade, Arno; Project leader A.Kwade@tu-braunschweig.de All: TU Braunschweig, Institute for Particle Technology Our main goal within project A02 is to unite two additive manufacturing (AM) processes, thereby, creating a hybrid AM process for structural concrete. The foundation of A02 is formed around the concrete 3D printing process Selective Paste Intrusion (SPI). SPI creates components in layers by first spreading coarse aggregates (usually quartz) on a surface or previous layer. Subsequently, the cement slurry is applied onto designated areas, where it fills void volumes between aggregate particles. The second …
Research Summary Report of A05
Category: Research Summary Report
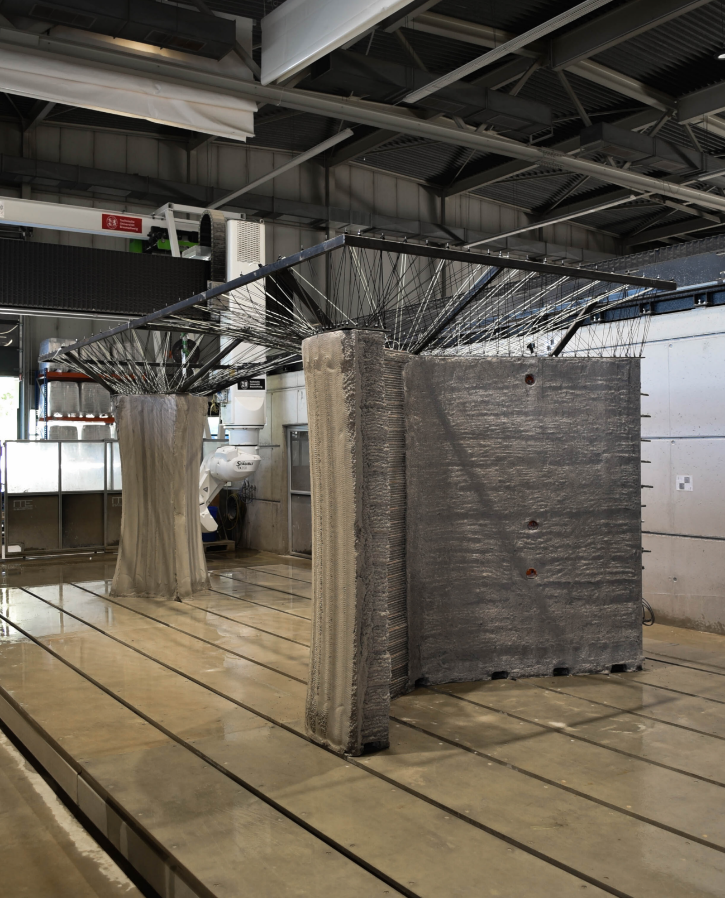
Integration of Individualized Prefabricated Fibre Reinforcement in Additive Manufacturing with Concrete [29.09.2023] Rothe, Tom; Doctoral researcher, t.rothe@tu-braunschweig.de, TU Braunschweig, Institute of Mechanics and Adaptronics (IMA) Hühne, Christian; Project Leader, Christian.Huehne@tu-braunschweig.de, TU Braunschweig, Institute of Mechanics and Adaptronics (IMA) Fig 2: Robotic integration of reinforcement into the column of the Shelltonics demonstrator The individual integration of fibre reinforcement into large concrete components produced by Additive Manufacturing allows new design freedoms and reduces concrete consumption due to reduced concrete cover. The project A05 develops strategies to integrate freely formable reinforcement strands for the different AM processes. For doing so, a Dynamic Winding Machine is developed and constantly updated. This machine is used to consolidate and impregnate a primary fibre strand …
Research Summary Report of A04
Category: Research Summary Report
Integrated Additive Manufacturing Processes for Reinforced Shotcrete 3D Printing (SC3DP) Elements with Precise Surface Quality [30.09.2023] David, Martin; Doctoral Researcher, m.david@tu-braunschweig.de, TU Braunschweig, Institute for Machine Tools and Production Technology (IWF) Summary and Current state of research Project A04 aims to investigate cooperative Additive Manufacturing (AM) processes based on Shotcrete 3D Printing (SC3DP) for the production of material-efficient, force-optimised, reinforced, load-bearing concrete components with precise surface quality and geometrical precision. The goal is to produce large-scale concrete elements using significantly lower amounts of reinforcement and concrete as compared to standard concrete construction principles. Hereby, different robot guided end effectors are subject to research in a flexible and automated process chain. Currently, the following key points are researched by the …
Research Summary Report of A07
Category: Research Summary Report
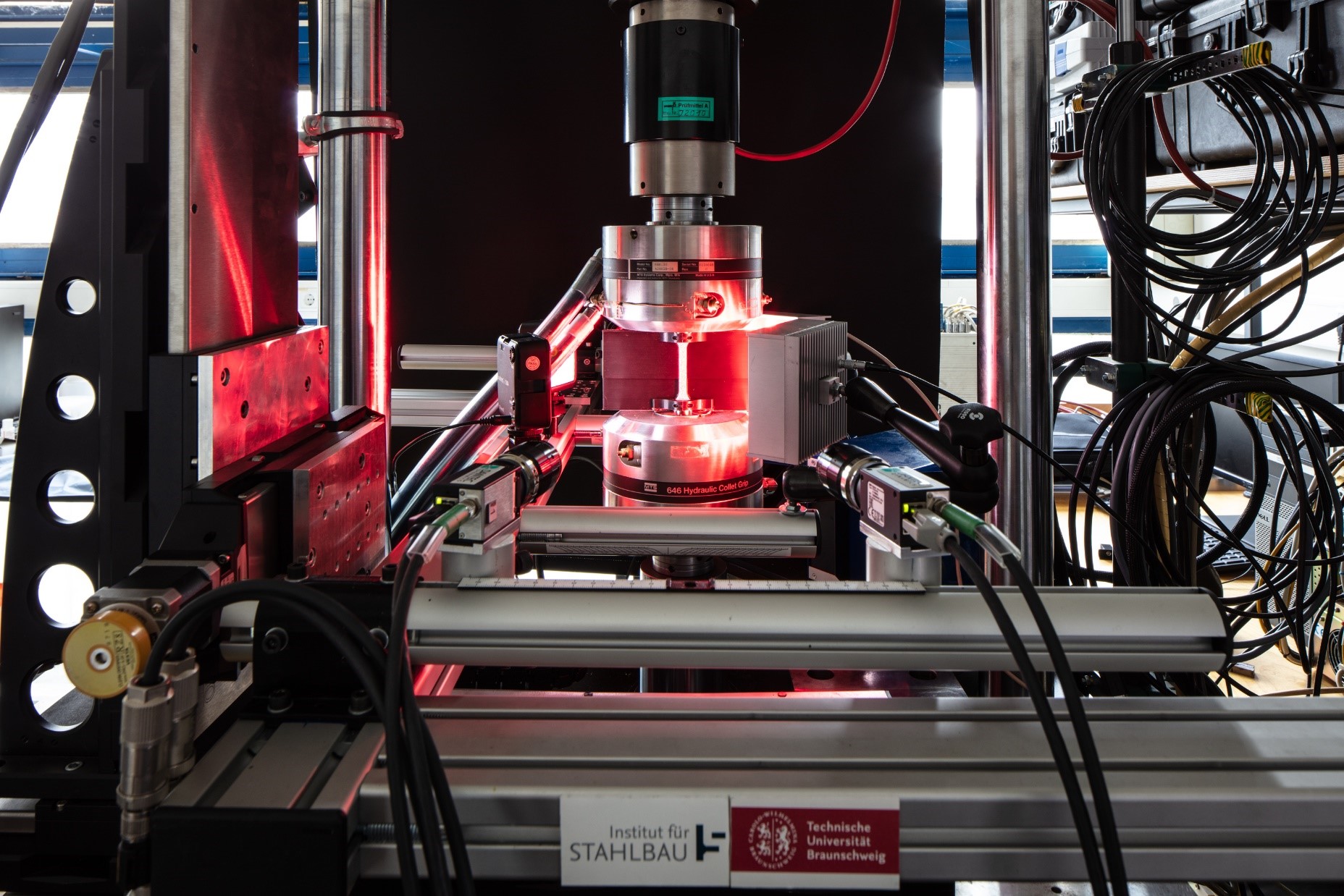
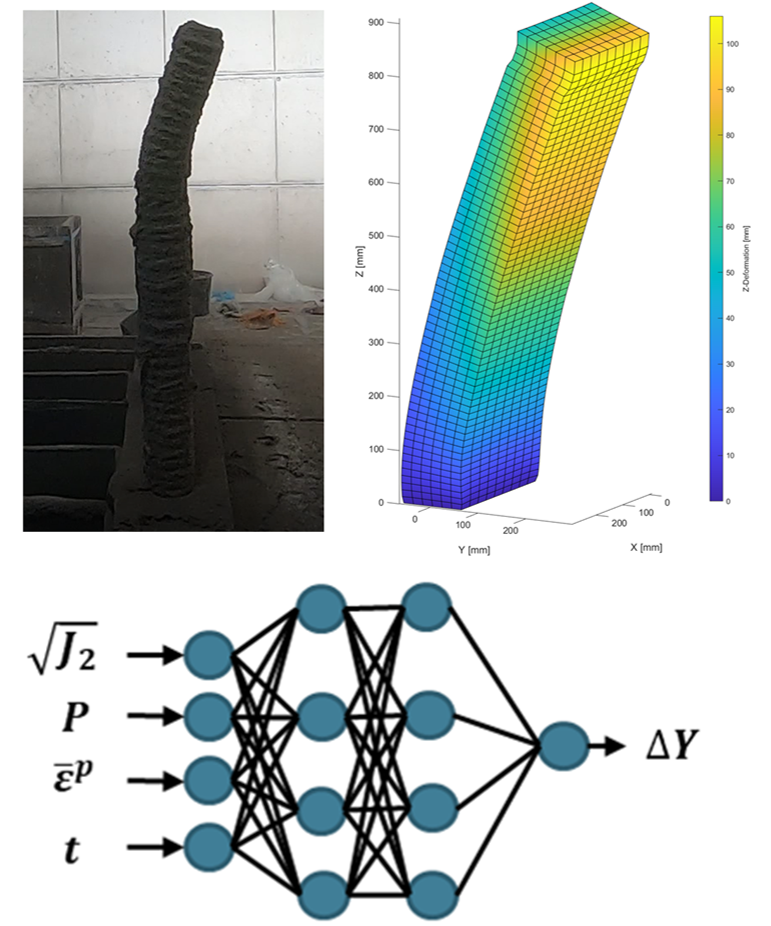
Wire and Arc Additive Manufacturing (WAAM) of Complex Individualized Steel Components [08.09.2023] Jahns, Hendrik; Doctoral researcher; h.jahns@stahlbau.tu-braunschweig.de Unglaub, Julian; Principle Investigator j.unglaub@stahlbau.tu-braunschweig.de Thiele, Klaus; Principle Investigator k.thiele@stahlbau.tu-braunschweig.de Institute of Steel Structures Technische Universität Braunschweig Project – main goal In project A07 the design, manufacturing and mechanical properties of complex individualized WAAM steel nodes for use in construction is investigated. A new method is developed to design force flow optimized steel nodes as connectors between semi-finished parts and anchorage structures considering the manufacturing possibilities of the WAAM-process and the resulting material behavior. The manufacturing possibilities will be identified by case study demonstrators, which represent occurring features of the designed node. The produced parts are characterized regarding their mechanical properties. …
Research Summary Report of A06
Category: Research Summary Report
Laser Powder-Bed Fusion (LPBF) of Steel Elements for Construction – Basics of Design and Mechanical Resilience [22.09.2023] Wenzler, David; doctoral researcher; david.wenzler@tum.de Technical University of Munich, Institute for Machine Tools and Industrial Management Diller, Johannes; doctoral researcher; johannes.diller@tum.de, Siebert, Dorina; doctoral researcher; dorina.siebert@tum.de Technical University of Munich, Chair of Metal Structures Project The project A06 aims to explore and evaluate the factors influencing the manufacturing of safe and durable structural steel elements by laser powder-bed fusion (LPBF). Thereby, the LPBF process, the post-treatment, and the influence of the part geometry on the microstructure and the mechanical properties will be investigated. From the results, correlations between these aspects will be determined. In the 1st funding period, the project focuses on …
Research Summary Report of A08
Category: Research Summary Report
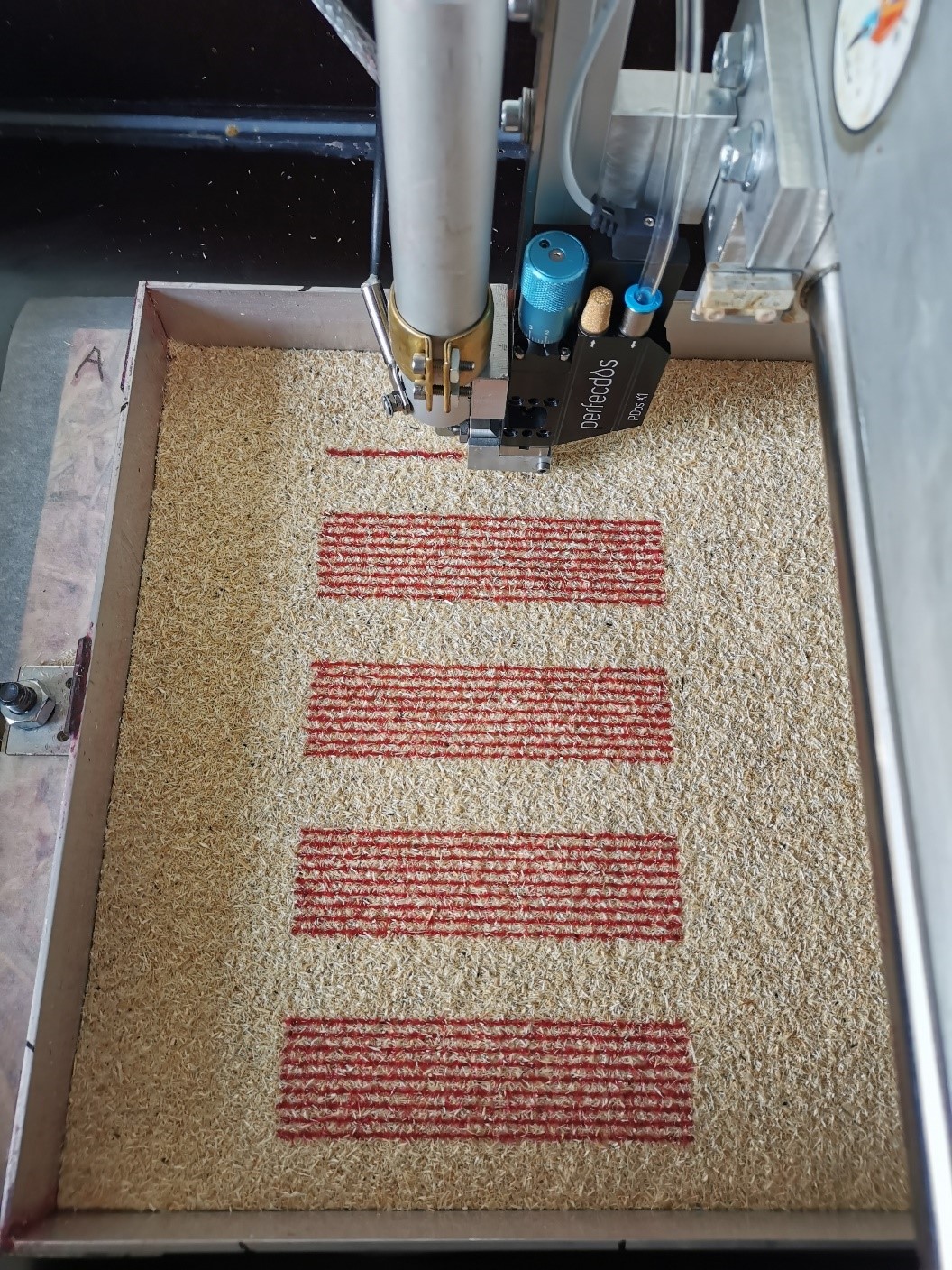
Structural Timber by Individual Layer Fabrication (ILF) [01.09.2023] Asshoff, Carsten; Doctoral researcher; carsten.asshoff@wki.fraunhofer.de Fraunhofer Institute for Wood Research Wilhelm-Klauditz-Institut WKI Main goal The main goal of the project ’A08 – Structural Timber by Individual Layer Fabrication (ILF)’ is to develop a process to additively manufacture large-scale, wood composite objects with a maximum content of wood material and strength values suited for applications in construction. In the course of the project multiple process variants and material combinations are explored. For this, the necessary machinery is developed in iterative steps and the mechanical properties of the resulting objects as well as the geometric capacity of the processes are investigated. Finally, multiple demonstrators are fabricated for showcase purposes. Summary Working …
Research Summary Report of B04
Category: Research Summary Report
Process Control and Adaptive Path Planning for Additive Manufacturing Processes Based on Industrial Robots with an Extended Degree of Freedom [26.08.2023] Ekanayaka, Virama; Doctoral researcher, v.ekanayaka@tu-braunschweig.de, TU Braunschweig, Institute of Machine Tools and Production Technology (IWF) Hürkamp, André; Project Leader, a.huerkamp@tu-braunschweig.de, TU Braunschweig, Institute of Machine Tools and Production Technology (IWF) Main goal The integration of robot-guided additive manufacturing in the construction industry increases the degree of automation and can thus lead to an increased productivity and increased component quality. In shotcrete 3D printing (SC3DP), reproducible manufacturing results and ensuring component quality are major challenges, as the properties of shotcrete depend on many different parameters (e.g. temperature, pressure, water-cement ratio, hardening accelerator). The goal of this research project is …
Research Summary Report of C03
Category: Research Summary Report
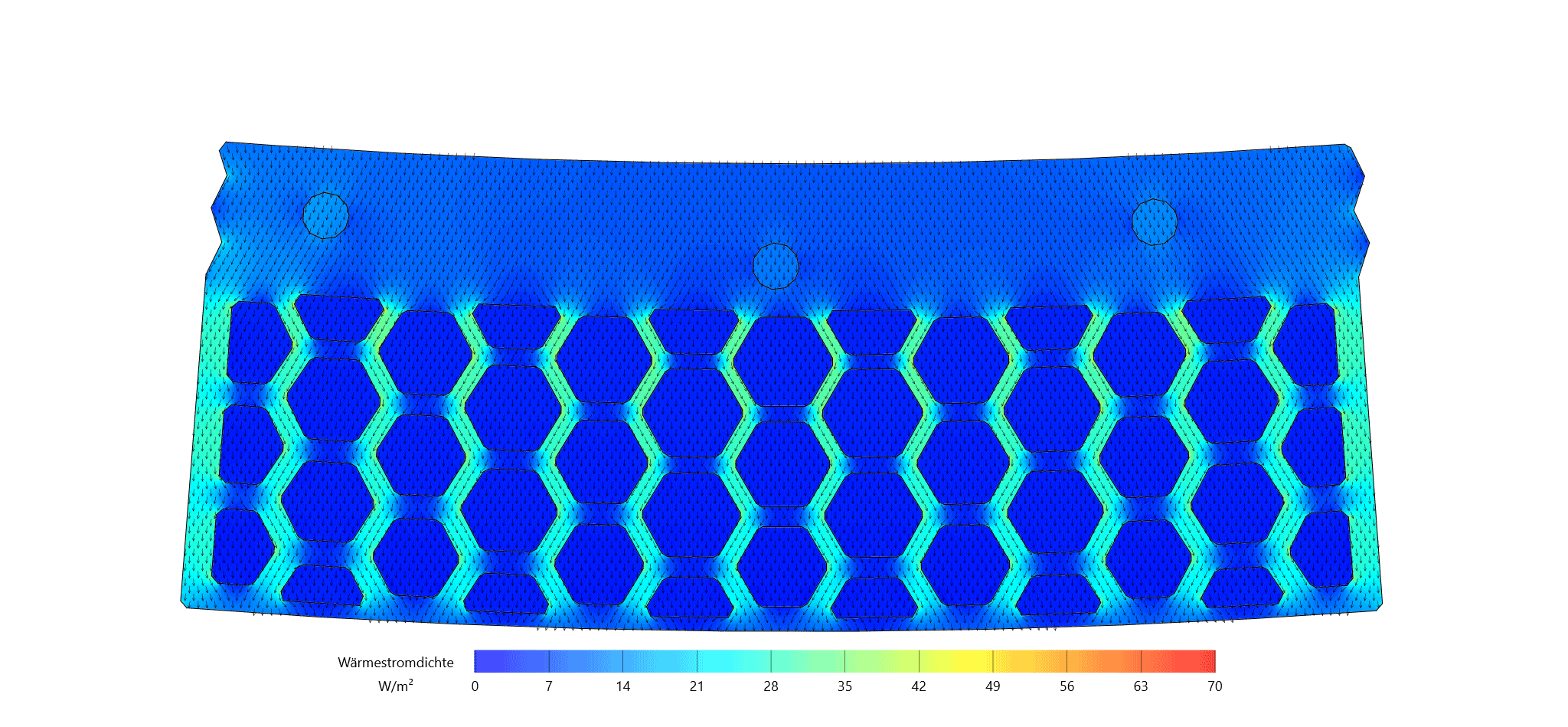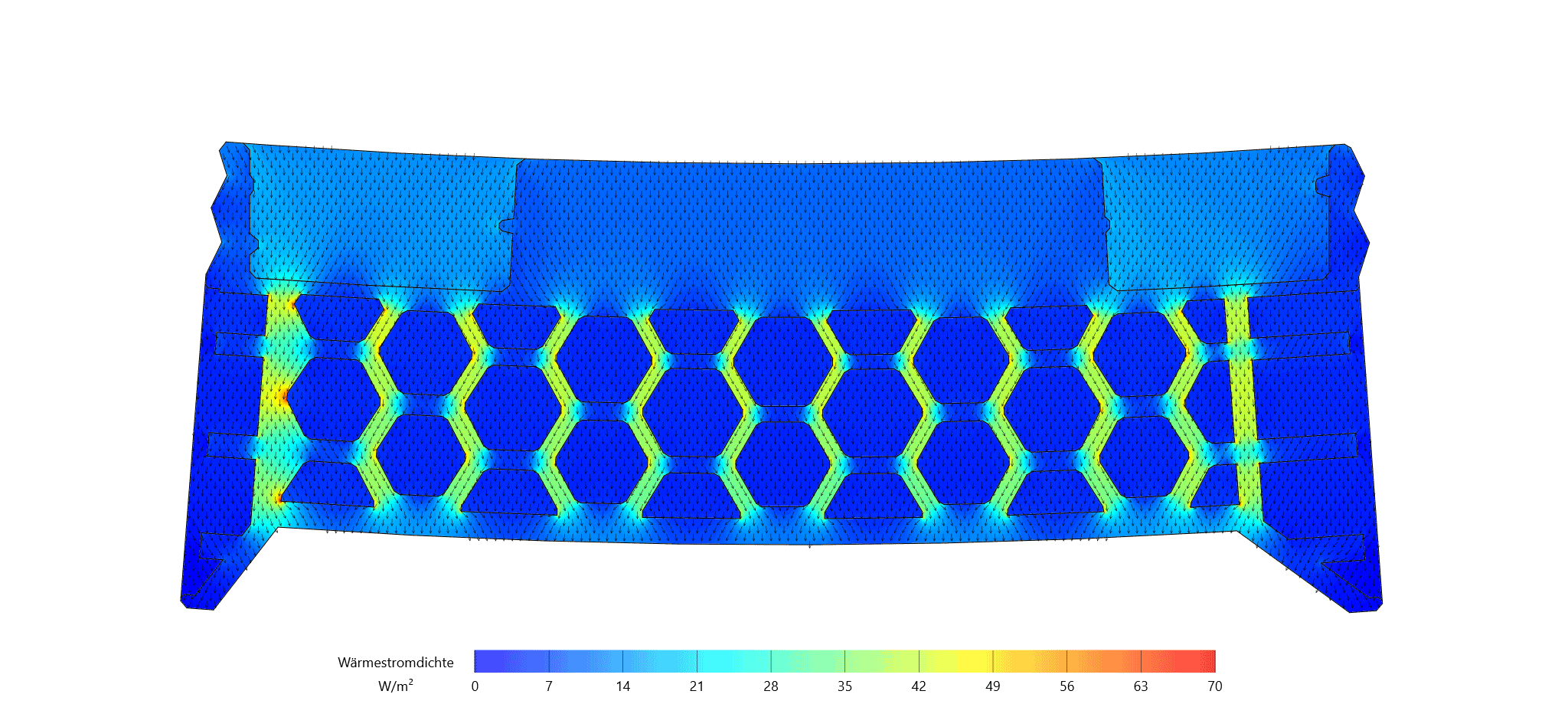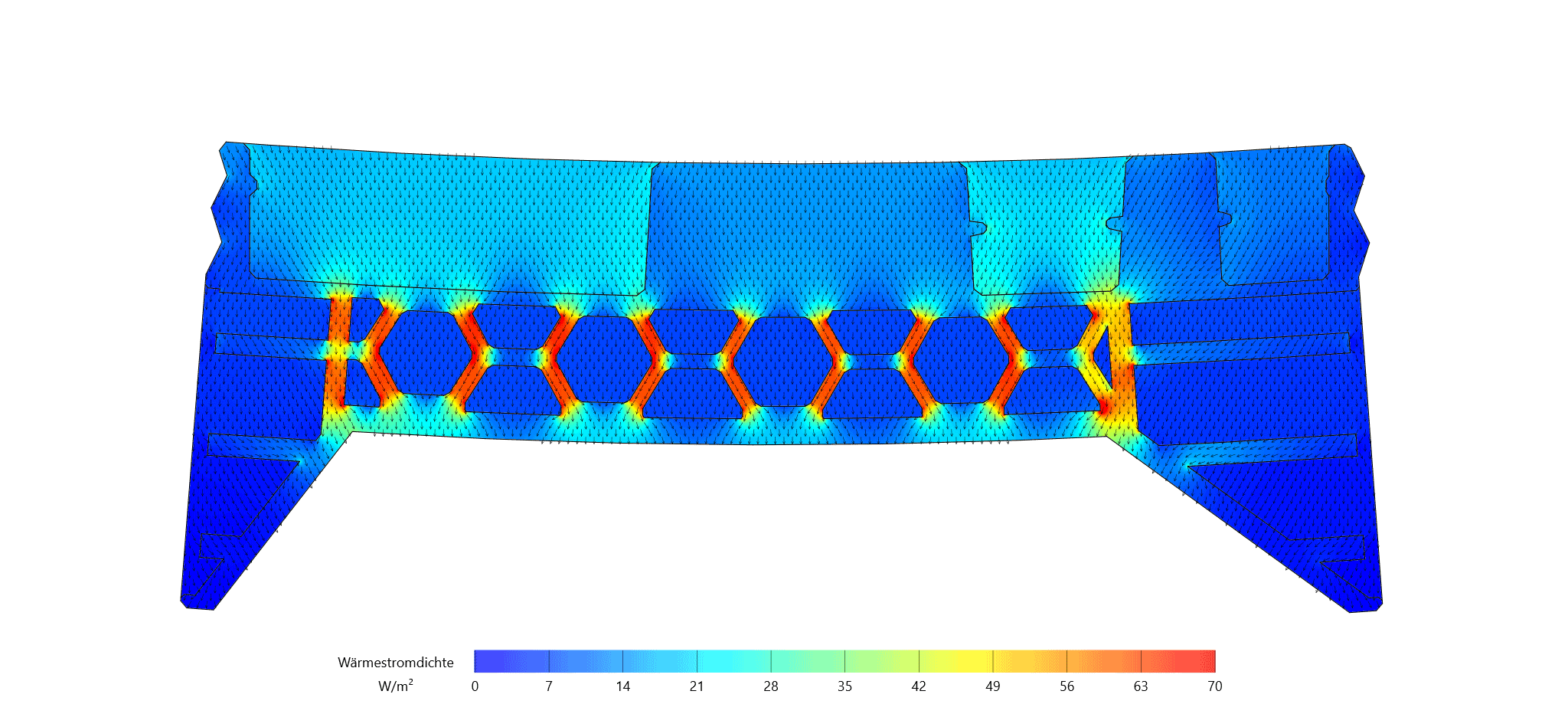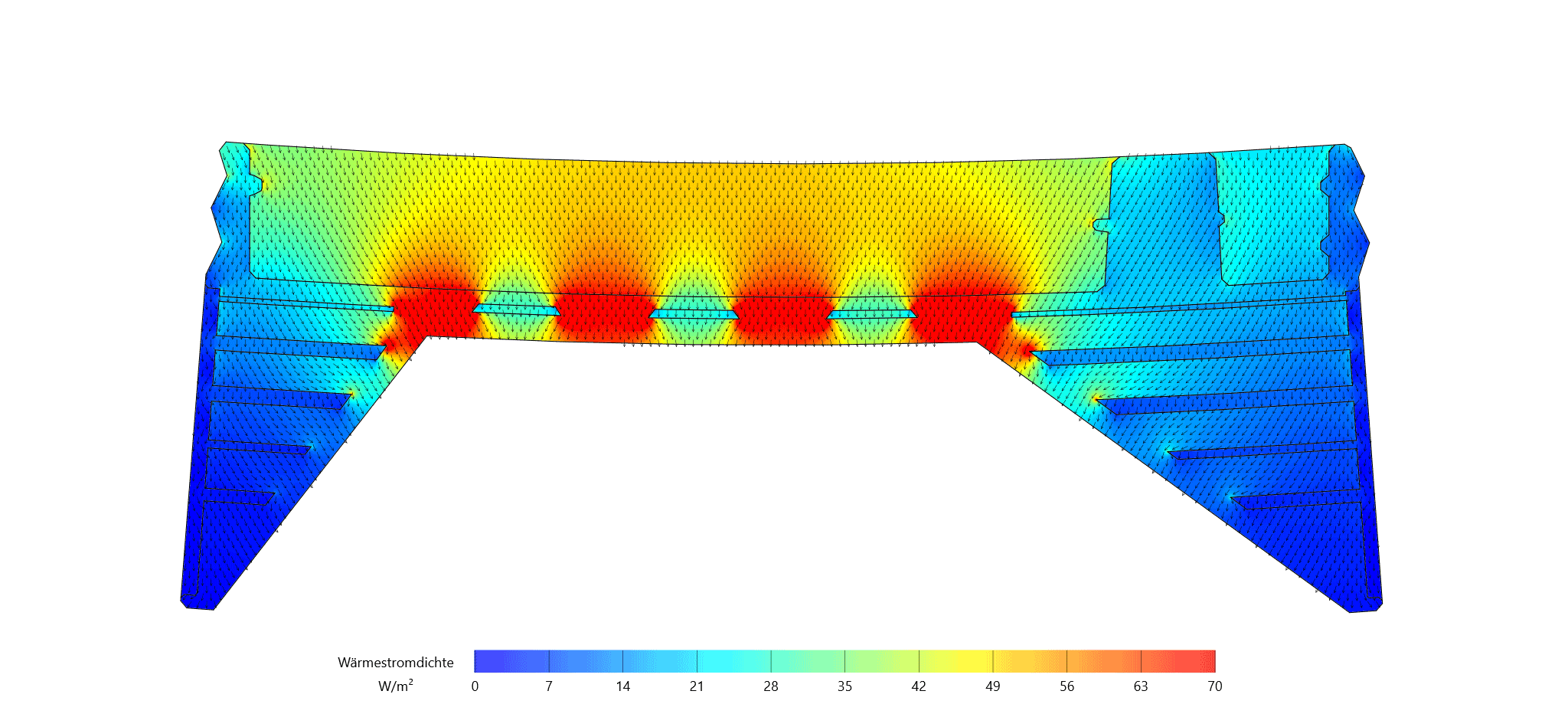
Integration of Passive and Active Functions in Additively Manufactured Construction Elements [25.08.2023] Auer, Thomas; PL, thomas.auer@tum.de * Briels, David; doctoral researcher, david.briels@tum.de * Nouman, Ahmad; doctoral researcher, ahmad.nouman@tum.de * all: Technical University of Munich, TUM School of Engineering and Design, Chair of Building Technology and Climate Responsive Design Main goal To fully leverage the potential of additive manufacturing (AM) processes explored within the AMC, a fundamental shift in the design of building elements is necessary. Through the capabilities of AM, we can create highly specialized components that seamlessly integrate and enhance both passive and active functions, encompassing building physics (such as heat transfer and acoustics) and building services (including heating, cooling, and ventilation). Our overarching goal is to achieve …
Research Summary Report of C06
Category: Research Summary Report
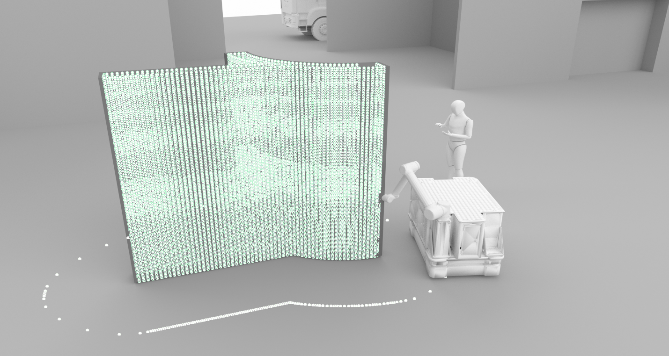
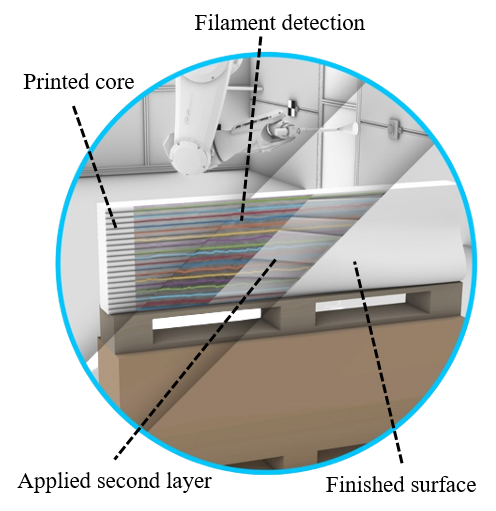
Integration of Additive Manufacturing in the Construction Process [18.08.2023] Mawas, Karam; Doctoral researcher, k.mawas@tu-braunschweig.de Gerke, Markus; Project leader, m.gerke@tu-braunschweig.de Maboudi, Mehdi; Associated scientist, m.maboudi@tu-braunschweig.de all: TU Braunschweig, Institute of Geodesy and Photogrammetry (IGP) Main goal To guarantee adherence to a resilient process and faithful realization of the designed model in the printed object, it is essential to implement ongoing and automated data capture and process inspection. Additionally, quality control plays a pivotal role in enabling the seamless integration of components into objects. Summary An essential phase within 3D printing is quality assurance. Incorporating automated quality control into the production cycle can significantly augment productivity. With the rapid construction capabilities offered by 3D concrete printing (3DCP), upholding stringent quality standards …