Research Summary Report
Research Summary Report of C01
Category: Research Summary Report
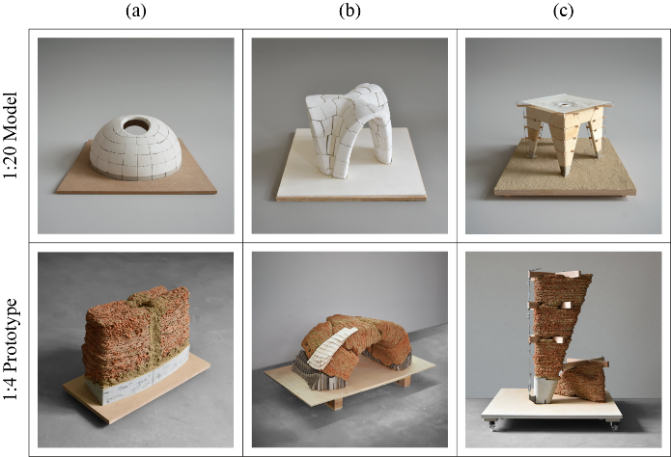
Bridging Scales – From Geometric Part Details to Construction Elements [06.02.2025] M. Sc. Matti Christmann Researcher, matti.christmann@uni-weimar.de Prof. Dr.-Ing. Stefan Kollmannsberger Project Leader, stefan.kollmannsberger@uni-weimar.de Bauhaus-Universität Weimar (BUW), Professur Data Engineering im Bauwesen (DEiB) Digital models for Additive Manufacturing (AM) must consider many different geometric scales. The scales range from micrometers up to tens of meters for metal- or concrete-based processes and mutually influence each other. Project C01 aims to develop consistent geometric and computational descriptions for the relevant AM products on all these scales. As-built structures naturally deviate from as-designed structures in geometry, topology, and material properties especially in AM. The consequences of such deviations upon the structural behavior …
Research Summary Report of B04
Category: Research Summary Report
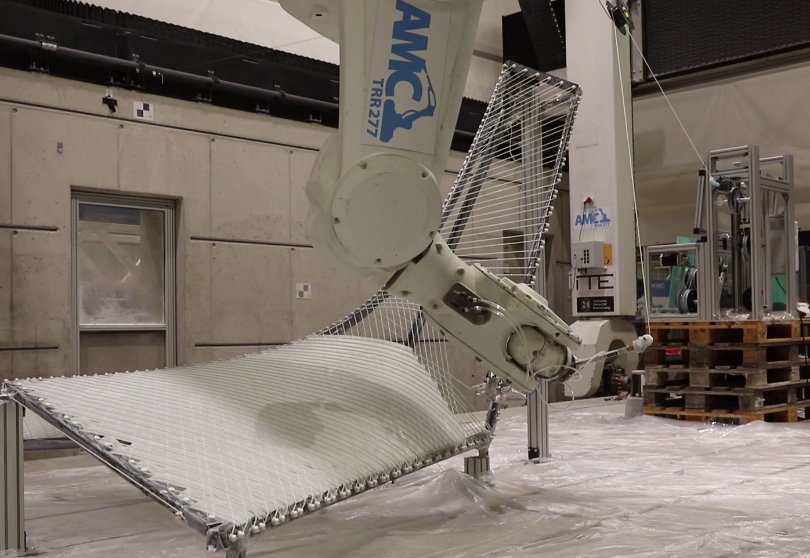
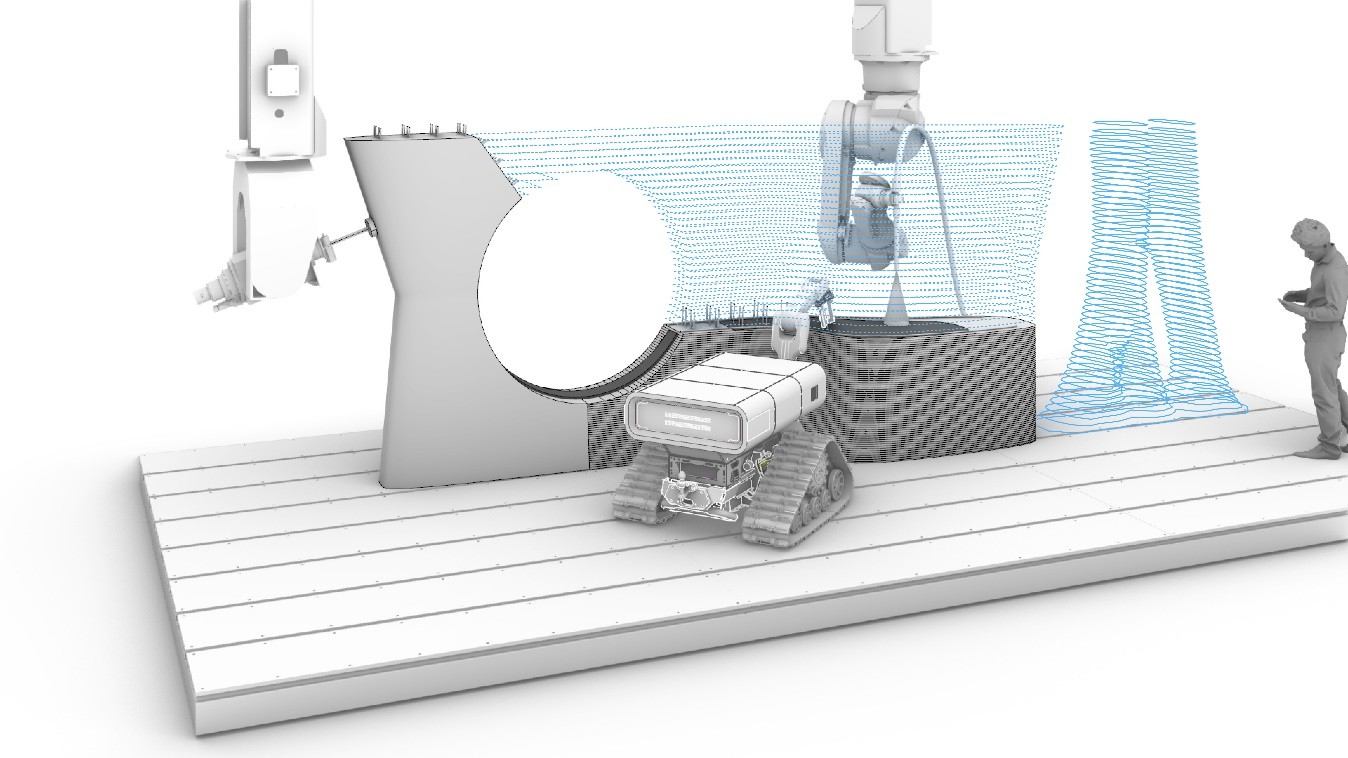
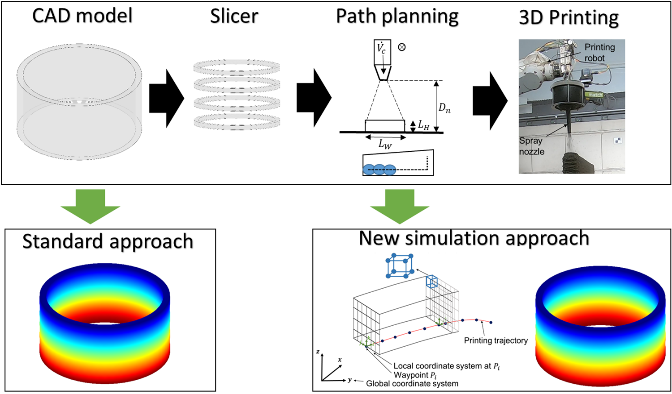
Process Control and Adaptive Path Planning for Additive Manufacturing Processes Based on Industrial Robots with an Extended Degree of Freedom [06.02.2025] Prof. Dr.-Ing. Annika Raatz Project Leader, raatz@match.uni-hannover.de M. Sc. Lukas Lachmayer Researcher, lachmayer@match.uni-hannover.de M. Sc. Hauke Heeren Researcher, heeren@match.uni-hannover.de Leibniz Universität Hannover (LUH), Institute of Assembly Technology and Robotics The research of project B04 is dedicated to extending the current state-of-the-art path planning and process control algorithms for concrete-based additive manufacturing. The objective is to enable reproducible production of multi-material components utilizing mobile robot systems in motion, known as …
Research Summary Report of A04
Category: Research Summary Report
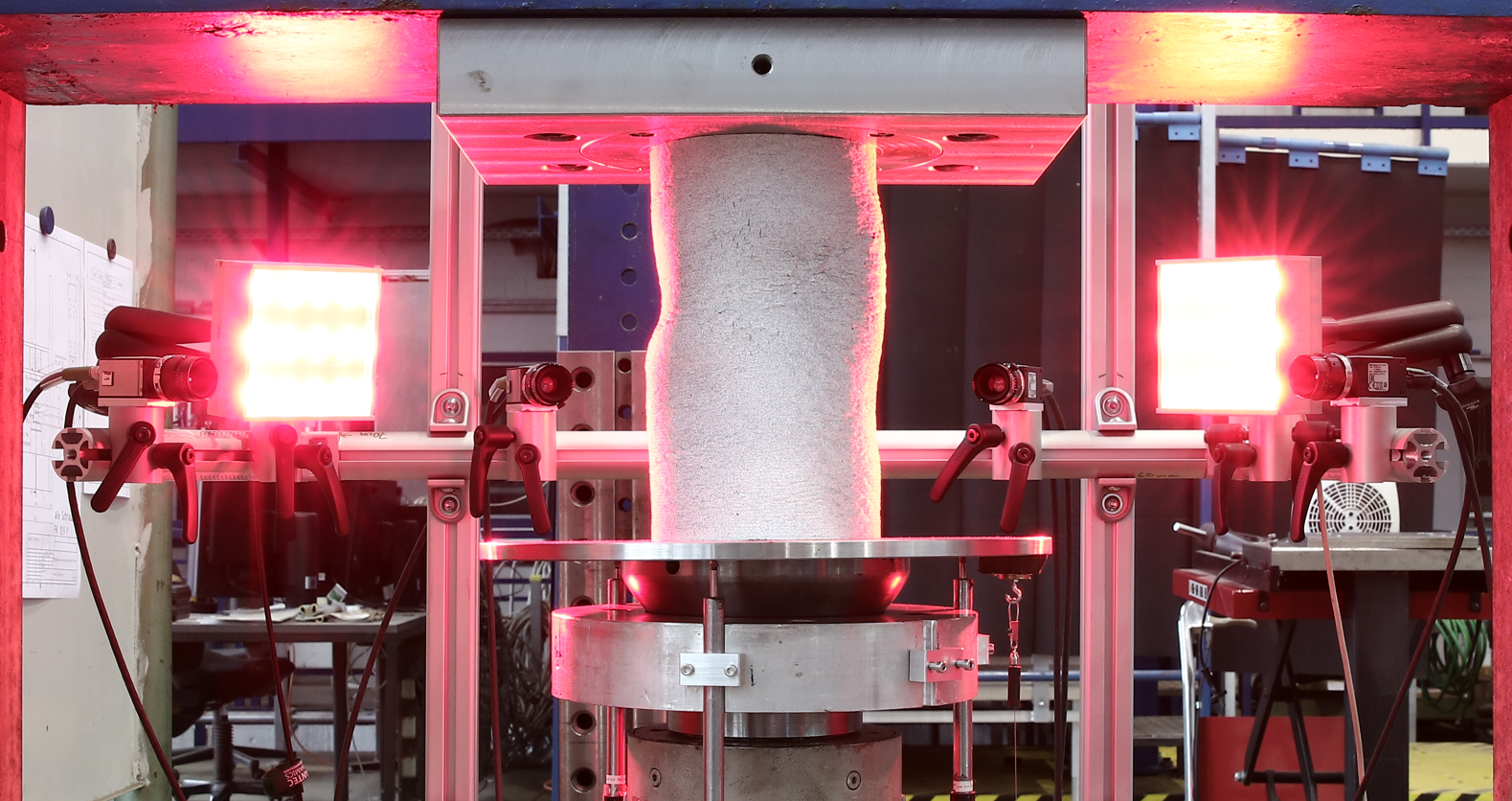
Integrated Additive Manufacturing Processes for Reinforced Shotcrete 3D Printing (SC3DP) Elements with Precise Surface Quality [29.01.2025] M. Sc. Robin Dörrie Researcher, r.doerrie@tu-braunschweig.de Technische Universität Braunschweig(TU BS), ITE Institute of Structural Design The project aims to fundamentally understand the Shotcrete 3D Printing (SC3DP) technology to manufacture sustainable, multi-objective optimised, reinforced concrete components with precise surface quality and improved building physics via functional integration. It seeks to minimise the carbon footprint of 3D printed structures by exploring various material strategies, such as reducing cement content by increasing the aggregate size or replacing cement with a different binder and design methods to optimise the usage of concrete in order to decrease the …
Research Summary Report of A03
Category: Research Summary Report
Extrusion of Near-Nozzle Mixed Concrete – Individually Graded in Density and in Rate of 3D Fibre Reinforcement [22.01.2025] M. Eng. Benedikt Grimm Researcher, benedikt.grimm@tum.de M. Sc. Christian Maximilian Hechtl Researcher, m.hechtl@tum.de Dr.-Ing. Thomas Kränkel Project leader, thomas.kraenkel@tum.de Prof. Dr.-Ing. Christoph Gehlen Project leader, gehlen@tum.de Technische Universität München(TUM), Chair of Material Science and Testing The goal of A03 is to establish a concrete extrusion process using a near nozzle mixing (NNM) approach to enable the gradual variation of material properties during printing (gradation). This approach allows for the creation of multifunctional components, such as structures …
Research Summary Report of C09
Category: Research Summary Report
Environmental Life Cycle Assessment – Determination of Ecological Sustainability Potentials by AMC [11.12.2024] M. Eng. Sophie Viktoria Albrecht Researcher, Sophie.albrecht@oth-regensburg.de Prof. Charlotte Thiel Project leader, charlotte.thiel@oth-regensburg.de Ostbayerische Technische Hochschule Regensburg (OTH), Construction Materials C09 aims to enhance the ecological sustainability of Additive Manufacturing in Construction (AMC) by quantifying and optimizing its environmental benefits through comprehensive Life Cycle Assessments (E-LCA) from cradle to cradle. This involves developing transparent Product Environmental Footprint Category Rules (PEFCR), identifying impactful reduction measures, and integrating circular design strategies to create durable, efficient, and reusable components. By incorporating these findings into Fabrication Information Modelling (FIM), C09 enables early-stage, sustainability-focused decision-making, fostering material-efficient, low-impact construction practices and reducing the environmental footprint of the building …
Research Summary Report of B06
Category: Research Summary Report
Material Modelling and Simulation of Deposition AM Processes on the Part Scale [11.12.2024] M. Sc. Quoc Tuan La Researcher, quoc-tuan.la@tu-braunschweig.de Prof. Dr.-Ing. Ralf Jänicke Project leader, r.janicke@tu-braunschweig.de Technische Universität Braunschweig, Institute of Applied Mechanics Prof. Dr.-Ing. habil. Stefan Kollmannsberger Project leader, stefan.kollmannsberger@uni-weimar.de Bauhaus-Universität Weimar, Professorship of Data Engineering in Civil Engineering The main goal of the project is to simulate the deposition process of additive manufacturing for complex geometries. The simulation focuses on Shotcrete 3D Printing (SC3DP) and includes identifying and calibrating a thixotropic material model. Additionally, Variationally consistent Computational Homogenization is employed to minimize computational costs. Summary Shotcrete 3D Printing (SC3DP) is a soft material that hardens over time through structure formation …
Research Summary Report of A01
Category: Research Summary Report
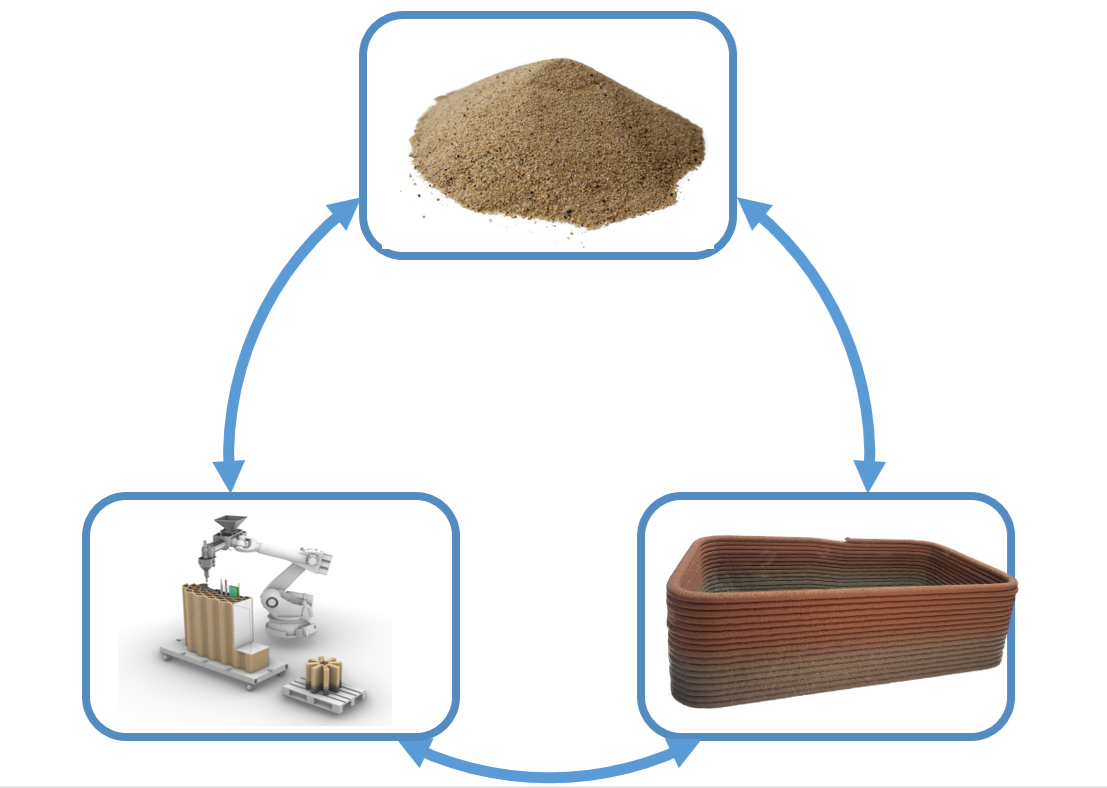
Particle-Bed 3D Printing by Selective Cement Activation (SCA) – Sustainability, process enhancement and material models [04.12.2024] M. Sc. Friedrich Herding Researcher, friedrich.herding@tum.de Prof. Dr.-Ing. Dirk Lowke Project leader, lowke@tum.de TU Munich (TUM), Chair of Binder Jetting Technology Our main research objective is the fundamental understanding of the material-process interactions in particle bed 3D printing (PB3DP) by Selective Cement Activation (SCA). This will allow for the manufacturing of concrete elements with high mechanical strength and dimensional accuracy. Besides we also investigate different ways of reinforcement integration, which is crucial for the manufacturing of load-bearing building components. Summary Selective Cement Activation (SCA) is a particle bed 3D printing technique that offers the possibility to precisely manufacture free-form …
Research Summary Report of A10
Category: Research Summary Report
Earth Additive Manufacturing (EAM) – Material and Process Combinations for AM with Earth-based Materials [29.11.2024] M. A. Ema Krakovská Researcher, ema.krakovska@tum.de Prof. Dr. Kathrin Dörfler Project leader, doerfler@tum.de all: TU Munich (TUM), Professorship of Digital Fabrication The main research objective of A10 is the conception and investigation of two novel Earth Additive Manufacturing (EAM) processes, their material-process interactions, and their evaluation in large-scale architectural applications. Focusing on the characterisation of earth-based material mixtures (PL Machner), the project investigates a) Sprayed Earth Additive Manufacturing (SEAM) as a deposition-based process (PL Kloft) and b) Intrusion Earth Additive Manufacturing (IEAM) as a particle-bed-based process (PL Dörfler). The research aims to assess earth-based materials for these processes with a …
Research Summary Report of C02
Category: Research Summary Report
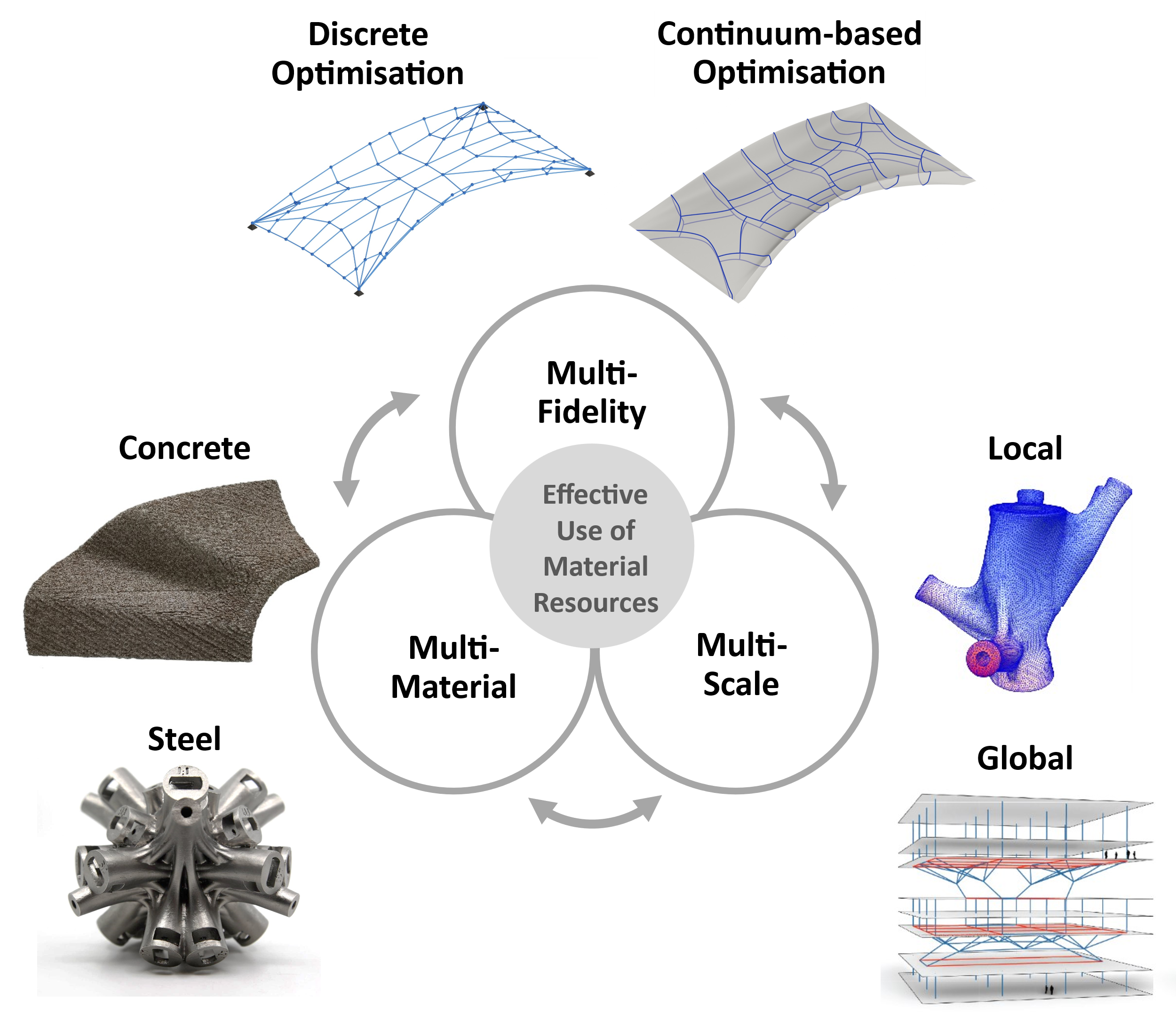
3D Structural Puzzle – Numerical Multi Scale Shape and Topology Optimisation Methods to Additively Manufacture Optimal Structures from Optimised Pieces [27.11.2024] M. Sc. Philipp Jakobs Researcher, philipp.jakobs@tum.de Prof. Dr.-Ing. Roland Wüchner Project leader, wuechner@tum.de all: TU Munich (TUM), Chair of Structural Analysis Current building practices often adopt a sequential design approach, where architectural, structural, and fabrication aspects are addressed independently, resulting in excessive material consumption. The CO2 project aims to establish a Holistic Design Framework (HDF) integrating the above-mentioned aspects. Within this framework, additive manufacturing facilitates structural optimisation by enabling the production of bespoke geometries for an effective use of material resources. Departing from the conventional sequential approach, the HDF concurrently integrates low-fidelity Discrete Optimisation Approaches …
Research Summary Report of A02
Category: Research Summary Report
Particle-Bed 3D Printing by Selective Cement Paste Intrusion (SPI) – Particle Surface Functionalisation, Particle Synthesis and Integration of WAAM Reinforcement [20.11.2024] M. Sc. Alexander Straßer Researcher, alexander.strasser@tum.de Dr.-Ing. Thomas Kränkel Researcher, thomas.kraenkel@tum.de Prof. Dr.-Ing. Christoph Gehlen Project leader, gehlen@tum.de all: TU Munich (TUM), Chair of Materials Science and Testing The goal of A02 is to implement reinforcement by Wire and Arc Additive Manufacturing (WAAM) in concrete elements produced by Selective Paste Intrusion (SPI), see Figure 1. The SPI and combined SPI + WAAM process will also be further investigated with a focus on ecological improvements. Both individual processes will first be examined separately. To achieve these goals, the SPI process will include optimization …
Research Summary Report of C05
Category: Research Summary Report
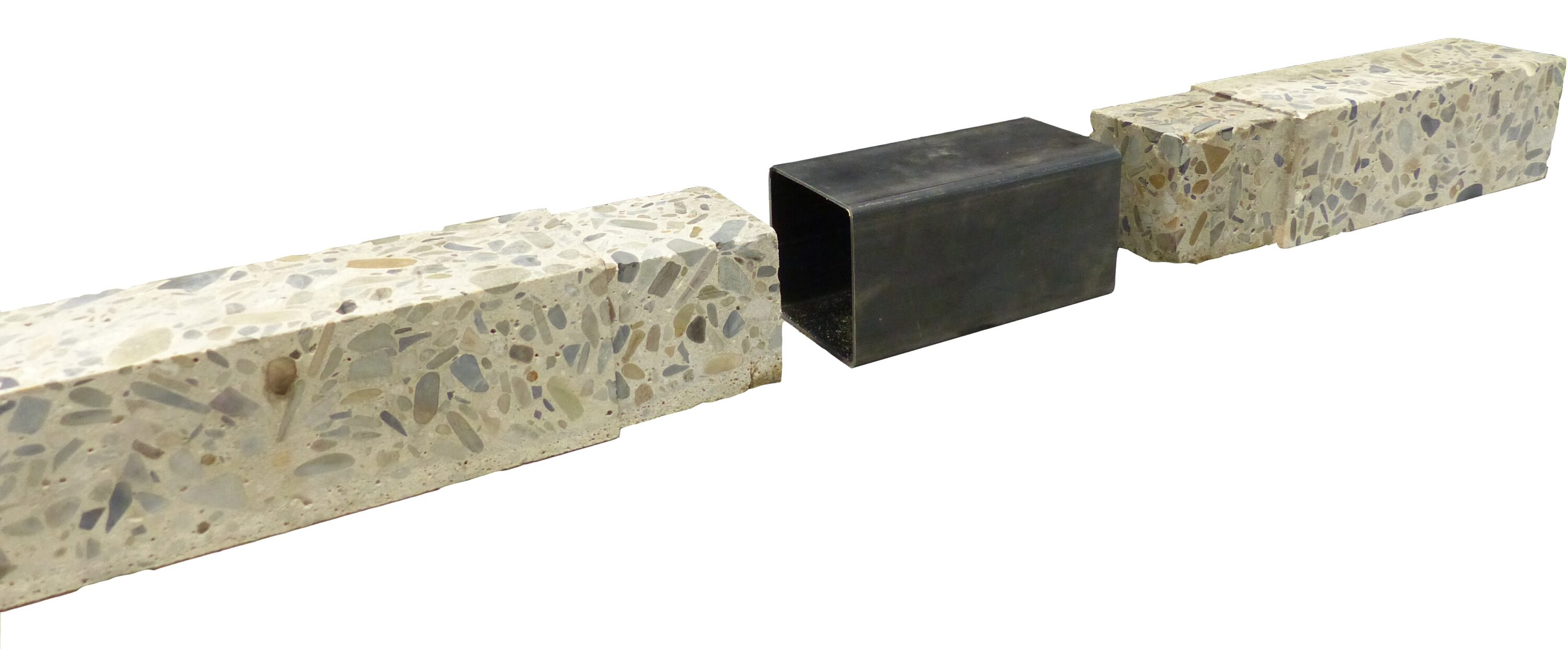
Jointing Principles for Combination of Concrete Elements Produced by Different Additive Manufacturing Processes [14.11.2024] Prof. Dr.-Ing. Harald Kloft Project leader, h.kloft@tu-braunschweig.de Dr.-Ing. Abtin Baghdadi Researcher, a.baghdadi@tu-braunschweig.de Dipl.-Ing. Lukas Ledderose Researcher, l.ledderose@tu-braunschweig.de TU Braunschweig, Institute of Structural Design (ITE) Prof. Dr.-Ing. Martin Empelmann Project leader, m.empelmann@ibmb.tu-braunschweig.de TU Braunschweig, Institute of Building Materials, Concrete Construction and Fire Safety (iBMB) In the second phase of the C05 project, research will focus on advancing connection methods and robotic manufacturing techniques, such as waterjet cutting and stamping in green-state concrete, while incorporating post-tensioning and steel connectors for higher load-bearing capacity and easier assemblage of AM concrete segments. The project will explore new design …
Research Summary Report of B03
Category: Research Summary Report
Modelling and Simulation of Shotcrete 3D Printing (SC3DP) Based on a Massively Parallel Multi-Phase, Multi-Component Coupled LBM-DEM Approach [14.11.2024] Prof. Dr. rer. nat. M. Geier Project leader, geier@irmb.tu-bs.de Dr.-Ing. K. Kutscher Researcher, kutscher@irmb.tu-bs.de Prof. Dr.-Ing. habil. M. Krafczyk Project leader, kraft@irmb.tu-bs.de Dr.-Ing. H. Alihussein Researcher, hussein@irmb.tu-bs.de TU Braunschweig, Institute for Computational Modeling in Civil Engineering, IRMB (Institut für rechnergestützte Modellierung im Bauingenieurwesen) The project is currently concerned with the simulation of a moving nozzle for the injection process using I3DCP. We are particularly interested in the influence of the movement of the nozzle on the printed strand. Summary The I3DCP is a three-phase problem where the …
Research Summary Report of A03
Category: Research Summary Report
Extrusion of Near-Nozzle Mixed Concrete –Individually Graded in Density and in Rate of 3D Fibre Reinforcement [30.10.2024] Dr. Ing. Bos, Freek Project leader, freek.bos@tum.de Cheng, Shengbo Researcher, shengbo.cheng@tum.de Technical University of Munich, Chair of Concrete and Masonry Structures (Lehrstuhl für Massivbau) Extrusion-based 3D Concrete Printing (3DCP) is the most widely investigated technology for additive manufacturing (AM) in construction. Near-Nozzle Mixing (NNM) has been introduced in the 1st funding period of project A03 as a variant that can overcome several limitations of conventional 3DCP. Instead of mixing at a distance, NNM mixes the material constituents at the print head, thereby drastically reducing the transportation distance through hoses and the associated pumping pressure required. Thus, pumping-related …
Research Summary Report of C04
Category: Research Summary Report
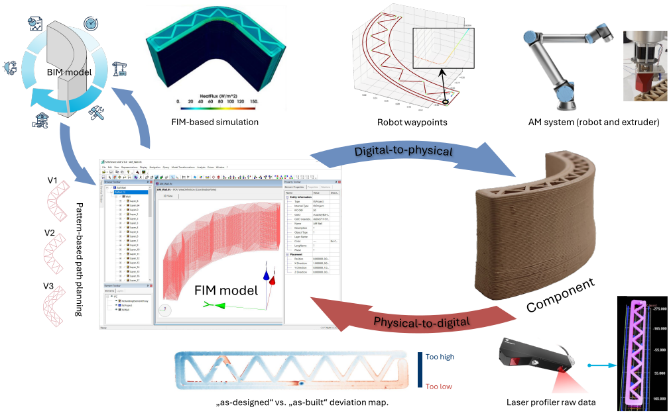
Integrating Digital Design and Additive Manufacturing through BIM-Based Decision Support and Digital Twin Methods [04.10.2024] Borrmann, André Project leader, andre.borrmann@tum.de Slepicka, Martin Researcher,martin.slepicka@tum.de All: Technical University of Munich, Chair of Computational Modeling and Simulation Additive Manufacturing (AM) is gaining more and more interest in the construction sector as it potentially offers many advantages, such as increased geometric freedom and productivity. However, these advantages come at a cost; additional effort is required in the data preparation for AM (a higher level of detail is necessary). Project C04 aims to simplify and streamline the necessary design and control processes and to interlink digital design (i.e. BIM) with automated fabrication. For this purpose, the Fabrication Information …
Research Summary Report of A02
Category: Research Summary Report
Particle-Bed 3D Printing by Selective Cement Paste Intrusion (SPI) – Particle Surface Functionalisation, Particle Synthesis and Integration of WAAM Reinforcement [27.09.2024] Hamilton, Leigh Duncan; Doctoral researcher; L.Hamilton@tu-braunschweig.de Zetzener, Harald; Leading researcher; H.Zetzener@tu-braunschweig.de Kwade, Arno; Project leader; A.Kwade@tu-braunschweig.de All: TU Braunschweig, Institute for Particle Technology To enable selective paste intrusion (SPI) for practical applications, the inclusion of reinforcement is mandatory. The focus of the first funding period was uniting SPI with wire arc additive manufacturing (WAAM) for reinforced concrete as well as functionalising and/or modifying particulate systems. During the first funding period, two main issues were identified: the need for ecological sustainable development for the combined process of SPI+WAAM and accelerated process velocities to improve the economic efficiency. Therefore, the …
Research Summary Report of A05
Category: Research Summary Report
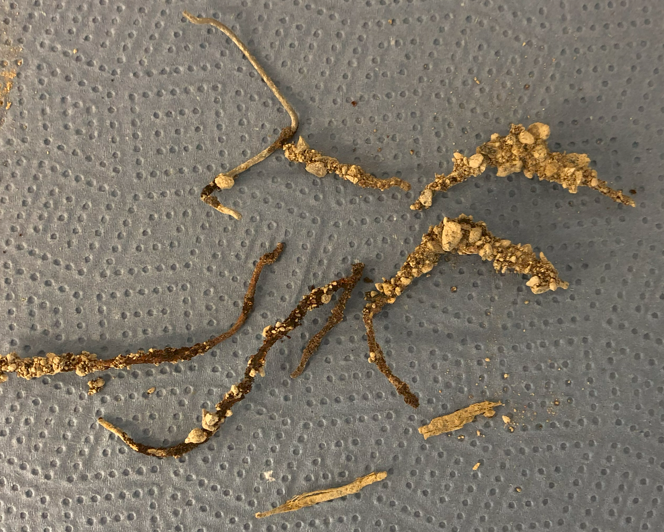
Integration of Individualized Prefabricated Fibre Reinforcement in Additive Manufacturing with Concrete [24.09.2024] Rothe, Tom; Doctoral researcher, t.rothe@tu-braunschweig.de, TU Braunschweig, Institute of Mechanics and Adaptronics (IMA) Hühne, Christian; Project Leader, Christian.Huehne@tu-braunschweig.de, TU Braunschweig, Institute of Mechanics and Adaptronics (IMA) The individual integration of fibre reinforcement into large additively manufactured concrete components allows new design freedom and reduces concrete consumption due to reduced concrete cover. Strategies for the integration of freely formable reinforcing strands for different AM processes are being developed in project A05. A Dynamic Winding Machine is used to prepare reinforcement strands. This machine is used to consolidate and impregnate a primary fibre strand and wind a secondary yarn around it as a surface structuring. Thus, these reinforcement strands …
Research Summary Report of A06
Category: Research Summary Report
Integrated Additive Manufacturing Processes for Reinforced Shotcrete 3D Printing (SC3DP) Elements with Precise Surface Quality [09.09.2024] Wenzler, David; doctoral researcher; david.wenzler@tum.de Technical University of Munich, Institute for Machine Tools and Industrial Management Blankenhagen, Jakob; doctoral researcher; jakob.blankenhagen@tum.de Technical University of Munich, Chair of Metal Structures Summary The project A06 aims to develop a methodology for producing safe and functional structural steel elements for construction using laser powder-bed fusion (LPBF). The LPBF steel Printdur HSA® will be qualified by using and transferring methodologies from the first funding period. The prediction of fatigue behaviour based on process monitoring data and machine learning will be explored. Lattice structures will be used to tailor the stiffness of the steel elements. These complex LPBF …
Research Summary Report of A04
Category: Research Summary Report
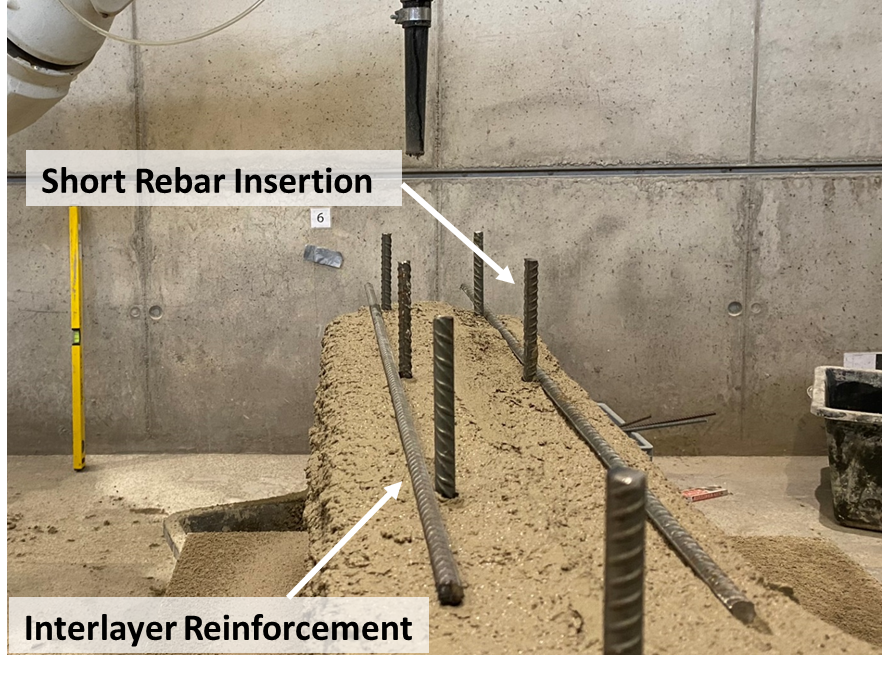
Integrated Additive Manufacturing Processes for Reinforced Shotcrete 3D Printing (SC3DP) Elements with Precise Surface Quality [30.08.2024] David, Martin; Doctoral Researcher, m.david@tu-braunschweig.de TU Braunschweig, Institute for Machine Tools and Production Technology (IWF) Main Goal Project A04 aims to investigate cooperative Additive Manufacturing (AM) processes based on Shotcrete 3D Printing (SC3DP) for the production of material-efficient, force-optimised, reinforced, load-bearing concrete components with precise surface quality and geometrical precision. The goal is to produce large-scale concrete elements using significantly less reinforcement and concrete compared to standard concrete construction principles. Hereby, different robot guided end effectors are subject to research in a flexible and automated process chain. Currently, the following key points are researched: Development of end effectors for the processing of free-from …
Research Summary Report of A07
Category: Research Summary Report
Wire and Arc Additive Manufacturing (WAAM) of Complex Individualized Steel Components [23.08.2024] Müggenburg, Marc; Doctoral Researcher, marc.mueggenburg@tu-braunschweig.de Unglaub, Julian; Project Leader,j.unglaub@tu-braunschweig.de Institute of Steel Structures Technische Universität Braunschweig Main Goal A07 focuses on understanding the interaction between DED-Arc (alias WAAM) components and existing structures, developing load-specific strengthening solutions and designing welding strategies. The specific challenges of adaptive design and adaptive manufacturing of large-scale high-strength steel DED-Arc components will be addressed and a digital twin including data from the design and manufacturing process, surface geometry and component performance will be elaborated. Physical and virtual component tests will be carried out to gain a comprehensive knowledge on buckling behavior, the effect of imperfections, load-carrying capacity and ductility. Overall, the project …
Research Summary Report of B04
Category: Research Summary Report
Process Control and Adaptive Path Planning for Additive Manufacturing Processes Based on Industrial Robots with an Extended Degree of Freedom [09.08.2024] Ekanayaka, Virama; Doctoral researcher, v.ekanayaka@tu-braunschweig.de, TU Braunschweig, Institute of Machine Tools and Production Technology (IWF) Hürkamp, André; Project Leader, a.huerkamp@tu-braunschweig.de, TU Braunschweig, Institute of Machine Tools and Production Technology (IWF) The integration of robot-guided additive manufacturing in the construction industry increases the degree of automation and can thus lead to an increased productivity and increased component quality. In shotcrete 3D printing (SC3DP), reproducible manufacturing results and ensuring component quality are major challenges, as the properties of shotcrete depend on many different parameters (e.g. temperature, pressure, water-cement ratio, hardening accelerator). The goal of this research project is to develop …