News
Research Summary Report C02
Category: Research Summary Report
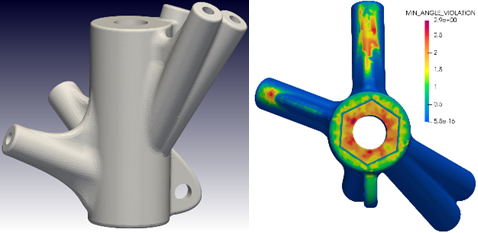
3D Structural Puzzle – Numerical Multi Scale Shape and Topology Optimisation Methods to Additively Manufacture Optimal Structures from Optimised Pieces [27.01.2022] Bletzinger, Kai-Uwe: Project Leader Najian Asl, Reza: Post-Doc Research Associate TU Munich, Chair of Structural Analysis Summary This project deals with structures considered as large 3D puzzles and multi scale optimization aspects. The goal is to create optimized individual structural pieces which are subsequently assembled to form an overall optimal structure. Additive manufacturing is the ideal meaning of greatest potential to combine industrial efficient production with individual design and structural layout. The main research question is to develop numerical, simulation-based optimization methods which allow for the design and creation of large, additively manufactured structures to be carried out …
Dr. Inka Mai is awarded with the “Klaus-Dyckerhoff-Preis für junge Wissenschaftler(innen)”
Category: Press release
6. Dyckerhoff Prizes 2021 go to Dr. Lei Lei, TU Munich and Dr. Inka Mai, TU Braunschweig The Dres. Edith and Klaus Dyckerhoff Foundation, Wiesbaden, Germany has awarded Dr. Lei Lei, Technical University of Munich (TUM) and Dr. Inka Mai of Technical University of Braunschweig (both Germany) with the 2021 Klaus Dyckerhoff Prize for Young Scientists. Dr. Lei, junior professor at Prof. Johann Plank’s group was acclaimed for her work on PCE superplasticizers in alkali-activated slag systems, she is currently working on her habilitation focussing on PCEs for environmentally friendly binders. Dr. Mai is part of Prof. Dirk Lowke’s group and excelled in the development of new technologies for 3D printing of mortars (e.g. shotcrete printing, large particle bed 3D …
Research Summary Report C04
Category: Research Summary Report
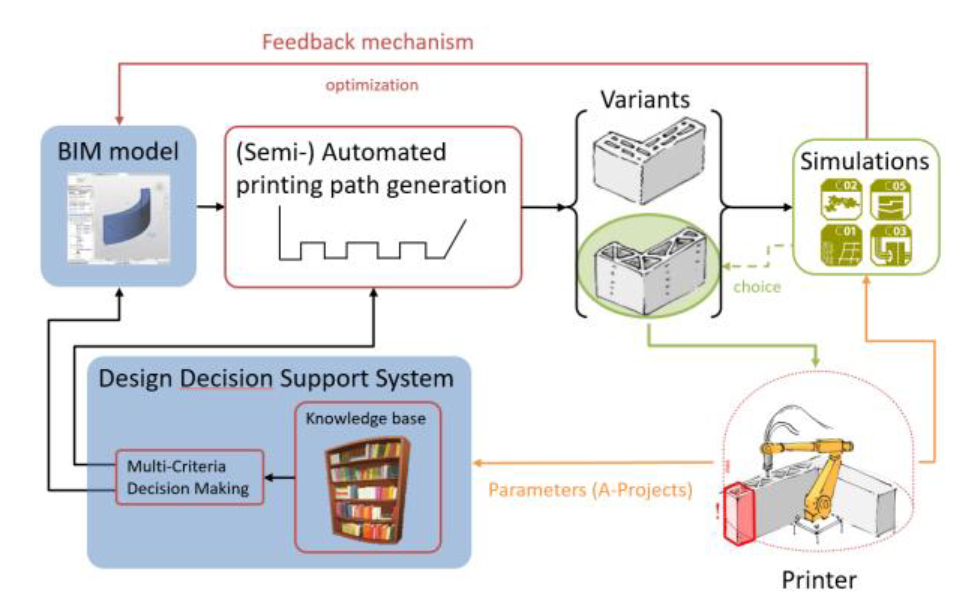
Integrating Digital Design and Additive Manufacturing through BIM-Based Decision Support and Digital Twin Methods [05.03.2021] Li, Chao; Doctoral researcher; chao1.li@tum.deTU Munich, Chair of Architectural Informatics Slepicka, Martin; Doctoral researcher; martin.slepicka@tum.deTU Munich, Chair of Computational Modeling and Simulation In the context of AMC, C04 workgroups attempt to cohesively integrate AM and BIM–based early design, through the design decision support and fabricationenhanced multi–LOD BIM models.Knowledge Base Formalization Domain–specific knowledge base usually serves as a backbone in a Knowledge–Based System (KBS).Furthermore, the knowledge base of proposed DDSS has to be formalized in an extensible, reusable and interoperable manner. In the first stage of work, C04 workgroups have conducted semi–structured interviews between other sub–projects (A01–A05, C01–C06). From the interviews, four groups of knowledge …
Research Summary Report A02
Category: Research Summary Report
Particle-Bed 3D Printing by Selective Cement Paste Intrusion (SPI) – Particle Surface Functionalisation, Particle Synthesis and Integration of WAAM Reinforcement [26.02.2021] Hamilton, Leigh Duncan; Researcher, leigh-duncan.hamilton@tu-bs.de Breitung-Faes, Sandra; Leading Researcher, s.breitung@tu-bs.de Kwade, Arno; PL, a.kwade@tu-bs.de All: TU Braunschweig, Institute for Particle Technology (iPAT) Selective cement paste intrusion (SPI) is an additive manufacturing method where aggregate particles are spread in small layers, followed by the local intrusion of the cement paste into the aggregate layers. These steps are repeated layer-by-layer and the consequent hardening forms the structure. In comparison to other AM processes, the necessity of support structures for cantilevers is redundant for SPI. In addition, research to date has shown that SPI-made components closely acquire isotropic compressive strength (>70 …
Research Summary Report A06
Category: Research Summary Report
Integration of Individualized Prefabricated Fibre Reinforcement in Additive Manufacturing with Concrete [19.02.2021] Rothe, Tom; Doctoral researcher, t.rothe@tu-bs.de, TU Braunschweig, Institute of Mechanics and Adaptronics (IMA) Hühne, Christian; Project leader, christian.huehne@dlr.de, TU Braunschweig, Institute of Mechanics and Adaptronics (IMA) One of the biggest challenges in 3D printing with cementitious materials is the integration of reinforcement. The project aims to develop textile-based reinforcement strategies for additive manufacturing with concrete and to utilize the advantages of textile reinforcement (e.g. corrosion resistance and material flexibility) for the production of material-efficient, individualized structures. These structures should be produced by a robotic winding process, which provides a high degree of freedom in shaping in combination with a minimal amount of tooling and formwork. To be …
Research Summary Report A06
Category: Research Summary Report
Laser Powder-Bed Fusion (LPBF) of Steel Elements for Construction – Basics of Design and Mechanical Resilience. [12.02.2021] Diller, Johannes; Doctoral researcher; Johannes.Diller@tum.de, Dorina Siebert, Doctoral researcher; dorina.siebert@tum.de TU Munich, Chair of Metal Structures Wenzler, David; Doctoral researcher; David.Wenzler@iwb.tum.de, Kolb, Cara; Doctoral researcher; Cara.Kolb@iwb.mw.tum.de TU Munich, Institute for Machine Tools and Industrial Management The reproducibility of the mechanical properties of PBF-LB/M parts needs to be increased. This requires a more detailed understanding of the correlation between the process parameters and the mechanical and metallurgical properties of the manufactured parts. In project A06 a first step towards this goal has been taken: With a thermography camera, the cooling rates during the fabrication of fatigue test specimens were measured. Two process parameter …
Research Summary Report A07
Category: Research Summary Report
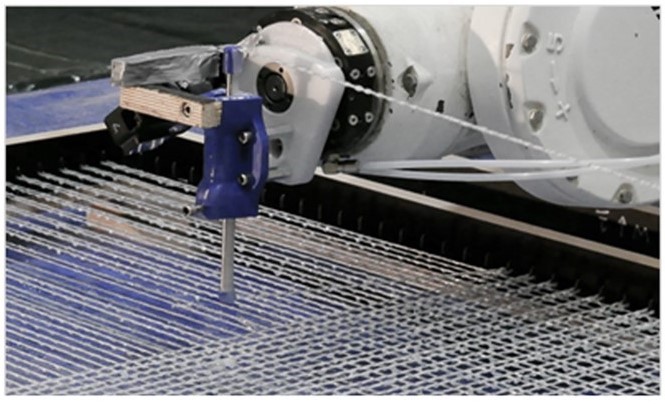
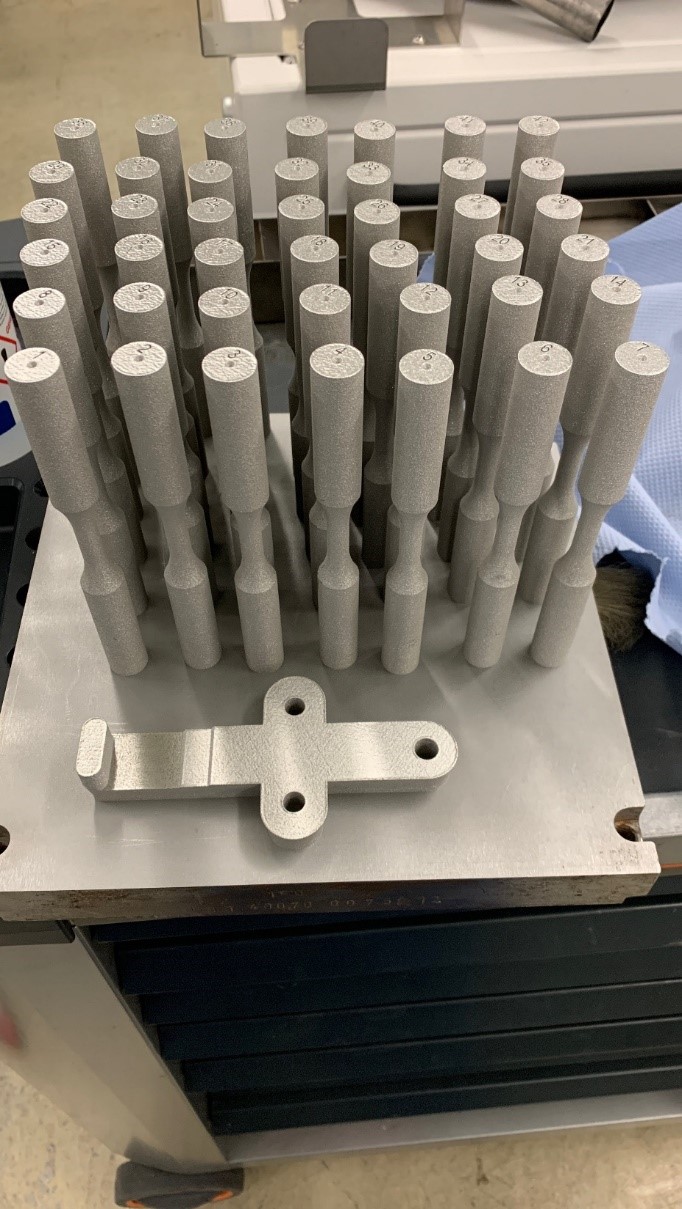
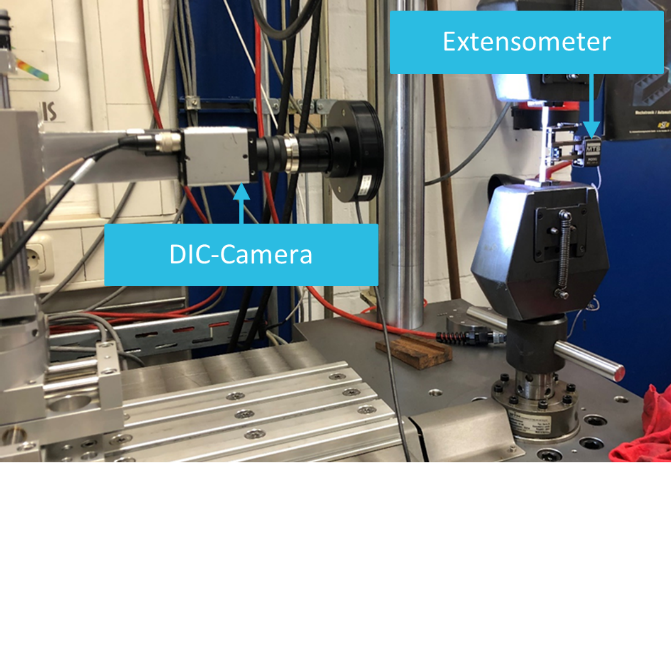
Wire and Arc Additive Manufacturing (WAAM) of Complex Individualized Steel Components [29.01.2021] Unglaub, Julian, Associate Researcher, Institute of Steel Structures Jahns, Hendrik, PhD Researcher, Institute of Steel Structures Thiele, Klaus, Project Leader, Institute of Steel Structures Project A07 investigates structural design, WAAM methods and component testing of complex, large-scale, individualized steel components. The objective is to connect conventionally manufactured steel components and semi-finished products with additively manufactured, complex steel components The Institute of Steel Structures develops a novel test method based on fill field strain data. This test method considers potentially anisotropic component behaviour, surface topographies, geometric irregularities and residual stresses in addition to the relevant material properties. Fig 1: Tension specimen with combined extensometer and DIC measurement …
Research Summary Report A08
Category: Research Summary Report
Structural Timber by Individual Layer Fabrication (ILF) [22.01.2021] Bunzel, Frauke; Project leader; frauke.bunzel@wki.fraunhofer.de Asshoff, Carsten; Doctoral researcher; carsten.asshoff@wki.fraunhofer.de Fraunhofer Institute for Wood Research Wilhelm-Klauditz-Institut WKI In order to produce future-oriented timber structures in the building industry that meet the requirements of ecological and economic sustainability, an additive manufacturing process with wood chips is being developed using the new approach of individual layer fabrication (ILF). In first steps, established wood chip fractions and adhesive systems from the wood-based materials industry are used e. g. for particleboards or oriented strand boards. For an acceptable adhesive-wood-chips ratio the amount of adhesive must be as low as possible, which is one of the challenges in developing ILF, see Fig. 1. In addition to …
Research Summary Report C06
Category: Research Summary Report
Integration of Additive Manufacturing in the Construction Process [08.01.2021] Mawas, Karam; Doctoral researcher, k.mawas@tu-braunschweig.de, TU Braunschweig, Institute of Geodesy and Photogrammetry (IGP) Gerke, Markus; Project leader, m.gerke@tu-braunschweig.de, TU Braunschweig, Institute of Geodesy and Photogrammetry (IGP) Maboudi, Mehdi; Associated scientist, m.maboudi@tu-braunschweig.de, TU Braunschweig, Institute of Geodesy and Photogrammetry (IGP) Riedel, Björn; Associated scientist, b.riedel@tu-braunschweig.de, TU Braunschweig, Institute of Geodesy and Photogrammetry (IGP) Additive Manufacturing (AM) allows us to print objects in unprecedented and novel ways, pushing the boundaries of what was previously possible in construction. By seamlessly embedding the process of the design directly into the printing process, ever more complex and free form objects can now be realized. Nonetheless, AM remains a challenging and involved process that is influenced by a variety …
Research Summary Report A07
Category: Research Summary Report
Wire and Arc Additive Manufacturing (WAAM) of Complex Individualized Steel Components [01.01.2021] Müller, Christoph; doctoral researcher, christoph.mueller@tu–braunschweig.de, TU Braunschweig , Institute for Structural Design (ITE) This sub–project of the SFB 277 deals with the design process of components for additive manufacturing by Wire and Arc Additive Manufacturing (WAAM). In contrast to large industrial sectors such as mechanical engineering, aeronautical engineering or medical technology, components in the construction industry have to be designed under different general conditions. If no building system is used to create a structure, the components are usually individual. These components are usually used in the building as a single part or in small quantities. With the implementation of additive manufacturing processes, these components are usually free–form …