Research Summary Report of A04
Integrated Additive Manufacturing Processes for Reinforced Shotcrete 3D Printing (SC3DP) Elements with Precise Surface Quality
[11.07.2025]
Megnet, Manuel1; Doctoral Researcher, m.megnet@tu-braunschweig.de
Dröder, Klaus1; Project leader, k.droeder@tu-braunschweig.de
TU Braunschweig, Institute of Machine Tools and Production Technology (IWF)
Main Goal:
Project A04 aims to investigate innovative Additive Manufacturing (AM) processes based on Shotcrete 3D Printing (SC3DP) for the production of material-efficient, force-optimised, reinforced, loadbearing concrete components with a precise surface quality and geometrical precision. The goal is to enable the production of large-scale concrete elements with a reduced necessity for reinforcements and concrete compared to conventional concrete construction principles. For this purpose, different robot guided end effectors are subject to research in a flexible and automated process chain.
Within this scope, the development of end effectors for the processing of free-from concrete surfaces is currently a key point of research.
Summary
On a larger scale, the manufacturing of reinforced elements with precise surface quality encompasses the integration of reinforcements as well as the surface finishing. The utilisation of a screwing motion is investigated for the-process integration of steel reinforcements [1]. Especially the utilisation of vibrations as a replacement for a screwing motion results in an enhanced bond between rebar and concrete, as evidenced by [2].
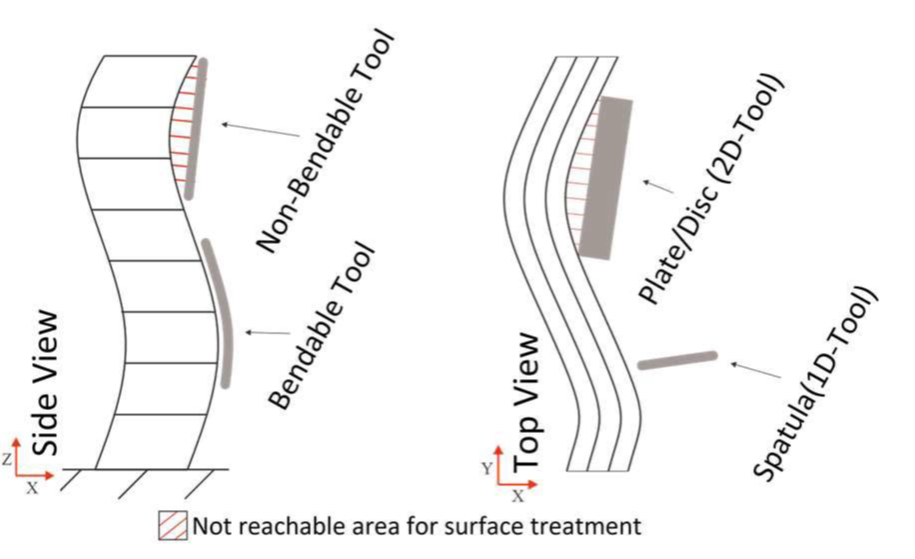
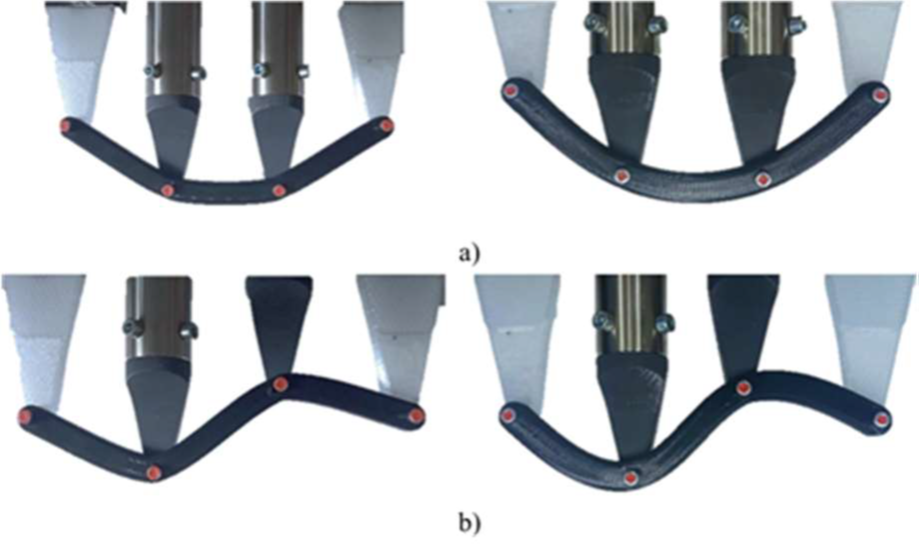
For achieving a smooth final surface of SC3DP elements, a rotating trowel was investigated. It was shown, that the time between printing and surface processing significantly influences the achieved surface quality [3]. However, without further adaptations, this tool is not able to smooth concave surfaces, which might result from the design freedom of AM processes (see Fig. 1).
References
[1] Dörrie, R., David, M., Freund, N., Lowke, D., Dröder, K., & Kloft, H. (2023). In-Process Integration of Reinforcement for Construction Elements During Shotcrete 3D Printing. Open Conference Proceedings,3.
https://doi.org/10.52825/ocp.v3i.224
[2] Freund, N., David, M., Dröder, K., Lowke, D. (2024). Vibrated Short Rebar Insertion – The Effect of Integration Time on the Resulting Bond Quality. In: Lowke, D., Freund, N., Böhler, D., Herding, F. (eds) Fourth RILEM International Conference on Concrete and Digital Fabrication. DC 2024. RILEM Bookseries, vol 53. Springer, Cham.
https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-70031-6_38
[3] Dörrie, R., David, M., Freund, N., Lowke, D., Dröder, K., Kloft, H. (2024). Surface Processing of Shotcrete 3D Printed Concrete Elements Using a Rotating Trowel Disc – Influence of Timing on Resulting Surface Quality. In: Lowke, D., Freund, N., Böhler, D., Herding, F. (eds) Fourth RILEM International Conference on Concrete and Digital Fabrication. DC 2024. RILEM Bookseries, vol 53. Springer, Cham.
https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-70031-6_46
[4] David, M., Dröder, K. (2024). Robot-Guided End Effector for an Automated Finishing of Concrete Free-Form Surfaces. In: Lowke, D., Freund, N., Böhler, D., Herding, F. (eds) Fourth RILEM International Conference on Concrete and Digital Fabrication. DC 2024. RILEM Bookseries, vol 53. Springer, Cham.
https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-70031-6_7