Research Summary Report of A04
Integrated Additive Manufacturing Processes for Reinforced Shotcrete 3D Printing (SC3DP) Elements with Precise Surface Quality
[11.07.2025]
Megnet, Manuel; Doctoral Researcher, m.megnet@tu-braunschweig.de
Jänicke, Ralf; Project Leader, r.janicke@tu-braunschweig.de
Kollmannsberger, Stefan; Project Leader, stefan.kollmannsberger@uni-weimar.de
TU Braunschweig, IAM and Bauhaus-Universität Weimar, IBMB
Main Goal
Project A04 aims to investigate innovative Additive Manufacturing (AM) processes based on Shotcrete 3D Printing (SC3DP) for the production of material-efficient, force-optimised, reinforced, load-bearing concrete components with a precise surface quality and geometrical precision. The goal is to enable the production of large-scale concrete elements with a reduced necessity for reinforcements and concrete compared to conventional concrete construction principles. For this purpose, different robot guided end effectors are subject to research in a flexible and automated process chain.
Within this scope, the development of end effectors for the processing of free-from concrete surfaces is currently a key point of research.
Summary
The primary research topics for the Institute of Machine Tools and Production Technology (IWF) in the project A04 are the processes and robot-guided end effectors. The SC3DP process facilitates the fabrication of reinforced concrete components. To achieve a consistent quality, it is imperative to monitor and regulate the process and especially the volume flows of the media. Consequently, research is being conducted on the development of sensor concepts for measuring the flow of concrete, air and accelerator through experimental evaluation. The measurement of concrete is a challenging process, primarily due to its high viscosity.
On a larger scale, the manufacturing of reinforced elements with precise surface quality encompasses the integration of reinforcements as well as the surface finishing. The utilisation of a screwing motion is investigated for the-process integration of steel reinforcements [1]. Especially the utilisation of vibrations as a replacement for a screwing motion results in an enhanced bond between rebar and concrete, as evidenced by [2].
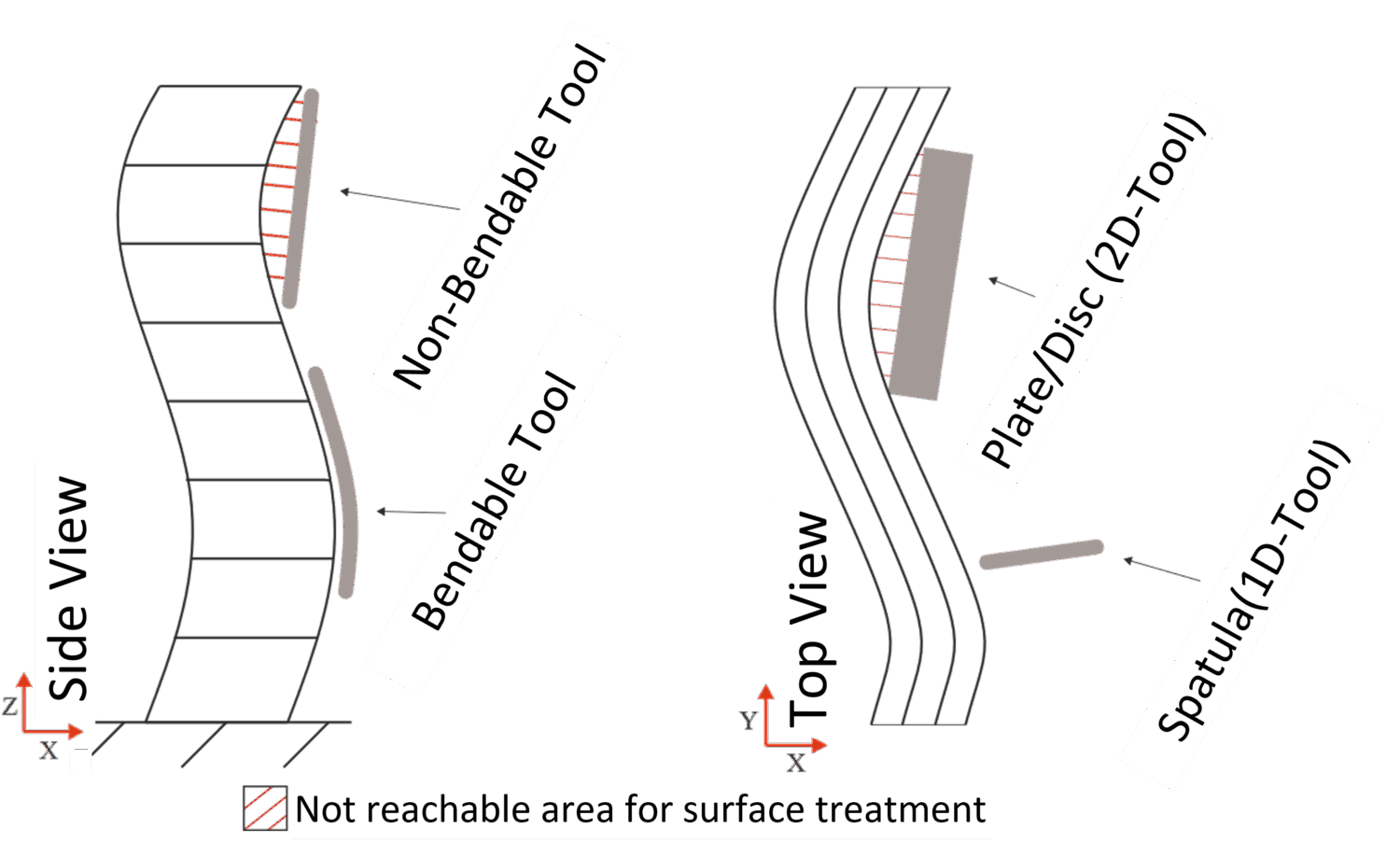
For achieving a smooth final surface of SC3DP elements, a rotating trowel was investigated. It was shown, that the time between printing and surface processing significantly influences the achieved surface quality [3]. However, without further adaptations, this tool is not able to smooth concave surfaces, which might result from the design freedom of AM processes (see Fig. 1).
A viscoplastic material model with time-dependent yield strength has been developed. The behavior of the material used in SC3DP is visualized in Figure 2. With no load applied, the yield stress of the material increases to its maximum value. Once a load is applied at , a linear elastic response develops until the material begins to yield. Thereafter, the yield stress decreases.
To study the influence of material parameters and printing process parameters, the material model is implemented in the open-source Finite Element framework Ferrite.jl. Furthermore, the interaction between the layers is considered, accounting for the bonding strength of the layers and the time-dependent strength development of the concrete mix.