Research Summary Report of A04
Integrated Additive Manufacturing Processes for Reinforced Shotcrete 3D Printing (SC3DP) Elements with Precise Surface Quality
[29.01.2025]
M. Sc. Robin Dörrie Researcher, r.doerrie@tu-braunschweig.de
Technische Universität Braunschweig(TU BS), ITE Institute of Structural Design
The project aims to fundamentally understand the Shotcrete 3D Printing (SC3DP) technology to manufacture sustainable, multi-objective optimised, reinforced concrete components with precise surface quality and improved building physics via functional integration. It seeks to minimise the carbon footprint of 3D printed structures by exploring various material strategies, such as reducing cement content by increasing the aggregate size or replacing cement with a different binder and design methods to optimise the usage of concrete in order to decrease the overall concrete volume used. Additionally, it focuses on establishing a reliable material and process control, emphasising fresh material laws for printability and durability, real-time monitoring of concrete properties, and component build-up strategies.
Current state of research
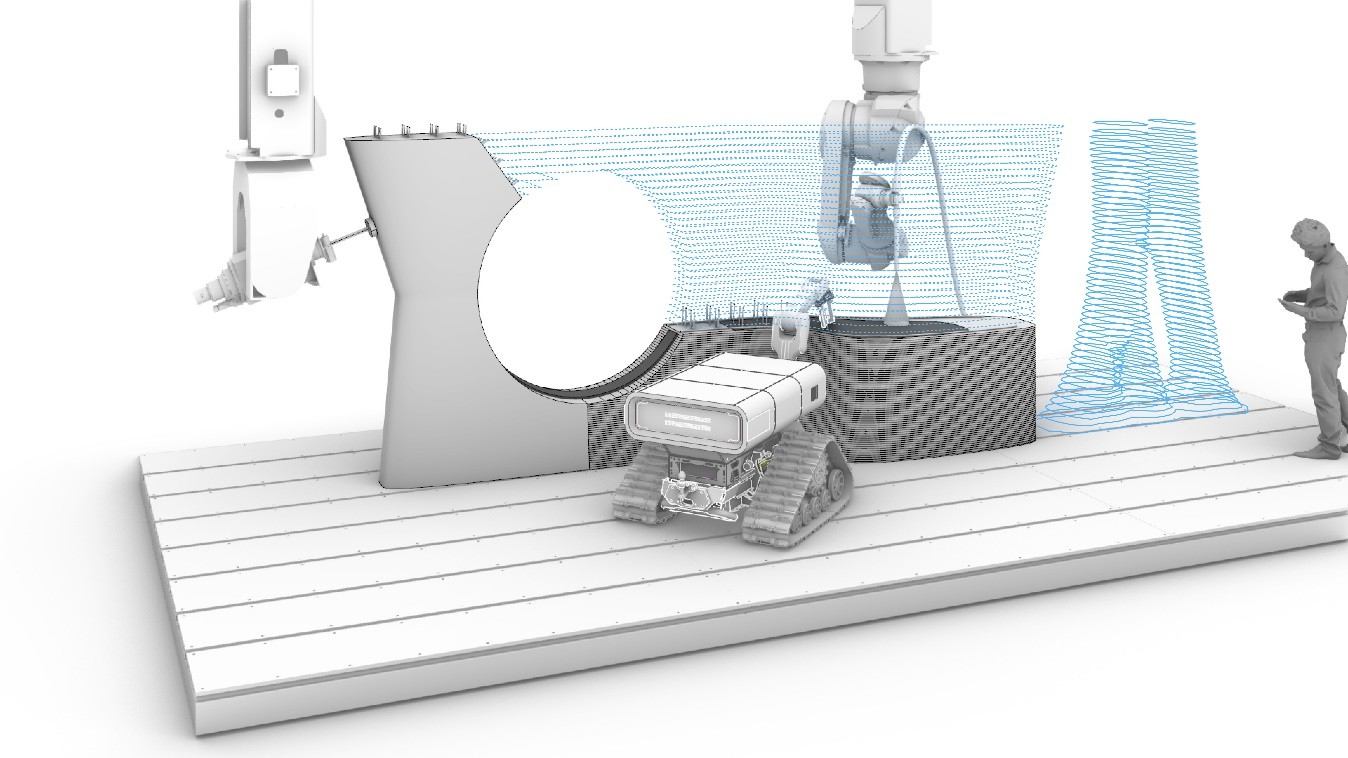
Looking back at 2024, WG Kloft was able to perform multiple experiments and reach several exciting advancements regarding the SC3DP process.
Starting in September, we had the opportunity to host an international workshop for students in the context of the Digital Concrete Conference 2024. In this workshop the SC3DP process was utilised to print a reinforced wall element and to apply a cover layer to a printed column. The printing took place at the Digital Building Fabrication Laboratory (DBFL) and the students had the opportunity to experience the research facilities of TU Braunschweig as well as meeting with other 3D printing enthusiasts from universities all over the world.
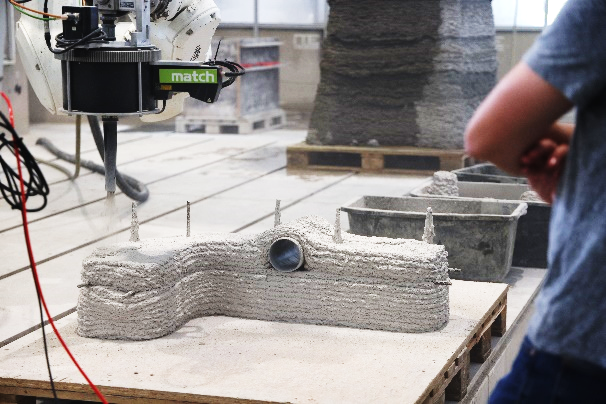
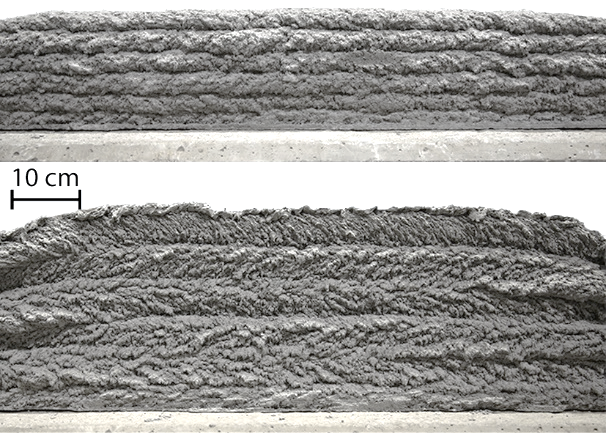
Moreover, in the end of the year, WG Kloft was investigating the influence of different parameters on the strand geometry. In these experiments it was of high importance to understand the fundamental connections and interactions between concrete volume flow, air volume flow, robotic alignment and many other parameters. The results showed, that the process offers a variety of strand geometries which can be utilised in different ways and application cases.
Currently A04 WG Kloft is working on the exploration of different optimisation algorithms to match with the geometric freedom of the SC3DP process to manufacture optimised loadbearing structures. The manufacturing of optimised elements requires advances in different fields regarding printing strategies, reinforcement integration or end effector development. Therefore, WG Kloft is working closely with different projects to achieve this goal.
Current publications
Dörrie, Robin, Harald Kloft, Bartłomiej Sawicki, Niklas Freund, and Dirk Lowke. “Automated Reinforcement Integration in Shotcrete 3D Printing Through Green State Milling.” In RILEM International Conference on Concrete and Digital Fabrication, pp. 319-326. Cham: Springer Nature Switzerland, 2024.
Dörrie, Robin, Martin David, Niklas Freund, Dirk Lowke, Klaus Dröder, and Harald Kloft. “Surface Processing of Shotcrete 3D Printed Concrete Elements Using a Rotating Trowel Disc–Influence of Timing on Resulting Surface Quality.” In RILEM International Conference on Concrete and Digital Fabrication, pp. 397-404. Cham: Springer Nature Switzerland, 2024.
Lachmayer, Lukas, Jelle Quantz, Hauke Heeren, Tobias Recker, Robin Dörrie, Harald Kloft, and Annika Raatz. “A spatial multi-layer control concept for strand geometry control in robot-based additive manufacturing processes.” In RILEM International Conference on Concrete and Digital Fabrication, pp. 119-126. Cham: Springer Nature Switzerland, 2024.